
Pyracantha is a genus of large, thorny evergreen shrubs in the family Rosaceae, with common names firethorn or pyracantha. They are native to an area extending from Southwest Europe east to Southeast Asia. They resemble and are related to Cotoneaster, but have serrated leaf margins and numerous thorns.

Kumaon is a revenue and administrative division in the Indian State of Uttarakhand. It spans over the eastern half of the state and is bounded on the north by Tibet, on the east by Nepal, on the south by the state of Uttar Pradesh, and on the west by Garhwal. Kumaon comprises six districts of the state: Almora, Bageshwar, Champawat, Nainital, Pithoragarh and Udham Singh Nagar.

Rudraksha refers to the dried stones or seeds of the genus Elaeocarpus specifically, Elaeocarpus ganitrus. These stones serve as prayer beads for Hindus, Buddhists and Sikhs. When they are ripe, rudraksha stones are covered by an inedible blue outer fruit so they are sometimes called "blueberry beads

Uttarakhand, formerly known as Uttaranchal, is a state in northern India. It is often referred to as the "Devbhumi" due to its religious significance and numerous Hindu temples and pilgrimage centres found throughout the state. Uttarakhand is known for the natural environment of the Himalayas, the Bhabar and the Terai regions. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China to the north; the Sudurpashchim Province of Nepal to the east; the Indian states of Uttar Pradesh to the south and Himachal Pradesh to the west and north-west. The state is divided into two divisions, Garhwal and Kumaon, with a total of 13 districts. The winter capital and largest city of the state is Dehradun, which is also a railhead. On 5 March 2020, Bhararisain, a town in the Gairsain Tehsil of the Chamoli district, was declared as the summer capital of Uttarakhand. The High Court of the state is located in Nainital, but is to be moved to Haldwani in future.

Carissa is a genus of shrubs or small trees native to tropical and subtropical regions of Africa, Australia and Asia. Until recently about 100 species were listed, but most of them have been relegated to the status of synonyms or assigned to other genera, such as Acokanthera.

Leycesteria formosa, the pheasant berry, is a deciduous shrub in the family Caprifoliaceae, native to the Himalayas and southwestern China. It is considered a noxious invasive species in Australia, New Zealand, the neighbouring islands of Micronesia, and some other places. In its native Himalaya the shrub is frequently used in the traditional medicine of the various countries and peoples encompassed within the region.

Agathosma crenulata is a flowering plant in the family Rutaceae, native to the lower elevation mountains of southwestern South Africa, where it occurs near streams in fynbos habitats. It is an evergreen shrub growing to 1.5-2.5 m tall. The leaves are opposite, oval, 15–35 mm long and 7–18 mm broad. The flowers are white or pale pink, with five petals; the fruit is a five-parted capsule which splits open to release the seeds.

Carissa carandas is a species of flowering shrub in the family Apocynaceae. It produces berry-sized fruits that are commonly used as a condiment in Indian pickles and spices. It is a hardy, drought-tolerant plant that thrives well in a wide range of soils. Common names in English include Bengal currant, Christ's thorn, Carandas plum, Karonda, Karanda and Kanna.

Pyracantha angustifolia is a species of shrub in the rose family known by the common names narrowleaf firethorn, slender firethorn and woolly firethorn. The flowers are white and produce small round pomes and can be orange to red in color. These fruits are astringent and bitter, making them inedible for humans, but they are a food source for birds. The leaves, fruit and seeds contain hydrogen cyanide, the source of the bitter taste. The stems and branches have sharp spines. This shrub is cultivated and grown in yards and gardens as an ornamental plant. It can be used to make hedges for home security. This species is native to China but has been introduced to North America and Australia. It is an invasive species in Hawaii and in other areas.

Pyracantha coccinea, the scarlet firethorn is the European species of firethorn or red firethorn that has been cultivated in gardens since the late 16th century. The tree has small white flowers. It produces small, bright red berries. Its leaves are slightly toothed and grow opposite to one another. The fruit is bitter and astringent, making it inedible when raw. The fruit can be cooked to make jellies, jams, sauces and marmalade. It ranges from southern Europe to western Asia. It has been introduced to North America and cultivated there as an ornamental plant since the 18th century.
Pyracantha atalantioides is a species of Firethorn shrub.

Pyracantha crenatoserrata, commonly known as Chinese firethorn or Yunnan firethorn, is a species of firethorn. It is a short shrub. It is cultivated for its decorative bright red pome fruit. The flowers are white. It survives in warm climates. It cannot tolerate frost, but it can withstand drought. This species originates from central China.

Oroxylum indicum is a species of flowering plant belonging to the monotypic genus Oroxylum and the family Bignoniaceae, and is commonly called Indian trumpet tree, oroxylum, Indian trumpet flower, broken bones, Indian caper, scythe tree or tree of Damocles. It can reach a height of 18 metres (59 ft). Various segments of the tree are used in traditional medicine, where it is known as Shyonaka or Sona Patha.

Cordia dichotoma is a species of flowering tree in the borage family, Boraginaceae, that is native to the Indomalayan realm, northern Australia, and western Melanesia.

Rubus ellipticus, commonly known as ainselu, golden evergreen raspberry, golden Himalayan raspberry, or yellow Himalayan raspberry, is an Asian species of thorny fruiting shrub in the rose family. It's native range stretches from the Indian subcontinent to southern China and Indochina and the Philippines.

Myrica esculenta is an tree or large shrub of the tropics. The native range of this species stretches from Nepal to southern China and western & central Malesia. It's common names include box myrtle, bayberry and kaphal. Its berries are edible and are consumed locally.

Solanum virginianum, also called Surattense nightshade, yellow-fruit nightshade, yellow-berried nightshade, Indian nightshade,Thai green eggplant, or Thai striped eggplant, is a medicinal plant used mostly in India. Some parts of the plant, such as the fruit, are poisonous. The common name is Kantakari. Solanum surattense Burm. f. and Solanum xanthocarpum Schrad. and Wendl. are synonyms of Solanum virginianum L..

Iris kemaonensis, the Kumaon iris, is a plant species in the genus Iris, it is also in the subgenus Iris and in the section Pseudoregelia. It is a rhizomatous perennial, from Tibetan China, Bhutan, India, Kashmir and Nepal. It has light green or yellowish green leaves, that extend after flowering time. It has a short stem, 1–2 fragrant flowers that are purple, lilac, lilac-purple or pale purple. They also have darker coloured blotches or spots. It is cultivated as an ornamental plant in temperate regions. It is often known as Iris kumaonensis, due to a publishing error.
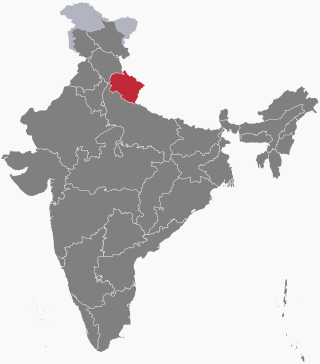
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Uttarakhand:
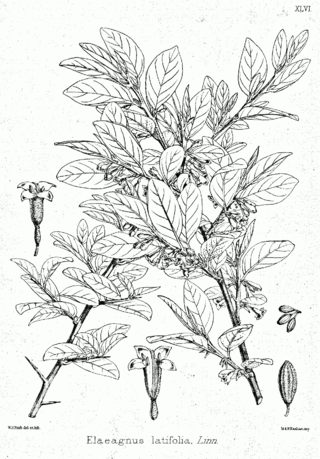
Elaeagnus latifolia, known as the bastard oleaster, or soh-sang, is a species of Elaeagnus native to India and Southeast Asia.





















