| Piping guans | |
|---|---|
 | |
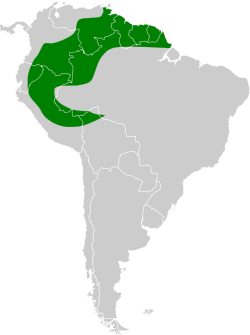
| A blue-throated piping guan | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Galliformes |
| Family: | Cracidae |
| Subfamily: | Penelopinae |
| Genus: | Pipile Bonaparte, 1856 |
| Type species | |
| Penelope leucolophos [1] | |
| Species | |
Pipile cujubi | |
The piping guans are a bird genus, Pipile, in the family Cracidae. A recent study, [2] evaluating mtDNA, osteology and biogeography data [2] concluding that the wattled guan belongs in the same genus as these and is a hypermelanistic piping guan. Thus, Pipile became a junior synonym of Aburria, though this conclusion was not accepted by the South American Checklist Committee, [3] or evaluated by the IOC, so the classification remains in Pipile.
The same results also showed that the light-faced taxa pipile, cumanensis and cujubi are not, as was sometimes suggested, conspecific. However, free interbreeding between A. cujubi and A. cumanensis grayi in eastern Bolivia, creating a "hybrid swarm", casts doubt on this conclusion for the two species named. [3] [4]
It was possible to confidently resolve that the white-faced species form a clade, whereas the more basal black-faced forms are of less certain relationship. Possibly, the black-fronted piping guan is the basalmost taxon, but the placement of the wattled guan in regard to its congeners is not all too well resolved. Blue wattles evolved only once, in a lineage which seems to have originated north of the Amazon River. The piping guans' radiation began in the latter half of the Early Pliocene, roughly 4–3.5 mya. The white-faced lineage emerged around 3 mya and its present diversity began to evolve around the Pliocene-Pleistocene boundary, when the ancestors of the red-throated piping guan and the blue-wattled taxa split. Due to not being calibrated by material evidence such as fossils, the divergence times cannot be estimated with a high confidence. [2]
The origin of the genus was possibly in the general area of eastern Bolivia, at the very margin of its current range. From the phylogeny outlined above, the piping guans would be expected to have originated in the southern Brazilian lowlands. However, although the relationships of the genera of guans are not entirely clear, it seems most likely that the group originated in the northern Andes region: The northernmost guan genera Chamaepetes and Penelopina appear to be basal divergences, and Pipile is most likely closer to Penelope (which represents a generally southward radiation out of the northern Andes) than to these.
Thus it appears most likely that the present genus diverged in the eastern foothills of the Andes somewhere in the vicinity of Bolivia, far to the northwest from where its origin would be presumed from the phylogeny and present-day distribution of Pipile alone. [5] [2] Two considerations are worthy of note: First, the time at which the ancestor of the piping guans diverged from Penelope has been roughly dated to the Burdigalian, some 20-15 mya, which leaves a considerable gap during which no surviving piping guan lineage evolved. [5] Secondly, it is notable that in the Late Pliocene, rising sea levels transformed much of the South American lowlands into brackish lagoon habitat unsuitable for piping guans. Thus, the present distribution is apparently a relict, and extinction of populations/displacement by the more resilient Penelope guans seems to have played as much or possibly more of a role in shaping the diversity of piping guans of our time than emergence of new lineages. [2]