
An antifungal medication, also known as an antimycotic medication, is a pharmaceutical fungicide or fungistatic used to treat and prevent mycosis such as athlete's foot, ringworm, candidiasis (thrush), serious systemic infections such as cryptococcal meningitis, and others. Such drugs are usually obtained by a doctor's prescription, but a few are available over the counter (OTC). The evolution of antifungal resistance is a growing threat to health globally.

Itraconazole, sometimes abbreviated ITZ, is an antifungal medication used to treat a number of fungal infections. This includes aspergillosis, blastomycosis, coccidioidomycosis, histoplasmosis, and paracoccidioidomycosis. It may be given by mouth or intravenously.

Fluconazole is an antifungal medication used for a number of fungal infections. This includes candidiasis, blastomycosis, coccidioidomycosis, cryptococcosis, histoplasmosis, dermatophytosis, and pityriasis versicolor. It is also used to prevent candidiasis in those who are at high risk such as following organ transplantation, low birth weight babies, and those with low blood neutrophil counts. It is given either by mouth or by injection into a vein.
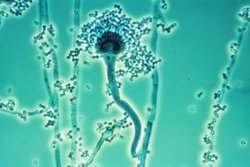
Aspergillus fumigatus is a species of fungus in the genus Aspergillus, and is one of the most common Aspergillus species to cause disease in individuals with an immunodeficiency.
Azoles are a class of five-membered heterocyclic compounds containing a nitrogen atom and at least one other non-carbon atom as part of the ring. Their names originate from the Hantzsch–Widman nomenclature. The parent compounds are aromatic and have two double bonds; there are successively reduced analogs with fewer. One, and only one, lone pair of electrons from each heteroatom in the ring is part of the aromatic bonding in an azole. Names of azoles maintain the prefix upon reduction. The numbering of ring atoms in azoles starts with the heteroatom that is not part of a double bond, and then proceeds towards the other heteroatom.

Terconazole is an antifungal drug used to treat vaginal yeast infection. It comes as a lotion or a suppository and disrupts the biosynthesis of fats in a yeast cell. It has a relatively broad spectrum compared to azole compounds but not triazole compounds. Testing shows that it is a suitable compound for prophylaxis for those that suffer from chronic vulvovaginal candidiasis.

Voriconazole, sold under the brand name Vfend among others, is an antifungal medication used to treat a number of fungal infections. This includes aspergillosis, candidiasis, coccidioidomycosis, histoplasmosis, penicilliosis, and infections by Scedosporium or Fusarium. It can be taken by mouth or used by injection into a vein.
A triazole is a heterocyclic compound featuring a five-membered ring of two carbon atoms and three nitrogen atoms with molecular formula C2H3N3. Triazoles exhibit substantial isomerism, depending on the positioning of the nitrogen atoms within the ring.

Anidulafungin (INN) is a semisynthetic echinocandin used as an antifungal drug. It was previously known as LY303366. It may also have application in treating invasive Aspergillus infection when used in combination with voriconazole. It is a member of the class of antifungal drugs known as the echinocandins; its mechanism of action is by inhibition of (1→3)-β-D-glucan synthase, an enzyme important to the synthesis of the fungal cell wall.

Posaconazole, sold under the brand name Noxafil among others, is a triazole antifungal medication.

Aspergillosis is a fungal infection of usually the lungs, caused by the genus Aspergillus, a common mould that is breathed in frequently from the air around, but does not usually affect most people. It generally occurs in people with lung diseases such as asthma, cystic fibrosis or tuberculosis, or those who have had a stem cell or organ transplant, and those who cannot fight infection because of medications they take such as steroids and some cancer treatments. Rarely, it can affect skin.

Echinocandins are a class of antifungal drugs that inhibit the synthesis of β-glucan in the fungal cell wall via noncompetitive inhibition of the enzyme 1,3-β glucan synthase. The class has been termed the "penicillin of antifungals," along with the related papulacandins, as their mechanism of action resembles that of penicillin in bacteria. β-glucans are carbohydrate polymers that are cross-linked with other fungal cell wall components, the fungal equivalent to bacterial peptidoglycan. Caspofungin, micafungin, and anidulafungin are semisynthetic echinocandin derivatives with limited clinical use due to their solubility, antifungal spectrum, and pharmacokinetic properties.

Isavuconazonium sulfate, sold under the brand name Cresemba, is a systemic antifungal medication of the triazole class which is used to treat invasive aspergillosis and mucormycosis.

Albaconazole is an experimental triazole antifungal. It has potential broad-spectrum activity. The drug blocks a number of CYP450 liver enzymes.

Chronic pulmonary aspergillosis is a long-term fungal infection caused by members of the genus Aspergillus—most commonly Aspergillusfumigatus. The term describes several disease presentations with considerable overlap, ranging from an aspergilloma—a clump of Aspergillus mold in the lungs—through to a subacute, invasive form known as chronic necrotizing pulmonary aspergillosis which affects people whose immune system is weakened. Many people affected by chronic pulmonary aspergillosis have an underlying lung disease, most commonly tuberculosis, allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, asthma, or lung cancer.
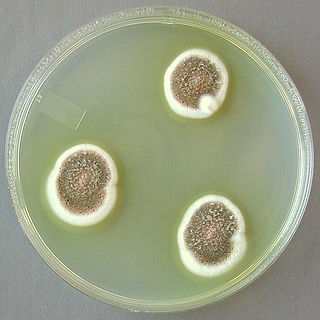
Aspergillus ustus is a microfungus and member of the division Ascomycota. It is commonly found in indoor environments and soil. Isolated cases of human infection resulting from A. ustus have been described; however the majority of these are nail infections.
Fungistatics are anti-fungal agents that inhibit the growth of fungus. The term fungistatic may be used as both a noun and an adjective. Fungistatics have applications in agriculture, the food industry, the paint industry, and medicine.
Scedosporiosis is the general name for any mycosis - i.e., fungal infection - caused by a fungus from the genus Scedosporium. Current population-based studies suggest Scedosporium prolificans and Scedosporium apiospermum to be among the most common infecting agents from the genus, although infections caused by other members thereof are not unheard of. The latter is an asexual form (anamorph) of another fungus, Pseudallescheria boydii. The former is a “black yeast”, currently not characterized as well, although both of them have been described as saprophytes.

Aspergillus alabamensis is a soil fungus in the division Ascomycota first described in 2009 as a segregated taxon of A. terreus. Originally thought to be a variant of A. terreus, A. alabamensis is situated in a distinctive clade identified by genetic analysis. While A. alabamensis has been found to be morphologically similar to Aspergillus terreus by morphological studies, the two differ significantly in active metabolic pathways, with A. alabamensis producing the mycotoxins citrinin and citreoviridin but lacking mevinolin.

Fosravuconazole is a triazole antifungal agent. In Japan, it is approved for the treatment of onychomycosis, a fungal infection of the nail. It is a prodrug that is converted into ravuconazole.















