
Smog, or smoke fog, is a type of intense air pollution. The word "smog" was coined in the early 20th century, and is a portmanteau of the words smoke and fog to refer to smoky fog due to its opacity, and odor. The word was then intended to refer to what was sometimes known as pea soup fog, a familiar and serious problem in London from the 19th century to the mid-20th century, where it was commonly known as a London particular or London fog. This kind of visible air pollution is composed of nitrogen oxides, sulfur oxide, ozone, smoke and other particulates. Man-made smog is derived from coal combustion emissions, vehicular emissions, industrial emissions, forest and agricultural fires and photochemical reactions of these emissions.

Indoor air quality (IAQ) is the air quality within buildings and structures. Poor indoor air quality due to indoor air pollution is known to affect the health, comfort, and well-being of building occupants. It has also been linked to sick building syndrome, respiratory issues, reduced productivity, and impaired learning in schools. Common pollutants of indoor air include: secondhand tobacco smoke, air pollutants from indoor combustion, radon, molds and other allergens, carbon monoxide, volatile organic compounds, legionella and other bacteria, asbestos fibers, carbon dioxide, ozone and particulates.

Exhaust gas or flue gas is emitted as a result of the combustion of fuels such as natural gas, gasoline (petrol), diesel fuel, fuel oil, biodiesel blends, or coal. According to the type of engine, it is discharged into the atmosphere through an exhaust pipe, flue gas stack, or propelling nozzle. It often disperses downwind in a pattern called an exhaust plume.

Air pollution is a concern in British Columbia, Canada because of its effects on health and visibility. Air quality is influenced in British Columbia(BC) by numerous mountain ranges and valleys, which complicate atmospheric pollution dispersion and can lead to high concentrations of pollutants such as particulate matter from wood smoke.

Diesel exhaust is the exhaust gas produced by a diesel engine, plus any contained particulates. Its composition may vary with the fuel type, rate of consumption or speed of engine operation, and whether the engine is in an on-road vehicle, farm vehicle, locomotive, marine vessel, or stationary generator or other application.
Environmental toxicants and fetal development is the impact of different toxic substances from the environment on the development of the fetus. This article deals with potential adverse effects of environmental toxicants on the prenatal development of both the embryo or fetus, as well as pregnancy complications. The human embryo or fetus is relatively susceptible to impact from adverse conditions within the mother's environment. Substandard fetal conditions often cause various degrees of developmental delays, both physical and mental, for the growing baby. Although some variables do occur as a result of genetic conditions pertaining to the father, a great many are directly brought about from environmental toxins that the mother is exposed to.

Low birth weight (LBW) is defined by the World Health Organization as a birth weight of an infant of 2,499 g or less, regardless of gestational age. Infants born with LBW have added health risks which require close management, often in a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU). They are also at increased risk for long-term health conditions which require follow-up over time.

Air pollution is the presence of substances in the atmosphere that are harmful to humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the environment. Air pollution can be chemical, physical or biological. There are many different types of air pollutants, such as gases, particulates and biological molecules. Air pollution can cause diseases, allergies, and even death; it can also cause harm to animals and crops and damage the natural environment or built environment. Air pollution can occur naturally or be caused by human activities.
Air pollution is the introduction of chemicals, particulate matter, or biological materials into the atmosphere that cause harm or discomfort to humans or other living organisms, or damage ecosystems. Health problems attributed to air pollution include premature death, cancer, organ failure, infections, behavioral changes, and other diseases. These health effects are not equally distributed across the U.S. population; there are demographic disparities by race, ethnicity, socioeconomic status, and education. Air pollution can derive from natural sources, such as wildfires and volcanoes, or from anthropogenic sources. Anthropogenic air pollution has affected the United States since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution.

Pollution in California relates to the degree of pollution in the air, water, and land of the U.S. state of California. Pollution is defined as the addition of any substance or any form of energy to the environment at a faster rate than it can be dispersed, diluted, decomposed, recycled, or stored in some harmless form. The combination of three main factors is the cause of notable unhealthy levels of air pollution in California: the activities of over 39 million people, a mountainous terrain that traps pollution, and a warm climate that helps form ozone and other pollutants. Eight of the ten cities in the US with the highest year-round concentration of particulate matter between 2013 and 2015 were in California, and seven out of the ten cities in the US with the worst ozone pollution were also in California. Studies show that pollutants prevalent in California are linked to several health issues, including asthma, lung cancer, birth complications, and premature death. In 2016, Bakersfield, California recorded the highest level of airborne pollutants of any city in the United States.

