Classification
The genus Phlyctaenopyga was first described in 1944 by Cabrera, for a species of Late Miocene glyptodont first ascribed to the genus Plohophorus , P. ameghini. Cabrera also attributed the species Nopachthus trouessarti to this genus, as Phlyctaenopyga trouessarti. Those two species were mainly distinguished by details of their osteoderms.
Phlyctaenopyga was a glyptodont, a clade of cingulates related to the modern armadillos, with a rigid carapace. Phlyctaenopyga seems to have been close to the genera Nopachthus and Plohophorus , within the tribe Sclerocalyptini.
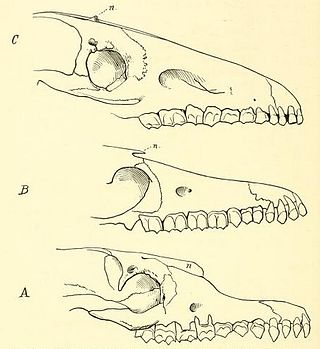
Scalabrinitherium is an extinct genus of mammals of the family Macraucheniidae. Fossils of this animal were found among the fossils of prehistoric xenarthrans in the Ituzaingó Formation of Argentina.

Hoplophorus is an extinct genus of glyptodont, a subfamily of armadillos. The only confidently known species was H. euphractus, found in Pleistocene deposits in Brazil, though fossils possibly from another species are known from Bolivia.

Propalaehoplophorus, also written as Propalaeohoplophorus, is an extinct genus of glyptodont, which lived in South America during the Early Miocene epoch.
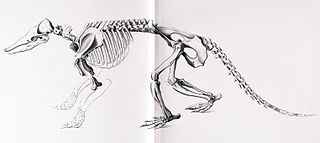
Stegotherium is an extinct genus of long-nosed armadillo, belonging to the Dasypodidae family alongside the nine-banded armadillo. It is currently the only genus recognized as a member of the tribe Stegotheriini. It lived during the Early Miocene of Patagonia and was found in Colhuehuapian rocks from the Sarmiento Formation, Santacrucian rocks from the Santa Cruz Formation, and potentially also in Colloncuran rocks from the Middle Miocene Collón Curá Formation. Its strange, almost toothless and elongated skull indicates a specialization for myrmecophagy, the eating of ants, unique among the order Cingulata, which includes pampatheres, glyptodonts and all the extant species of armadillos.

Neosclerocalyptus was an extinct genus of glyptodont that lived during the Pliocene, Pleistocene, and Holocene of Southern South America, mostly Argentina. It was small compared to many Glyptodonts at only around 2 meters long and 360 kilograms.
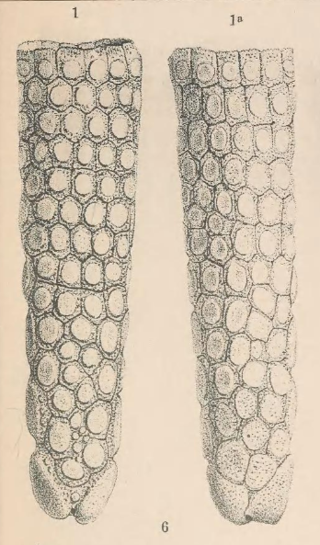
Lomaphorus is a possibly dubious extinct genus of glyptodont that lived during the Pleistocene in eastern Argentina. Although many species have been referred, the genus itself is possibly dubious or synonymous with other glyptodonts like Neoslerocalyptus from the same region.
Proeuphractus is an extinct genus of xenarthran, related to the modern armadillos. It lived from the Early to the Late Miocene, and its fossilized remains were discovered in South America.

Prozaedyus is an extinct genus of chlamyphorid armadillo that lived during the Middle Oligocene and Middle Miocene in what is now South America.
Glyptatelus is an extinct genus of glyptodont. It lived from the Late Eocene to the Middle Oligocene in what is now Argentina and Bolivia.
Protoglyptodon is an extinct genus of glyptodont. It lived during the Late Miocene, and its fossilized remains were found in South America.
Palaehoplophorus is an extinct genus of glyptodont. It lived from the Middle to the Late Miocene, and its fossilized remains were discovered in South America.
Urotherium is an extinct genus of Glyptodont. It lived from the Late Miocene to the Late Pliocene, and its fossilized remains were found in South America.
Plohophorus is an extinct genus of glyptodont. it lived from the Late Miocene to the Late Pliocene, and its fossilized remains were discovered in South America.
Eosclerocalyptus is an extinct genus of glyptodont. It lived during the Late Miocene, and its fossilized remains were discovered in South America.
Coscinocercus is an extinct genus of Glyptodont. It lived during the Late Miocene, and its fossilized remains were discovered in South America.
Comaphorus is a dubious extinct genus of glyptodont. It lived during the Late Miocene in Argentina, but only one fossil has ever been referred to the animal.
Asterostemma is an extinct genus of glyptodont. It lived during the Middle Miocene, and its fossilized remains were discovered in South America.

Cochlops is an extinct genus of glyptodont. It lived from the Early to Middle Miocene, and its fossilized remains have been found in South America.
Dasypus neogaeus is an extinct species of armadillo, belonging to the genus Dasypus, alongside the modern nine-banded armadillo. The only known fossil is a single osteoderm, though it has been lost, that was found in the Late Miocene strata of Argentina.

Peltephilidae is a family of South American cingulates (armadillos) that lived for over 40 million years, but peaked in diversity towards the end of the Oligocene and beginning of the Miocene in what is now Argentina. They were exclusive to South America due to its geographic isolation at the time, one of many of the continent's strange endemic families. Peltephilids are one of the earliest known cingulates, diverging from the rest of Cingulata in the Early Eocene.
This page is based on this
Wikipedia article Text is available under the
CC BY-SA 4.0 license; additional terms may apply.
Images, videos and audio are available under their respective licenses.











