The South Saskatchewan River is a major river in Canada that flows through the provinces of Alberta and Saskatchewan.

Alberta is a Canadian province. Located in Western Canada, the province has an area of 661,190 square kilometres (255,290 sq mi) and is bounded to the south by the U.S. state of Montana along 49° north for 298 kilometres (185 mi); to the east at 110° west by the province of Saskatchewan for 1,223 kilometres (760 mi); and at 60° north the Northwest Territories for 644 kilometres (400 mi). The southern half of the province borders British Columbia along the Continental Divide of the Americas on the peaks of the Rocky Mountains, while the northern half borders British Columbia along the 120th meridian west.

The Peace River is a 1,923-kilometre-long (1,195 mi) river in Canada that originates in the Rocky Mountains of northern British Columbia and flows to the northeast through northern Alberta. The Peace River joins the Athabasca River in the Peace-Athabasca Delta to form the Slave River, a tributary of the Mackenzie River. The Finlay River, the main headwater of the Peace River, is regarded as the ultimate source of the Mackenzie River. The combined Finlay–Peace–Slave–Mackenzie river system is the 13th longest river system in the world.

The Liard River flows through Yukon, British Columbia and the Northwest Territories, Canada. Rising in the Saint Cyr Range of the Pelly Mountains in southeastern Yukon, it flows 1,115 kilometres (693 mi) southeast through British Columbia, marking the northern end of the Rocky Mountains and then curving northeast back into Yukon and Northwest Territories, draining into the Mackenzie River at Fort Simpson, Northwest Territories. The river drains approximately 277,100 square kilometres (107,000 sq mi) of boreal forest and muskeg.

Grande Prairie-Wapiti is provincial electoral district in northwestern Alberta, Canada. It is one of 87 mandated to return a single member to the Legislative Assembly of Alberta using the first past the post method of voting.

Hythe is a village surrounded by the County of Grande Prairie No. 1 in northwestern Alberta, Canada. It is located on Highway 43 approximately 58 km (36 mi) northwest of the City of Grande Prairie and 73 km (45 mi) southeast of the City of Dawson Creek, British Columbia.
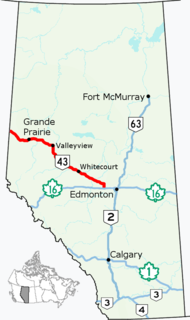
Alberta Provincial Highway No. 43, commonly referred to as Highway 43, is a major highway in northern and central Alberta, Canada that connects Edmonton to the British Columbia border via the Peace Country, forming the northernmost portion of the CANAMEX Corridor in Alberta. It stretches approximately 499 km (310 mi) from Highway 16 near Carvel west of Edmonton to the British Columbia border west of Demmitt. It is designated as a core route in Canada's National Highway System, comprising a portion of a key international corridor that stretches from Alaska into Mexico.

The Smoky River is a river in western Alberta, Canada. It is a major tributary of the Peace River. The descriptive name refers to the presence of "smouldering beds of coal in the riverbank" noted by the Cree Indians.

The Little Smoky River is a tributary of the Smoky River in west-central Alberta, Canada.

Crab Creek is a stream in the U.S. state of Washington. Named for the presence of crayfish, it is one of the few perennial streams in the Columbia Basin of central Washington, flowing from the northeastern Columbia River Plateau, roughly 5 km (3.1 mi) east of Reardan, west-southwest to empty into the Columbia River near the small town of Beverly. Its course exhibits many examples of the erosive powers of extremely large glacial Missoula Floods of the late Pleistocene, which scoured the region. In addition, Crab Creek and its region have been transformed by the large-scale irrigation of the Bureau of Reclamation's Columbia Basin Project (CBP), which has raised water table levels, significantly extending the length of Crab Creek and created new lakes and streams.

Alberta Provincial Highway No. 666, commonly referred to as Highway 666, is a highway in the province of Alberta, Canada. It runs mostly west-east, on mostly existing township and range roads in the Municipal District of Greenview No. 16 in Northern Alberta, for 37 km.

Kiskatinaw is a tributary of the Peace River in northeastern British Columbia, Canada.

The Pouce Coupe River is a major tributary of the Peace River in Alberta and British Columbia, Canada. Its name is officially spelled Pouce Coupé River, but it is commonly written without the acute accent.
The Kakwa River is a tributary of the Smoky River in western Alberta, Canada.

Slesse Creek is a creek in Whatcom County, Washington and British Columbia. It is a tributary of the Chilliwack River and is known as Silesia Creek south of the border and Slesse Creek north of it.

Elmworth is a hamlet in northern Alberta, Canada within the County of Grande Prairie No. 1. It is located on Highway 722 north of the Wapiti River and east of the British Columbia border. It has an elevation of 715 metres (2,346 ft). The Elmworth natural gas field stretches west and south of the hamlet.
The Kakisa River is a major tributary of the Mackenzie River in the Northwest Territories of Canada.
The locality of Hinton Trail, about 40 km south-west of Grande Prairie, developed at the north end of the Hinton Trail which ran from Jasper to Hinton, and then on to "the grande prairie". From Hinton, the trail followed Nose Creek north up to the Wapiti River, crossing it and heading overland to the Redwillow River about a half mile west of where the first Hinton Trail Post Office was set up in the home of Stan Ronksley on the NW quarter of section 5, township 70, range 10, west of the 6th meridian. The Ronksley home was across from Craigellachie School, a one-room log school built in 1922. The school also served as the community gathering place until the Hinton Trail Hall was built in 1947. The school closed in 1948, and the post office in 1968. The Hinton Trail Hall and a marker showing where the Hinton Trail crossed through the area about ½ mile east of the hall still mark this locality. Information on the people who lived in the Hinton Trail district can be found in Beaverlodge to the Rockies and its Supplement.