
The Murray River is a river in south-eastern Australia. It is Australia's longest river at 2,508 km (1,558 mi) extent. Its tributaries include five of the next six longest rivers of Australia. Together with that of the Murray, the catchments of these rivers form the Murray–Darling basin, which covers about one-seventh the area of Australia. It is widely considered Australia's most important irrigated region.
Cadastral divisions in Victoria are called counties, which are further subdivided into parishes and townships, for cadastral or land administration purposes. Cadastral divisions of county, parish and township form the basis for formal identification of the location of any piece of land in the state. There are 37 counties and 2004 parishes and 909 townships. Parishes were subdivided into sections of various sizes for sale as farming allotments, or designated as a town and then divided into sections and these subdivided into crown allotments. However, many parishes do not follow county borders, some being located in more than one county.

Boundary Bend is a small town in the state of Victoria, Australia. It is near the junction of the Murray River and Murrumbidgee River. It is located about 50 kilometres east along the Murray Valley Highway from the twin towns of Robinvale in Victoria and Euston in New South Wales, about 90 km north of Swan Hill. At the 2016 census, Boundary Bend and the surrounding area had a population of 132.

Robinvale is a town on the south bank of the Murray River in north western Victoria, Australia. It is connected by a bridge to Euston on the other side of the river in New South Wales. At the 2016 census, Robinvale had a population of 3,313, however a population study conducted by the Rural City of Swan Hill that was undertaken in 2019 identified Robinvale had an estimated population of between 7,000 in November and 8,800 in March each year.

Corowa is a town in the state of New South Wales in Australia. It is on the bank of the Murray River, the border between New South Wales and Victoria, opposite the Victorian town of Wahgunyah. It is the largest town in the Federation Council and was the administrative centre of the former Corowa Shire. The name could have derived from an Aboriginal word referring to the curra pine which yielded gum used by Aboriginal people to fasten the heads of spears to the shafts. Another translation is "rocky river".

The Mallee covers the most northwesterly part of Victoria, bounded by the South Australian and New South Wales borders. Definitions of the south-eastern boundary vary, however, all are based on the historic Victorian distribution of mallee eucalypts. These trees dominate the surviving vegetation through most of Mallee,. Its biggest settlements are Mildura and Swan Hill.

Swan Hill is a city in the northwest of Victoria, Australia on the Murray Valley Highway and on the south bank of the Murray River, downstream from the junction of the Loddon River. At June 2018, Swan Hill had a population of 11,103.

Whadjuk, alternatively Witjari, are a Noongar people of the Western Australian region of the Perth bioregion of the Swan Coastal Plain.

Lake Boga is a town in Victoria, Australia, located next to the lake of the same name. It is situated within the Rural City of Swan Hill within the Mallee region of north-west Victoria. At the 2016 census, Lake Boga had a population of 985. The town is located 325 kilometres (202 mi) north west of Melbourne and 17 kilometres (11 mi) south east of the regional centre Swan Hill.

Lands administrative divisions of Australia are the cadastral divisions of Australia for the purposes of identification of land to ensure security of land ownership. Most states term these divisions as counties, parishes, hundreds, and other terms. The eastern states of Queensland, New South Wales, Victoria, and Tasmania were divided into counties and parishes in the 19th century, although the Tasmanian counties were renamed land districts in the 20th century. Parts of South Australia (south-east) and Western Australia (south-west) were similarly divided into counties, and there were also five counties in a small part of the Northern Territory. However South Australia has subdivisions of hundreds instead of parishes, along with the Northern Territory, which was part of South Australia when the hundreds were proclaimed. There were also formerly hundreds in Tasmania. There have been at least 600 counties, 544 hundreds and at least 15,692 parishes in Australia, but there are none of these units for most of the sparsely inhabited central and western parts of the country.
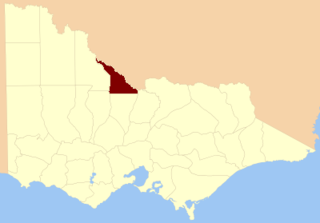
The County of Gunbower is one of the 37 counties of Victoria which are part of the cadastral divisions of Australia, used for land titles. It is located to the south of the Murray River, from Swan Hill to Echuca.
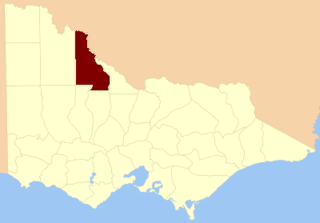
The County of Tatchera is one of the 37 counties of Victoria which are part of the cadastral divisions of Australia, used for land titles. It is located to the south of the Murray River, and to the south west of Swan Hill, with its western boundary at 143°E, and part of the southern boundary at 36°S.

The Wemba-Wemba are an Aboriginal Australian group in north-Western Victoria and south-western New South Wales, Australia, including in the Mallee and the Riverina regions. They are also known as the Wamba-Wamba.

Beveridge Island is an island in Victoria, Australia, within the locality of Tyntynder in the Rural City of Swan Hill.

The Little Murray River, an anabranch of the Murray River and part of the Murray-Darling basin, is located in the Mallee district of north western Victoria, in eastern Australia.

The Barapa Barapa people are an indigenous Australian people whose territory covered parts of southern New South Wales and northern Victoria. They had close connections with the Wemba-Wemba.
Big Rivers is a grape growing zone in Australia. It covers the southwestern corner of the state of New South Wales. The zone currently includes four wine regions, which cover the main areas of grape growing in the zone, but not all of them.
The Watiwati are an indigenous Australian aboriginal people traditionally living on both sides of the Murray River, from Victoria to New South Wales.
The Wotjobaluk are an Aboriginal Australian people of the state of Victoria. They are closely related to the Wergaia people.

Murray Downs is a locality in the Murray River Council, New South Wales, Australia. It is directly across the border from Swan Hill.


















