| Nanolania Temporal range: Early Triassic, | |
|---|---|
 | |
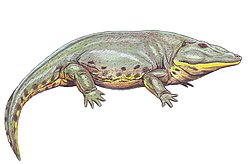
| Restoration of Nanolania anatopretia | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Order: | † Temnospondyli |
| Suborder: | † Stereospondyli |
| Family: | † Rhytidosteidae |
| Genus: | † Nanolania Yates, 2000 |
| Type species | |
| †Nanolania anatopretia Yates, 2000 | |
Nanolania is an extinct genus of rhytidosteid temnospondyl from the early Triassic period (Induan stage) of south central Queensland, Australia. It is known from the holotype QMF 12293, a postorbital fragment associated with lower jaw fragments and from the associated paratypes QMF 14480, a laterally complete skull with mandibles, QMF 35247, a poorly preserved skull with right mandibular ramus, QMF 35393, a badly preserved partial skull and QMF 39666, a posterior orbital and mandibular fragment, recovered from the Arcadia Formation in the Rewan Group. This genus was named by Adam M. Yates in 2000, and the type species is Nanolania anatopretia. [1]