The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to the Falkland Islands:
Contents
- General reference
- Geography of the Falkland Islands
- Environment of the Falkland Islands
- Regions of the Falkland Islands
- Demography of the Falkland Islands
- Government and politics of the Falkland Islands
- Branches of the government of the Falkland Islands
- Foreign relations of the Falkland Islands
- Law and order in the Falkland Islands
- Military of the Falkland Islands
- Local government in the Falkland Islands
- History of the Falkland Islands
- Culture of the Falkland Islands
- Art in the Falkland Islands
- Sports in the Falkland Islands
- Economy and infrastructure of the Falkland Islands
- Education in the Falkland Islands
- See also
- References
- External links
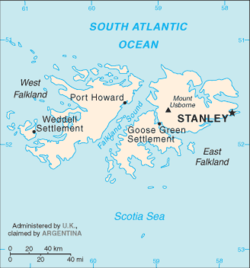
The Falkland Islands (Spanish : Islas Malvinas) are an archipelago located in the South Atlantic Ocean on the Patagonian Shelf. The principal islands are about 310 miles (500 kilometres) east of the Patagonian coast at a latitude of about 52°S. The archipelago which has an area of 4,700 square miles (12,173 square kilometres) comprises East Falkland, West Falkland and 776 smaller islands. The islands, a British Overseas Territory, enjoy a large degree of internal self-government with the United Kingdom guaranteeing good government and taking responsibility for their defence and foreign affairs. The capital is Stanley on East Falkland.
Controversy exists over the Falklands' original discovery and subsequent colonisation by Europeans. At various times there have been French, British, Spanish, and Argentine settlements. Britain re-established its rule in 1833, though the islands continue to be claimed by Argentina. In 1982, following Argentina's invasion of the islands, the two-month-long undeclared Falklands War between both countries resulted in the surrender of all Argentine forces and the return of the islands to British administration.
The population, estimated at 2,841, primarily consists of native Falkland Islanders, the vast majority being of British descent. Other ethnicities include French, Gibraltarian, and Scandinavian. Immigration from the United Kingdom, Saint Helena, and Chile has reversed a former population decline. The predominant and official language is English. Under the British Nationality Act of 1983, Falkland Islanders are legally British citizens.
The islands lie on the boundary of the Subarctic maritime climate and Temperate maritime climate zones with both major islands having mountain ranges reaching to 2,300 feet (700 m). The islands are home to large bird populations, although many no longer breed on the main islands because of the effects of introduced species. Major economic activities include fishing, tourism, sheep farming with an emphasis on high-quality wool exports, and oil exploration. Oil exploration, licensed by the Falkland Islands Government, remains controversial as a result of maritime disputes with Argentina.