Ethanol (also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic chemical compound. It is a simple alcohol with the chemical formula C2H6O. Its formula can be also written as CH
3−CH
2−OH or C
2H
5OH (an ethyl group linked to a hydroxyl group), and is often abbreviated as EtOH. Ethanol is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid with a slight characteristic odor. It is a psychoactive substance, recreational drug, and the active ingredient in alcoholic drinks.
An elixir is a sweet liquid used for medical purposes, to be taken orally and intended to cure one's illness. When used as a pharmaceutical preparation, an elixir contains at least one active ingredient designed to be taken orally.
In chemical nomenclature, the IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry is a method of naming organic chemical compounds as recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). It is published in the Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry. Ideally, every possible organic compound should have a name from which an unambiguous structural formula can be created. There is also an IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry.

Parabens are a class of widely used preservatives in cosmetic and pharmaceutical products. Chemically, they are a series of parahydroxybenzoates or esters of parahydroxybenzoic acid. Parabens are effective preservatives in many types of formulas. These compounds, and their salts, are used primarily for their bactericidal and fungicidal properties. They are found in shampoos, commercial moisturizers, shaving gels, personal lubricants, topical/parenteral pharmaceuticals, suntan products, makeup, and toothpaste. They are also used as food preservatives.

Cinnamic acid is an organic compound with the formula C6H5CH=CHCOOH. It is a white crystalline compound that is slightly soluble in water, and freely soluble in many organic solvents. Classified as an unsaturated carboxylic acid, it occurs naturally in a number of plants. It exists as both a cis and a trans isomer, although the latter is more common.

Ethyl acetate is the organic compound with the formula CH
3−COO−CH
2−CH
3, simplified to C
4H
8O
2. This colorless liquid has a characteristic sweet smell and is used in glues, nail polish removers, and in the decaffeination process of tea and coffee. Ethyl acetate is the ester of ethanol and acetic acid; it is manufactured on a large scale for use as a solvent.
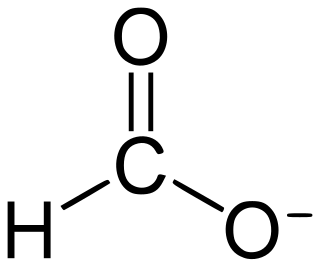
Formate (IUPAC name: methanoate) is the anion derived from formic acid. Its formula is represented in various equivalent ways: HCOO− or CHOO− or HCO2−. It is the product of deprotonation of formic acid. It is the simplest carboxylate anion. A formate (compound) is a salt or ester of formic acid.

Xanthate usually refers to a salt with the formula ROCS−
2M+
(R = alkyl; M+ = Na+, K+), thus O-esters of dithiocarbonate. The name xanthates is derived from Greek ξανθός xanthos, meaning “yellowish, golden”, and indeed most xanthate salts are yellow. They were discovered and named in 1823 by Danish chemist William Christopher Zeise. These organosulfur compounds are important in two areas: the production of cellophane and related polymers from cellulose and (in mining) for extraction of certain ores. They are also versatile intermediates in organic synthesis. Xanthates also refer to esters of xanthic acid. These esters have the structure ROC(=S)SR′.
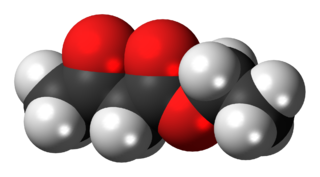
The organic compound ethyl acetoacetate (EAA) is the ethyl ester of acetoacetic acid. It is a colorless liquid. It is widely used as a chemical intermediate in the production of a wide variety of compounds. It is used as a flavoring for food.

Methylparaben, also methyl paraben, one of the parabens, is a preservative with the chemical formula CH3(C6H4(OH)COO). It is the methyl ester of p-hydroxybenzoic acid.
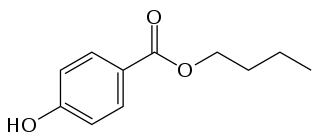
Butylparaben, or butyl p-hydroxybenzoate, is an organic compound with the formula C
4H
9O
2CC
6H
4OH. It is a white solid that is soluble in organic solvents. It has proven to be a highly successful antimicrobial preservative in cosmetics. It is also used in medication suspensions, and as a flavoring additive in food.

Propylparaben, the n-propyl ester of p-hydroxybenzoic acid, occurs as a natural substance found in many plants and some insects, although it is manufactured synthetically for use in cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and foods. It is a member of the class of parabens. It is a preservative typically found in many water-based cosmetics, such as creams, lotions, shampoos, and bath products. As a food additive, it has the E number E216.
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, also known as p-hydroxybenzoic acid (PHBA), is a monohydroxybenzoic acid, a phenolic derivative of benzoic acid. It is a white crystalline solid that is slightly soluble in water and chloroform but more soluble in polar organic solvents such as alcohols and acetone. 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid is primarily known as the basis for the preparation of its esters, known as parabens, which are used as preservatives in cosmetics and some ophthalmic solutions. It is isomeric with 2-hydroxybenzoic acid, known as salicylic acid, a precursor to aspirin, and with 3-hydroxybenzoic acid.
215 is the natural number following 214 and preceding 216.

Sodium methylparaben (sodium methyl para-hydroxybenzoate) is a compound with formula Na(CH3(C6H4COO)O). It is the sodium salt of methylparaben.

Heptylparaben (heptyl p-hydroxybenzoate) is a compound with formula C7H15(C6H4OHCOO). It is a paraben which is the heptyl ester of p-hydroxybenzoic acid.
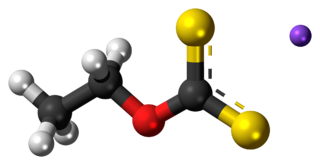
Sodium ethyl xanthate (SEX) is an organosulfur compound with the chemical formula CH3CH2OCS2Na. It is a pale yellow powder, which is usually obtained as the dihydrate. Sodium ethyl xanthate is used in the mining industry as a flotation agent. A closely related potassium ethyl xanthate (KEX) is obtained as the anhydrous salt.

Isopropylparaben is a paraben.
















