
The South Island is the largest of the three major islands of New Zealand in surface area, the others being the smaller but more populous North Island and sparsely populated Stewart Island. It is bordered to the north by Cook Strait, to the west by the Tasman Sea, to the south by the Foveaux Strait and Southern Ocean, and to the east by the Pacific Ocean. The South Island covers 150,437 square kilometres (58,084 sq mi), making it the world's 12th-largest island, constituting 56% of New Zealand's land area. At low altitudes, it has an oceanic climate. The major centres are Christchurch, with a metropolitan population of 521,881, and the smaller Dunedin. The economy relies on agriculture, fishing, tourism, and general manufacturing and services.
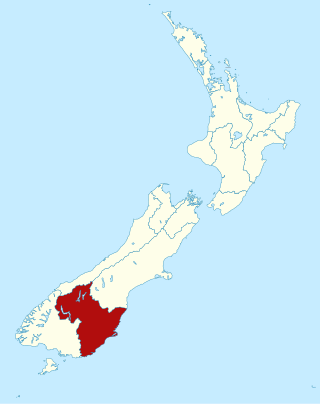
Otago is a region of New Zealand located in the southern half of the South Island administered by the Otago Regional Council. It has an area of approximately 32,000 square kilometres (12,000 sq mi), making it the country's second largest local government region. Its population was 257,200 in June 2024.

Oamaru is the largest town in North Otago, in the South Island of New Zealand, it is the main town in the Waitaki District. It is 80 kilometres (50 mi) south of Timaru and 120 kilometres (75 mi) north of Dunedin on the Pacific coast; State Highway 1 and the railway Main South Line connect it to both cities. With a population of 14,350, Oamaru is the 28th largest urban area in New Zealand, and the third largest in Otago behind Dunedin and Queenstown. The town is the seat of Waitaki District, which includes the surrounding towns of Kurow, Weston, Palmerston, and Hampden, which combined have a total population of 23,200.

Riverton, officially Riverton / Aparima, is a small New Zealand town 30 kilometres (19 mi) west of Invercargill, on the south-eastern shorelines of the Jacobs River Estuary. The estuary is formed by the Aparima and Pourakino rivers, leading through a narrow outflow channel into Foveaux Strait. Accessible via State Highway 99 on the Southern Scenic Route, the main part of the town is on flat land and the northern end of Oreti Beach. South Riverton is built on the hills between the eastern shore of the estuary and Taramea Bay.
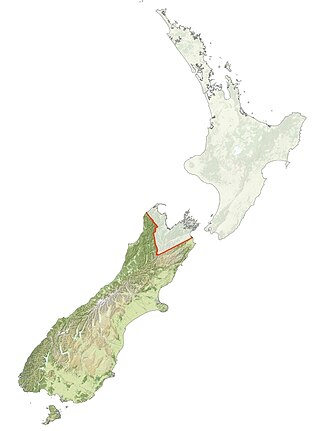
Ngāi Tahu, or Kāi Tahu, is the principal Māori iwi (tribe) of the South Island. Its takiwā is the largest in New Zealand, and extends from the White Bluffs / Te Parinui o Whiti, Mount Mahanga and Kahurangi Point in the north to Stewart Island / Rakiura in the south. The takiwā comprises 18 rūnanga corresponding to traditional settlements. According to the 2018 census an estimated 74,082 people affiliated with the Kāi Tahu iwi.

Dunedin is the second-largest city in the South Island of New Zealand, and the principal city of the Otago region. Its name comes from Dùn Èideann, the Scottish Gaelic name for Edinburgh, the capital of Scotland. The city has a rich Māori, Scottish, and Chinese heritage.

Mosgiel is an urban satellite of Dunedin in Otago, New Zealand, fifteen kilometres west of the city's centre. Since the re-organisation of New Zealand local government in 1989 it has been inside the Dunedin City Council area. Mosgiel has a population of approximately 15,150 as of June 2024. A nickname for Mosgiel is "The pearl of the plain". Its low-lying nature does pose problems, making it prone to flooding after heavy rains. Mosgiel takes its name from Mossgiel Farm, Ayrshire, the farm of the poet Robert Burns, the uncle of the co-founder in 1848 of the Otago settlement, the Reverend Thomas Burns.

Waitaki District is a territorial authority district that is located in the Canterbury and Otago regions of the South Island of New Zealand. It straddles the traditional border between the two regions, the Waitaki River, and its seat is Oamaru.

Otakou is a settlement within the boundaries of the city of Dunedin, New Zealand. It is located 25 kilometres from the city centre at the eastern end of Otago Peninsula, close to the entrance of Otago Harbour. Though a small fishing village, Otakou is important in the history of Otago for several reasons. The settlement is the modern centre and traditional home of the Ōtākou rūnanga (assembly) of Ngāi Tahu. In 1946 Otakou Fisheries was founded in the township; this was later to become a major part of the Otago fishing industry.

Moeraki is a small fishing village on the east coast of the South Island of New Zealand. It was once the location of a whaling station. In the 1870s, local interests believed it could become the main port for the north Otago area and a railway line, the Moeraki Branch, was built to the settlement and opened in 1877. However, the port could not compete with Oamaru and the lack of traffic as well as stability problems caused by difficult terrain led to the closure of the railway in 1879 after only two years' operation.

Dunback, formerly Waihemo, is a small town in the Otago region of New Zealand. It is located between Palmerston and Ranfurly on Highway 85. It has a population of about 200 people. Most of these people live in the rural areas near the town.
Waitaha is an early Māori iwi, which inhabited the South Island of New Zealand. They were largely absorbed via marriage and conquest – first by the Ngāti Māmoe and then by Ngāi Tahu – from the 16th century onward. Today those of Waitaha descent are represented by the Ngāi Tahu iwi. Like Ngāi Tahu today, Waitaha was itself a collection of various ancient iwi. Kāti Rākai was said to be one of Waitaha's hapū.

Āraiteuru was a canoe of some of Ngāi Tahu's ancestors in Māori tradition.

The villages and then city that lay at the head of Otago Harbour never existed in isolation, but have always been a staging ground between inland Otago and the wider world. While Dunedin's current official city limits extend north to Waikouaiti, inland to Middlemarch and south to the Taieri River mouth, this articles focus is the history of the Dunedin urban area, only mentioning Mosgiel, the Otago Peninsula, Port Chalmers and inland Otago for context.
The Otago region of New Zealand is one of the more isolated places of the inhabited earth. Its high latitude, elevation and distance from larger foreign and domestic population centres have defined Otago at each stage of its history.
Uruaokapuarangi was one of the great ocean-going, voyaging canoes that was used in the migrations that settled the South Island according to Māori tradition.
Wakari is a residential suburb of the New Zealand city of Dunedin. It is located 2.5 kilometres (1.6 mi) to the northwest of the city centre, immediately to the west of the ridge which runs to the west of the city's centre. Wakari lies to the north of the upper reaches of the Kaikorai Valley, and is also north of the suburb of Kaikorai. The suburbs of Roslyn and Maori Hill are situated on the ridge immediately to the southeast and east of Wakari. The suburb of Halfway Bush lies to the northwest, and the smaller suburb of Helensburgh lies to the north.

Atholl John Anderson is a New Zealand archaeologist who has worked extensively in New Zealand and the Pacific. His work is notable for its syntheses of history, biology, ethnography and archaeological evidence. He made a major contribution to the evidence given by the iwi (tribe) Ngāi Tahu to the Waitangi Tribunal.

Puketapu is a prominent hill in Otago, in New Zealand's South Island, overlooking the town of Palmerston. The name Puketapu is Māori meaning "sacred hill".




















