
Arcadia is an extinct genus of temnospondyl amphibians in the family Rhytidosteidae from the early Triassic. The remains were found in and named after the Arcadia Formation of Australia.
Chomatobatrachus is a genus of prehistoric temnospondyl from the Triassic.
Erythrobatrachus is an extinct genus of trematosaurian temnospondyl within the family Trematosauridae. The sole species Erythrobatrachus noonkanbahensis was separated to a monotypic genus, distinguishing it from related taxa when the description was published in 1972. The type material was a matrix cast revealing the impression of several fragments of skull excavated at the Blina Shale formation in the northwest of the Australian continent. The genus name is derived from ancient Greek, combining terms for red, erythro, with frog, batrachos, to describe the iron staining of the fossilised amphibian specimens. The type location described by the specific epithet was Noonkanbah Station.

Derwentia is an extinct genus of trematosaurian temnospondyl within the family Rhytidosteidae. It is known from a single skull found from the Knocklofty Sandstone of Tasmania, which is Early Triassic in age.
Cosgriffius is an extinct genus of trematosaurian temnospondyl within the family Trematosauridae. It was described in 1993 by Samuel P. Welles based on a single partial skull from the well-known Meteor Crater Quarry in Arizona that also produced more abundant remains of the capitosaur Wellesaurus peabodyi. The skull was long and slender, features typically associated with the trematosaurid subfamily Lonchorhynchinae. This is the only trematosaurid known from western North America.
Nannospondylus is an extinct genus of dvinosaurian temnospondyl within the family Trimerorhachidae. It is known from the Chickasha Formation in Oklahoma.

Rewana is an extinct genus of prehistoric temnospondyls. Two species have been described from the Arcadia Formation of Australia.

Yuanansuchus is an extinct genus of mastodonsauroid temnospondyl. Fossils have been found from the Xinlingzhen formation in Yuan'an County, Hubei, China and date back to the Anisian stage of the Middle Triassic.

Mahavisaurus is an extinct genus of rhytidosteid temnospondyl from the early Triassic period of Iraro, Madagascar. It is known from the holotype MNHN MAE 3037, a nearly complete skull, recovered from the Middle Sakamena Formation. This genus was named by J. P. Lehman in 1966, and the type species is Mahavisaurus dentatus.

Platyrhinops is an extinct genus amphibamid temnospondyl from the Late Carboniferous of Ohio and the Czech Republic. It is known from many partial skeletons from the Linton site in Saline Township, Ohio and at least 6 partial specimens from the Nýřany site from the Nýřany Member of the Kladno Formation in the Czech Republic.
Plagiorophus is an extinct genus of prehistoric plagiosaurid. It is known from the Middle Triassic Bukobay Formation (Ladinian) and Donguz Formation (Anisian) of Russia.
Plagiobatrachus is an extinct genus of plagiosaurid temnospondyl. It is known from the Rewan Formation, an Early Triassic formation in Australia.
Peltostega is an extinct genus of prehistoric trematosaurians. The type is the only known species, Peltostega erici It is known from the Early Triassic Kongressfjellet Formation of Svalbard and Jan Mayen.
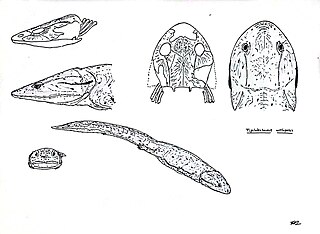
Tupilakosaurus is an extinct genus of dvinosaurian temnospondyl within the family Tupilakosauridae.

Tertrema is an extinct genus of trematosaurian temnospondyl within the family Trematosauridae. It is known from skull material from the Vikinghøgda Formation on Spitsbergen Island in Svalbard. Relative to most trematosaurids, Tertrema has a proportionally short snout and widely spaced occipital condyles. While typically placed in the subfamily Trematosaurinae, a 2021 phylogenetic analysis suggested that it was actually nested among the long-snouted lonchorhynchine trematosaurids.

Sinobrachyops placenticephalus is an extinct temnospondyl amphibian from Middle Jurassic-aged Shaximiao Formation in the Sichuan basin, China. S. placenticephalus is one of the youngest known labyrinthodont amphibians.
Syndyodosuchus is an extinct genus of temnospondyl within the family Actinodontidae. It is known from the Permian Inta Formation of European Russia.
Stoschiosaurus is an extinct genus of trematosaurian temnospondyl within the family Trematosauridae. It lived during the Early Triassic in what is now Greenland. Fossils were found in the Wordie Creek Formation.
Mattauschia is an extinct genus of trematopid temnospondyls from the Late Carboniferous of the Czech Republic.

The Bukobay Svita is a Middle Triassic geological unit in Russia. It is composed primarily of red or grey lacustrine sediments, reconstructing a humid and marshy depositional environment. Bukobay is the youngest section of a Triassic terrestrial succession exposed south of the Ural Mountains. It is equivalent to a biostratigraphic unit, the Bukobay Gorizont, which is also called the "Bukobay Horizon" or "Mastodonsaurus" fauna).























