The Eastern Highlands moist deciduous forests, presently known as East Deccan moist deciduous forests, is a tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests ecoregion in east-central India. The ecoregion covers an area of 341,100 square kilometers (131,700 sq mi), extending across portions of Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Odisha, and Telangana states.

The Caucasus mixed forests is a temperate broadleaf and mixed forests ecoregion in the Caucasus Mountains, as well as the adjacent Lesser Caucasus range and the eastern end of the Pontic Mountains.

The Crimean Submediterranean forest complex is an ecoregion on the Black Sea coast of Russia and Ukraine. It is in the temperate broadleaf and mixed forests biome.

The North Saharan steppe and woodlands is a desert ecoregion, in the deserts and xeric shrublands biome, that forms the northern edge of the Sahara. It extends east and west across Northern Africa, south of the Mediterranean dry woodlands and steppe ecoregion of the Maghreb and Cyrenaica, which is part of the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub biome. Winter rains sustain shrublands and dry woodlands that form an ecotone between the Mediterranean climate regions to the north and the hyper-arid Sahara Desert ecoregion to the south.

The Mediterranean dry woodlands and steppe is a Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub ecoregion of North Africa. It occupies interior plateaus and mountain ranges of the Maghreb region, lying generally between the coastal Mediterranean woodlands and forests to the north and the Sahara to the south.

The Illyrian deciduous forests is a terrestrial ecoregion in southern Europe, which extends along the eastern coast of the Adriatic Sea. It belongs to the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub biome, and is in the Palearctic realm.

The Italian sclerophyllous and deciduous forests ecoregion, part of the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub biome, is in Italy. The ecoregion covers most of the Italian Peninsula and includes both evergreen and deciduous forests.

The Tyrrhenian-Adriatic sclerophyllous and mixed forests is an ecoregion in southern Italy, Sicily, Sardinia, Corsica, the Dalmatian Islands of Croatia, and Malta.

Tugay is a form of riparian forest or woodland associated with fluvial and floodplain areas in arid climates. These wetlands are subject to periodic inundation, and largely dependent on floods and groundwater rather than directly from rainfall. Tugay habitats occur in semi-arid and desert climates in Central Asia. Because Tugay habitat is usually linear, following the courses of rivers in arid landscapes, Tugay communities often function as wildlife corridors. They have disappeared or become fragmented over much of their former range.

The Eastern Anatolian montane steppe is a temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands ecoregion. It is located in the Armenian Highlands, covering parts of eastern Turkey, Armenia, Azerbaijan, southern Georgia, and northwestern Iran.

The Qionglai-Minshan conifer forests are a World Wide Fund for Nature ecoregion in Southwest China. These forests are classified as temperate coniferous forests and are part of the Palearctic realm.

The Qilian Mountains Conifer Forests ecoregion is an ecoregion that consists of a series of isolated conifer forests on the northern slopes of the Qilian Mountain Range, on the northeast edge of the Tibetan Plateau in Qinghai and Gansu provinces of north-central China.

The Tian Shan montane conifer forests ecoregion covers the "forest belt" of the Tian Shan mountains - generally the north-facing slopes that get enough moisture, and are warm enough, for trees to grow. This conifer belt is found mostly between 1,500 and 2,700 meters.

The Tian Shan foothill arid steppe ecoregion covers the northern and western approaches to the Tian Shan mountains, centered on Lake Issyk-Kul in Kyrgyzstan. This region receives more moisture from Central Asia, thereby supporting more vegetation and diversity of plant and animal species than the deserts to the south.

The Central Asian riparian woodlands ecoregion is spread out across the deserts and plains of central Asia between the Aral Sea and the mountains 2,000 kilometres (1,200 mi) to the east. The long narrow components of the ecoregion follow the large rivers fed by snowmelt, and provide critical habitat for migratory birds as they travel through the arid region. The vegetation is referred to as tugai, characterized by low tangles of trees and brush along the edges of the rivers and associated wetlands, and fed by groundwater instead of precipitation.

The Gissaro-Alai open woodlands ecoregion covers the western foothills winding around two western offshoots of the Tian Shan Mountains in western Tajikistan, and parts of eastern Uzbekistan and western Kyrgyzstan, in Central Asia. The woodlands are typically of Juniper trees and shrubs, fitting the altitude zone situated between the desert valley floor, and the tree line, above which the mountain ridges are glaciated and barren.

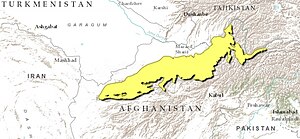
The East Afghan montane conifer forests ecoregion covers a series of unconnected conifer forests along the border between Afghanistan and Pakistan, at elevations of 2,000 metres (6,600 ft) to 3,400 metres (11,200 ft) above sea level. The ecoregion supports the near-threatened Markhor (Capra falconeri chiltanensis), known as the Screw-horned goat, the national animal of Pakistan. The forests of the ecoregion have been heavily thinned for timber.

The Azerbaijan shrub desert and steppe is a deserts and xeric shrublands ecoregion in western Asia. It lies in the lowlands west of the Caspian Sea, and covers portions of Azerbaijan, Georgia, and Iran.

The Central Afghan Mountains xeric woodlands ecoregion covers the xeric (dry) eastern and southern slopes of the central mountain range of Afghanistan, between the sandy desert to the south and the alpine meadows in the higher, wetter region to the north. Despite the 'woodlands' in the ecoregion name, very little of the territory is forested – less than 1% – but is instead sparse vegetation or herbaceous cover.

The Baluchistan xeric woodlands ecoregion covers the middle elevations of a series of mountain ranges of western Pakistan and northeastern Afghanistan, reaching 1,200 kilometres (750 mi) from the Arabian Sea in the south to the Hindu Kush Mountains and the Himalayas in the north. The characteristic vegetation is xeric (dry) woodlands of shrubs and herbaceous cover. The region has rich biodiversity but relatively few endemic species.