Air Pollution in Mexico City has been of concern to the city's population and health officials for decades. In the 20th century, Mexico City's population rapidly increased as industrialization brought thousands of migrants from all over the world. Such a rapid and unexpected growth led to the UN declaring Mexico City as the most polluted city in the world in 1992. This was partly due to Mexico City's high altitude, which causes its oxygen levels to be 25% lower. Carbon-based fuels also do not combust completely. Other factors include the proliferation of vehicles, rapid industrial growth, and the population boom. The Mexican government has several active plans to reduce emission levels which require citizen participation, vehicular restrictions, increase of green areas, and expanded bicycle accessibility.

Air pollution is the release of pollutants into the air that are detrimental to human health and the Earth. In Canada, air pollution is regulated by standards set by the Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment (CCME), an inter-governmental body of federal, provincial and territorial Ministers responsible for the environment. Air pollution from the United States and to lesser extent Canada; caused by metal smelting, coal-burning for utilities, and vehicle emissions has resulted in acid rain, has severely impacted Canadian waterways, forest growth, and agricultural productivity.
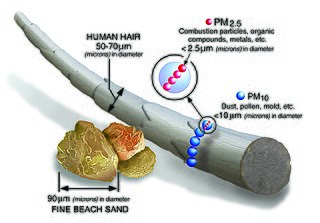
Particulates or atmospheric particulate matter are microscopic particles of solid or liquid matter suspended in the air. The term aerosol refers to the particulate/air mixture, as opposed to the particulate matter alone, though it is sometimes defined as a subset of aerosol terminology. Sources of particulate matter can be natural or anthropogenic. They have impacts on climate and precipitation that adversely affect human health, in ways additional to direct inhalation.

Air pollution in India is a serious environmental issue. Of the 30 most polluted cities in the world, 21 were in India in 2019. As per a study based on 2016 data, at least 140 million people in India breathe air that is 10 times or more over the WHO safe limit and 13 of the world's 20 cities with the highest annual levels of air pollution are in India. The main contributors to India's particulate air pollution include industrial and vehicular emissions, construction dust and debris, dependence on thermal power for electricity, waste burning, and use of wood and dung by low-income and rural households for cooking and heating. 51% of India's air pollution is caused by industrial pollution, 27% by vehicles, 17% by crop burning and 5% by other sources. Air pollution contributes to the premature deaths of 2 million Indians every year. Emissions come from vehicles and industry, whereas in rural areas, much of the pollution stems from biomass burning for cooking and keeping warm. In autumn and spring months, large scale crop residue burning in agriculture fields – a cheaper alternative to mechanical tilling – is a major source of smoke, smog and particulate pollution. India has a low per capita emissions of greenhouse gases but the country as a whole is the third largest greenhouse gas producer after China and the United States. A 2013 study on non-smokers has found that Indians have 30% weaker lung function than Europeans.
Toxic hotspots are locations where emissions from specific sources such as water or air pollution may expose local populations to elevated health risks, such as cancer. These emissions contribute to cumulative health risks of emissions from other sources nearby. Urban, highly populated areas around pollutant emitters such as old factories and waste storage sites are often toxic hotspots.

Air pollution in Iran is a significant health and environmental and health hazard. Iran ranks as the third most polluted country in the world. Iran ranks as the sixth most emitting country in the world.

Nitrogen dioxide poisoning is the illness resulting from the toxic effect of nitrogen dioxide. It usually occurs after the inhalation of the gas beyond the threshold limit value. Nitrogen dioxide is reddish-brown with a very harsh smell at high concentrations, at lower concentrations it is colorless but may still have a harsh odour. Nitrogen dioxide poisoning depends on the duration, frequency, and intensity of exposure.
Environmental health policy is governmental action intended to prevent exposure to environmental hazards or to "eliminate the effects of exposure to environmental hazards".
Particulate pollution is pollution of an environment that consists of particles suspended in some medium. There are three primary forms: atmospheric particulate matter, marine debris, and space debris. Some particles are released directly from a specific source, while others form in chemical reactions in the atmosphere. Particulate pollution can be derived from either natural sources or anthropogenic processes.

Research indicates that living in areas of high pollution has serious long term health effects. Living in these areas during childhood and adolescence can lead to diminished mental capacity and an increased risk of brain damage. People of all ages who live in high pollution areas for extended periods place themselves at increased risk of various neurological disorders. Both air pollution and heavy metal pollution have been implicated as having negative effects on central nervous system (CNS) functionality. The ability of pollutants to affect the neurophysiology of individuals after the structure of the CNS has become mostly stabilized is an example of negative neuroplasticity.














