
Lystrosaurus is an extinct genus of herbivorous dicynodont therapsids from the late Permian and Early Triassic epochs. It lived in what is now Antarctica, India, China, Mongolia, European Russia and South Africa. Four to six species are currently recognized, although from the 1930s to 1970s the number of species was thought to be much higher. They ranged in size from that of a small dog to 8 feet long.

Ericiolacerta is an extinct genus of small therocephalian therapsids from the early Triassic of South Africa and Antarctica. Ericiolacerta, meaning "hedgehog lizard", was named by D.M.S. Watson in 1931. The species E. parva is known from the holotype specimen which consists of a nearly complete skeleton found in the Lystrosaurus Assemblage Zone within the Katberg Formation of the Beaufort Group in South Africa, and from a partial jaw found in the Lower Triassic Fremouw Formation in Antarctica. Ericiolacerta was around 20 centimetres (7.9 in) in length, with long limbs and relatively small teeth. It probably ate insects and other small invertebrates. The therocephalians – therapsids with mammal-like heads – were abundant in Permian times, but only a few made it into the Triassic. Ericiolacerta was one of those. It is possible that they gave rise to the cynodonts, the only therapsid group to survive into post-Triassic times. Cynodonts gave rise to mammals.

Lydekkerinidae is a family of stereospondyl temnospondyls that lived in the Early Triassic period. During this time period, lydekkerinids were widely distributed, with putative remains reported from Russia, Greenland, India, South Africa, Madagascar, Australia, and Antarctica. In contrast to most other stereospondyls, lydekkerinids were relatively small-bodied. The type genus is Lydekkerina, the namesake of the family and the best-known lydekkerinid.

Broomistega is an extinct genus of temnospondyl amphibian in the family Rhinesuchidae. It is known from one species, Broomistega putterilli, which was renamed in 2000 from Lydekkerina putterilli Broom 1930. Fossils are known from the Early Triassic Lystrosaurus Assemblage Zone of the Beaufort Group in the Karoo Basin of present-day South Africa, a region that had been an enclave of Gondwana. Specimens of B. putterilli were once thought to represent young individuals of another larger rhinesuchid such as Uranocentrodon, but the species is now regarded as a paedomorphic taxon, possessing the features of juvenile rhinesuchids into adulthood.

Cryobatrachus is an extinct genus of temnospondyl amphibian from the Early Triassic of Antarctica. The type species is Cryobatrachus kitchingi. It is known from a partial skull and an imprint of the skull roof, both found in the Fremouw Formation of the Transantarctic Mountains at about 85° south latitude and described in 1974. Many small bone fragments have also been identified, although they cannot be attributed with certainty to C. kitchingi. Cryobatrachus has been classified in the family Lydekkerinidae, as it is similar in appearance to the genus Lydekkerina from South Africa. Because only a small number of features distinguish it from other lydekkerinids, Cryobatrachus kitchingi has more recently been considered a nomen dubium, meaning that its distinction from other better-known species may be unwarranted.

Lydekkerina is an extinct genus of stereospondyl temnospondyl. It is the type genus of the family Lydekkerinidae. Fossils have been collected from Early Triassic deposits in South Africa and Australia. The type species is L. huxleyi, first described in 1889. While most other stereospondyls were semiaquatic, Lydekkerina was exclusively terrestrial.

Lapillopsis is an extinct genus of stereospondyl temnospondyl within the family Lapillopsidae. Fossils belonging to the genus have been found in the Arcadia Formation of Queensland, Australia.
Rotaurisaurus is an extinct genus of temnospondyls from the family Lapillopsidae. This genus is known only from an incomplete crushed skull and associated left jaw, together given the designation UTGD 87795. The generic name, Rotaurisaurus, is a combination of Latin words translating to "circle-eared lizard". This references the shape of its otic notches, which acquire a circular form due to being partially enclosed by the tabular bones at the back of the skull. The specific name, contundo, references the specimen's poor level of preservation, as it is derived from the Latin word for "squashed".
Platycraniellus is an extinct genus of carnivorous cynodonts from the Early Triassic. It is known from the Lystrosaurus Assemblage Zone of the Normandien Formation in South Africa. P. elegans is the only species in this genus based on the holotype specimen from the Ditsong National Museum of Natural History in Pretoria, South Africa. Due to limited fossil records for study, Platycraniellus has only been briefly described a handful of times.

Micropholis is an extinct genus of dissorophoid temnospondyl. Fossils have been found from the Lystrosaurus Assemblage Zone of the Karoo Basin in South Africa and are dated to the Induan. Fossils have also been found from the lower Fremouw of Antarctica.Micropholis is the only post-Permian dissorophoid and the only dissorophoid in what is presently the southern hemisphere and what would have been termed Gondwana during the amalgamation of Pangea.

Owenetta is an extinct genus of owenettid procolophonian parareptile. Fossils have been found from the Beaufort Group in the Karoo Basin of South Africa. Although most procolophonians lived during the Triassic, Owenetta existed during the Wuchiapingian and Changhsingian stages of the Late Permian as well as the early Induan stage of the Early Triassic. It is the type genus of the family Owenettidae, and can be distinguished from other related taxa in that the posterior portion of the supratemporal bears a lateral notch and that the pineal foramen is surrounded by a depressed parietal surface on the skull table.
Pneumatostega is an extinct genus of rhytidosteid temnospondyl from the early Triassic period of Cape Province of South Africa. It is known from the holotype BPI F981, a dorsal mould of a skull roof and from the referred specimen SAM 11188, partial skull fragments and postcranial remains recovered from the Lystrosaurus Assemblage Zone in the Beaufort Group near Middelburg. This genus was named by J. W. Cosgriff and J. M. Zawiskie in 1979, and the type species is Pneumatostega potamia.

