
Trematosauroidea are an important group of Triassic temnospondyl amphibians. They flourished briefly during the Early Triassic, occurring worldwide before declining at the start of the Middle Triassic, although the group continued until the Late Triassic. They were medium-sized temnospondyls with wedge-shaped tails, narrow skulls, and, in advanced forms, elongated snouts. The latter feature was probably an adaptation for feeding on fish. The largest and most specialized family, the Trematosauridae, are the only batrachomorphs to have adapted to a marine lifestyle with the exception of the modern crab-eating frog.
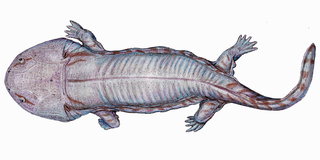
The Stereospondyli are a group of extinct temnospondyl amphibians that existed primarily during the Mesozoic period. They are known from all seven continents and were common components of many Triassic ecosystems, likely filling a similar ecological niche to modern crocodilians prior to the diversification of pseudosuchian archosaurs.

Metoposauroidea is an extinct superfamily of temnospondyls that lived from the Middle to Upper Triassic in North America, Europe and North Africa. Metoposauroidea includes the families Metoposauridae and Latiscopidae.

Trematolestes is an extinct genus of temnospondyl amphibian from the Lower Keuper of southern Germany. It was first named by Rainer R. Schoch in 2006 and the type species is Trematolestes hagdorni. It is the first trematosaurid represented by a nearly complete skeleton.
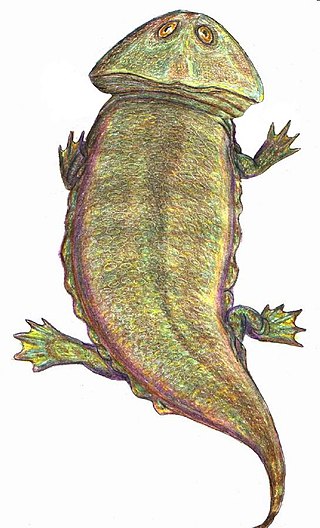
Plagiosaurus is an extinct genus of temnospondyl amphibian - Arthur Smith Woodward regarded it as a synonym of Plagiosternum. They were paedomorphic, retaining the larval gills on adulthood. They had weak simplified vertebrae, consisting of large intercentra and neural arches, the stereospondyl condition.

Plagiosauridae is a clade of temnospondyls of the Middle to Late Triassic. Deposits of the group are most commonly found in non-marine aquatic depositional environments from central Europe and Greenland, but other remains have been found in Russia, Scandinavia, and possibly Thailand.

Trematosaurinae is a subfamily of temnospondyl amphibians within the family Trematosauridae. Like all trematosaurids, they were marine piscivores, resembling crocodiles in their general build. Unlike the long, almost gharial-like snouts of the Lonchorhynchinae, the Trematosaurinae had more "normal" crocodile-like skulls.

The Mastodonsauroidea are an extinct superfamily of temnospondyl amphibians known from the Triassic. Fossils belonging to this superfamily have been found in North America, Greenland, Europe, Asia, and Australia. Ferganobatrachus from the Jurassic of Asia was initially assigned to this superfamily, but is now considered to be congeneric with the brachyopid Gobiops.
Almasaurus is an extinct genus of trematosaurian temnospondyl within the family Latiscopidae. It is known from several skulls and some postcranial material found from the Argana Formation in Morocco, which dates back to the Late Triassic.

Hadrokkosaurus is an extinct genus of brachyopid temnospondyl amphibian from the Middle Triassic of the southwestern United States. It includes a single species, Hadrokkosaurus bradyi, known from the Moenkopi Formation of Arizona.

Xenotosuchus is an extinct genus of mastodonsaurid temnospondyl within the family Mastodonsauridae known from the Triassic of South Africa. The genus is based on a skull originally described as Parotosuchus, an animal which it resembled in general build and habit.

Plagiosuchus is an extinct genus of plagiosaurid temnospondyl. It is known from several collections from the Middle Triassic of Germany.

Stenotosaurus is an extinct genus of capitosaurian temnospondyl within the family Stenotosauridae. It is known from three species, all of which lived during the Anisian stage of the Middle Triassic. Fossils have been found in England and Germany.

Capitosauria is an extinct group of large temnospondyl amphibians with simplified stereospondyl vertebrae. Mainly living as piscivores in lakes and rivers, the Capitosauria and its sister taxon Trematosauria were the only major labyrinthodonts that existed during the Mesozoic in ecological niches broadly similar to those of modern crocodiles, and some grew to very large sizes. At 6 meters in length, the Mid-Triassic Mastodonsaurus giganteus is not only thought to have been the largest capitosaur, but possibly also the largest amphibian to have lived. The latest known remains are from the Rhaetian of Germany and are referred to Cyclotosaurus.
Vladlenosaurus is an extinct genus of capitosaurian temnospondyl from Russia. It lived during the late Vetlugian. Based on the type of deposits it was found in, Vladlenosaurus probably inhabited lacustrine, or lake, habitats. The type species is V. alexeyevi, named in 2000.

Stenotosauridae is an extinct family of mastodonsauroid temnospondyls. It has included genera such as Stenotosaurus, Wellesaurus, and Procyclotosaurus.
Meyerosuchus is an extinct genus of mastodonsauroidean temnospondyl. Fossils have been found from the Early Triassic Hardegsen Formation in southern Germany. Meyerosuchus is present in late Olenekian deposits of the Middle Buntsandstein. The type species M. fuerstenberganus was named in 1966, although remains have been known since 1855. Meyerosuchus is closely related to Stenotosaurus; both genera are grouped in the family Stenotosauridae and the two genera may even be synonymous.
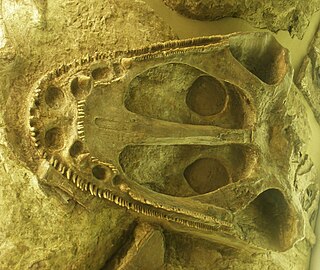
Heptasaurus is an extinct genus of Triassic capitosaurian temnospondyl within the family Mastodonsauridae.

Callistomordax is an extinct genus of temnospondyl amphibian from the Middle Triassic of Germany. The type and only species, Callistomordax kugleri, was named in 2008. It is known from several well-preserved skeletons found in the Erfurt Formation, part of the Lower Keuper, which dates back to the late Ladinian stage.

Megalophthalma is an extinct genus of temnospondyl amphibian belonging to the family Plagiosauridae. It is represented by the single type species Megalophthalma ockerti from the Middle Triassic Erfurt Formation in southern Germany, which is itself based on a single partial skull and a fragment of the lower jaw. Megalophthalma is distinguished from other temnospondyls by its very large orbits or eye sockets, which occupy most of the skull and are bordered by thin struts of bone. Like those of most plagiosaurids, the skull flat, wide, and roughly triangular. The orbits are pentagon-shaped. The bones at the back of the skull are highly modified and show similarities with those of the plagiosaurid Plagiosternum. Both Megalophthalma and Plagiosternum lack prefrontal and postfrontal bones. In fact, Megalophthalma and Plagiosternum are thought to form their own clade or evolutionary grouping within Plagiosauridae called Plagiosterninae. In overall form Megalophthalma and Plagiosternum are intermediate between the basal plagiosaurid Plagiosuchus and the derived Gerrothorax.


















