History
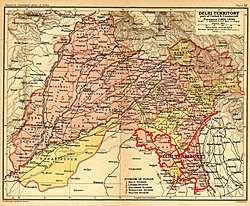
The state of Pataudi was established in 1804 by the British East India Company, when Faiz Talab Khan, an Afghan Pashtun warlord of the Barech tribe, who was made the first Nawab, aided them in their battle against the Maratha Empire, during the Second Anglo-Maratha War. [1] The family traces their origin to 16th century India, when their ancestors came from present day Afghanistan to India during the period of the Lodi dynasty. [1] The 8th Nawab, Iftikhar Ali Khan Pataudi, played cricket for both England and India and captained the latter. His son the last Nawab also captained the Indian cricket team.
At the end of the British Raj and with the political integration of India in 1948, the princely state of Pataudi was absorbed into the new Dominion of India (later Republic of India). In 1971, by virtue of the 26th amendment to the Constitution of India, the Government of India abolished all official symbols of princely India, including titles, privileges, and remuneration (privy purses). [2] [3]
The former Pataudi Palace was a hotel for some time, but is now owned privately by Saif Ali Khan, the current patriarch of the Pataudi family.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.