Teraterpeton is an extinct genus of trilophosaurid archosauromorphs. It is known from a partial skeleton from the Late Triassic Wolfville Formation of Nova Scotia, described in 2003. It has many unique features seen in no other related form, including an elongated, toothless snout and large openings for the nostrils. Because of this, Teraterpeton was originally placed in its own family, Teraterpetidae, related to Trilophosaurus. Newer studies generally place it within Trilophosauridae.

Derwentiinae is a subfamily of rhytidosteid temnospondyls from the Permian and Triassic periods of Australia and India. It includes the genera Arcadia, Deltasaurus, Derwentia, Indobrachyops, and Rewana. Derwentiinae was named in a 2011 study that analyzed the phylogenetic relationships of rhytidosteids. It was a replacement name for the family Derwentiidae, which was named in 2000.

Warrenisuchus is an extinct genus of temnospondyl from the Early Triassic of Queensland, Australia. It belongs to a diverse group of Triassic temnospondyls called Capitosauria. The type species Warrenisuchus aliciae was erected in 2009. W. aliciae was originally described as a species of Parotosuchus in 1988, which is known from other species that have been found in Europe, Africa, and Antarctica. In 2000 it was then assigned to a new genus called Rewanobatrachus along with the newly named species R. gunganj, which was declared the type species of the genus. However, R. gunganj was later reclassified as a species of Watsonisuchus, invalidating the name Rewanobatrachus and requiring that R. aliciae be placed in its own genus, which was named Warrenisuchus. However, several studies suggest that Warrenisuchus aliciae may be a species of Watsonisuchus as well. Unlike most capitosaurs, Warrenisuchus is known from many juvenile skulls less than 4 centimetres (1.6 in) in length.

Teyujagua is an extinct genus of small, probably semi-aquatic archosauromorph reptile that lived in Brazil during the Early Triassic period. The genus contains the type and only known species, T. paradoxa. It is known from a well-preserved skull, and probably resembled a crocodile in appearance. It was an intermediary between the primitive archosauromorphs and the more advanced Archosauriformes, revealing the mosaic evolution of how the key features of the archosauriform skull were acquired. Teyujagua also provides additional support for a two-phase model of archosauriform radiation, with an initial diversification in the Permian followed by a second adaptive radiation in the Early Triassic.

Manubrantlia was a genus of lapillopsid temnospondyls from the Early Triassic Panchet Formation of India. This genus is only known from a single holotype left jaw, given the designation ISI A 57. Despite the paucity of remains, the jaw is still identifiable as belonging to a relative of Lapillopsis. For example, all three of its coronoid bones possessed teeth, the articular bone is partially visible in lateral (outer) view, and its postsplenial does not contact the posterior meckelian foramen. However, the jaw also possesses certain unique features which justify the erection of a new genus separate from Lapillopsis. For example, the mandible is twice the size of any jaws referred to other lapillopsids. The most notable unique feature is an enlarged "pump-handle" shaped arcadian process at the back of the jaw. This structure is responsible for the generic name of this genus, as "Manubrantlia" translates from Latin to the English expression "pump-handle". The type and only known species of this genus is Manubrantlia khaki. The specific name refers to the greenish-brown mudstones of the Panchet Formation, with a color that had been described as "khaki" by the first British geologists who studied the formation.
Latiscopus disjunctus is a small Late Triassic temnospondyl collected in 1940 by a Works Projects Administration crew working near Otis Chalk, Texas that was described by John Wilson in 1948.
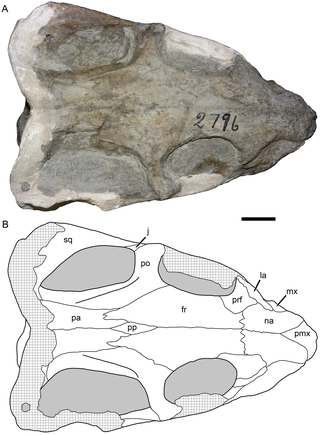
Thliptosaurus is an extinct genus of small kingoriid dicynodont from the latest Permian period of the Karoo Basin in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. It contains the type and only known species T. imperforatus. Thliptosaurus is from the upper Daptocephalus Assemblage Zone, making it one of the youngest Permian dicynodonts known, living just prior to the Permian mass extinction. It also represents one of the few small bodied dicynodonts to exist at this time, when most other dicynodonts had large body sizes and many small dicynodonts had gone extinct. The unexpected discovery of Thliptosaurus in a region of the Karoo outside of the historically sampled localities suggests that it may have been part of an endemic local fauna not found in these historic sites. Such under-sampled localities may contain 'hidden diversities' of Permian faunas that are unknown from traditional samples. Thliptosaurus is also unusual for dicynodonts as it lacks a pineal foramen, suggesting that it played a much less important role in thermoregulation than it did for other dicynodonts.
Vetusodon is an extinct genus of cynodonts belonging to the clade Epicynodontia. It contains one species, Vetusodon elikhulu, which is known from four specimens found in the Late Permian Daptocephalus Assemblage Zone of South Africa. With a skull length of about 18 centimetres (7.1 in), Vetusodon is the largest known cynodont from the Permian. Through convergent evolution, it possessed several unusual features reminiscent of the contemporary therocephalian Moschorhinus, including broad, robust jaws, large incisors and canines, and small, single-cusped postcanine teeth.




















