
The mackerel, tuna, and bonito family, Scombridae, includes many of the most important and familiar food fishes. The family consists of 51 species in 15 genera and two subfamilies. All species are in the subfamily Scombrinae, except the butterfly kingfish, which is the sole member of subfamily Gasterochismatinae.

The beardfishes consist of a single extant genus, Polymixia, of deep-sea marine ray-finned fish named for their pair of long hyoid barbels. They are classified in their own order Polymixiiformes. But as Nelson says, "few groups have been shifted back and forth as frequently as this one, and they were recently added to Paracanthoptergii". For instance, they have previously been classified as belonging to the Beryciformes, and are presently considered either paracanthopterygians or the sister group to acanthopterygians. They are of little economic importance.

The Congridae are the family of conger and garden eels. Congers are valuable and often large food fishes, while garden eels live in colonies, all protruding from the sea floor after the manner of plants in a garden. The family includes over 220 species in 32 genera.

The Asiatic glassfishes are a family, the Ambassidae, of freshwater and marine ray-finned fishes that were formerly classified in the order Perciformes, but most authorities consider this order to be paraphyletic and that the Ambassidae are of uncertain affinities, incertae sedis, but within the subseries Ovalentaria. The species in the family are native to Asia, Oceania, the Indian Ocean, and the western Pacific Ocean. The family includes eight genera and about 51 species. Some species are known as perchlets.

The Carangidae are a family of ray-finned fish that includes the jacks, pompanos, jack mackerels, runners, trevallies, and scads. It is the largest of the six families included within the order Carangiformes. Some authorities classify it as the only family within that order but molecular and anatomical studies indicate that there is a close relationship between this family and the five former Perciform families which make up the Carangiformes.

Haemulidae is a family of fishes in the order Perciformes known commonly as grunts. It is made up of the two subfamilies Haemulinae (grunters) and Plectorhynchinae (sweetlips), which in turn contain about 133 species in 19 genera. These fish are found in tropical fresh, brackish, and salt waters around the world. They are bottom-feeding predators, and named for the ability of Haemulinae to produce sound by grinding their teeth. They also engage in mutualistic relationship with cleaner gobies of genus Elacatinus, allowing them to feed on ectoparasites on their bodies.

Anisotremus is a genus of grunts native to the eastern Pacific and western Atlantic Oceans. The name of this genus is compound of anisto meaning “different” and tremus meaning “hole”, referring to the different sized paired pores on each side of the head.
Jefitchia is an extinct genus of drum. Species lived from 48.6–33.9 mya. Jefitchia have been uncovered in Texas, Louisiana, and Portugal.
Eokrefftia is an extinct genus of lanternfish that inhabited the seas around Europe and Australia throughout the Paleogene. Known only from its distinctive fossilized otoliths, it appears to be one of the earliest definitive fossil members of the lanternfish lineage. It may belong to the extinct subfamily Eomyctophinae.
Ampheristus is an extinct genus of prehistoric marine ray-finned fish. It was a basal or stem member of the family Ophidiidae, which contains modern cusk-eels. Fossils are known from worldwide from the Late Cretaceous to the late Paleogene, making it a rather successful survivor of the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event.

Ctenodentex is an extinct genus of prehistoric seabream from the middle Eocene of Europe. It contains a single species, C. laekeniensis, from the Bartonian-aged Wemmel Member of the Maldegem Formation in Belgium. It was initially described as Dentex laekeniensis before being placed in its own genus, Ctenodentex, although some authors continue to classify it in Dentex.

Dapalis is an extinct genus of prehistoric glassfish known from the Middle Eocene to the Early Miocene. It is known from both freshwater and estuarine habitats of much of mainland Europe.

The Catostomidae are the suckers of the order Cypriniformes, with about 78 species in this family of freshwater fishes. The Catostomidae are almost exclusively native to North America. The only exceptions are Catostomus catostomus, found in both North America and Russia, and Myxocyprinus asiaticus found only in China. In the Ozarks they are a common food fish and a festival is held each year to celebrate them. The bigmouth buffalo, Ictiobus cyprinellus, can reach an age up to 127 years, making it the oldest known freshwater teleost by more than 50 years.

Drombus is a genus of gobies native to fresh, brackish and marine waters of the Indian Ocean and the western Pacific Ocean.

Orthopristis chrysoptera, the pigfish, hogfish, piggy perch, redmouth grunt or sailor's choice, is a species of marine ray-finned fish, a grunt belonging to the family Haemulidae. It is found in the western Atlantic Ocean. This name derives from the grunting or chattering noise these fish make by rubbing their pharyngeal teeth together.

Haemulinae is a subfamily of the Haemulidae and consists of the genera of that family which are regarded as being of New World origin, although they are now widespread. The subfamily is distinguished from the Plectorhynchinae by having a short dorsal fin which contains 13-16 soft rays, as opposed to the long dorsal fin with 17-26 soft rays of the subfamily Plectorhynchinae.
Aturobatis is an extinct genus of Myliobatiform ray from the Eocene epoch. It contains a single described species, A. aquensis; however, the range of variation in this species is not well understood and it is unclear whether all specimens attributed to the genus are the same species. It is also unknown to which family this genus belongs. The type locality is the Lutetian of southern France. This genus is also known from the Ypresian of the United States, the Lutetian Lisbon Formation of Alabama, and the Priabonian Samlat Formation of Dakhla, Morocco.
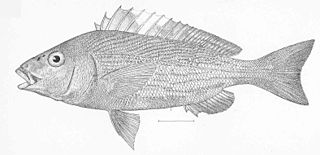
Orthopristis reddingi, the bronze-striped grunt, is a species of ray-finned fish, a grunt belonging to the family Haemulidae. It is endemic to Mexico, occurring from central Baja California, including the southern Sea of Cortez, to central Mexico. It is found in schools over sandy substrates in coastal waters and the juveniles are frequently recorded in tidal pools. They are found at depths between 5 and 30 m. This species was first formally described in 1895 by the American ichthyologists David Starr Jordan and Robert Earl Richardson, the type locality was given as La Paz, Baja California Sur. The specific name honours in Benjamin B. Redding (1824-1882), the politician who was the first Fish Commissioner of California.
This list of fossil fish research presented in 2022 is a list of new fossil taxa of jawless vertebrates, placoderms, cartilaginous fishes, bony fishes, and other fishes that were described during the year, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to paleoichthyology that occurred in 2022.
This list of fossil fish research presented in 2023 is a list of new fossil taxa of jawless vertebrates, placoderms, cartilaginous fishes, bony fishes, and other fishes that were described during the year, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to paleoichthyology that occurred in 2023.














