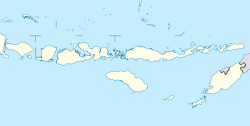
Rote Island is an island of Indonesia, part of the East Nusa Tenggara province of the Lesser Sunda Islands. According to legend, this island got its name accidentally when a lost Portuguese sailor arrived and asked a farmer where he was. The surprised farmer, who could not speak Portuguese, introduced himself, "Rote".

Sikka is a regency within East Nusa Tenggara province, Indonesia, on the island of Flores. It is bordered to the west by Ende Regency and to the east by East Flores Regency. It covers an area of 1,731.91 km2 and had a population of 300,301 at the 2010 census and 321,953 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2022 was 326,999. The capital is the town of Maumere, which comprises the districts of Alok Barat, Alok and Alok Timur.

Bulungan Regency is a regency of North Kalimantan Province in Indonesia. It covers an area of 13,181.92 km2 and had a population of 112,663 at the 2010 Census and 151,844 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2022 was 157,593. The administrative centre is at Tanjung Selor.

Jember Regency is a regency of East Java province, Indonesia. The land area is 3,306.69 km2, and the population was 2,332,726 at the 2010 census and 2,536,729 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2022 was 2,584,233. Its administrative capital is the urban area of Jember, which with 360,568 inhabitants in mid 2022 is the third largest urban area in East Java province but does not have municipality or city status as it is split between three separate administrative districts (kecamatan). Jember is famous for its tobacco farms and traditional food called tape which is made of fermented cassava.

Tanah Bumbu is one of the regencies in the Indonesian province of South Kalimantan. It was formerly part of Kotabaru Regency, but was split off on 25 February 2003 to form a separate regency, following dissatisfaction on the Kalimantan mainland territories with administration from Laut Island. It covers an area of 4,890.3 km2 and had a population of 267,929 at the 2010 Census and 322,646 at the 2020 Census; the latest official estimate is 335,079. The regency's capital is the town of Batulicin.
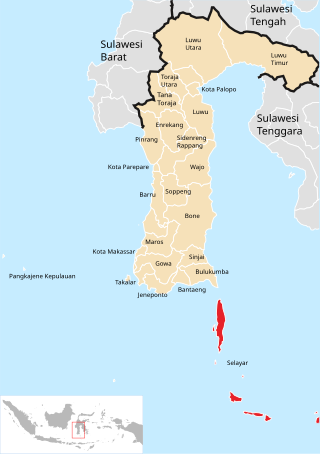
The Selayar Islands Regency is a regency of Indonesia in South Sulawesi province that covers the Selayar Islands, which lie southeast of the southern peninsula of Sulawesi. The archipelago consists of the group's main island, which is surrounded by 41 smaller islands around its coast; further to the southeast lies a widespread group of islands, including the huge atoll of Takabonerate. The regency covers an area of 1,357.03 km2, and had a population of 103,596 at the 2000 Census, 122,055 at the Census of 2010 and 137,071 at that of 2020. The official estimate for mid 2022 was 139,145. The administrative centre is the town of Benteng on Selayar Island. The Selayar Straits separate the regency from Sulawesi island.

West Sumba Regency is a regency in East Nusa Tenggara Province of Indonesia. Established in 1958, the regency was considerably reduced on 22 May 2007 with the creation of new Regencies on Sumba Island under Law UU No.16 of that year. Its area is now 737.42 km2, and its population was 110,993 at the 2010 census and 145,097 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2022 was 152,407. It has its seat (capital) in (Kota) Waikabubak.

Belu Regency is a regency in East Nusa Tenggara province of Indonesia. Situated on the north of Timor island, it adjoins the separate nation of East Timor to the east. Established on 20 December 1958, Belu Regency has its seat (capital) in the large town of Atambua.

Batubara Regency is a regency on North Sumatra's eastern shoreline, with Limapuluh as its seat. It was carved out from the seven most westerly coastal districts of Asahan Regency with effect from 15 June 2007. The new regency covers an area of 885.89 km2, and had a population of 375,885 at the 2010 Census and 410,678 at the 2020 Census, of whom 206,551 were male and 204,127 were female; the official estimate as at mid 2022 was 416,367.

East Sumba Regency is geographically the largest of the four regencies which divide the island of Sumba, within East Nusa Tenggara Province of Indonesia. It occupies 64% of the entire island, being much less densely populated than the western third. The town of Waingapu is the capital of East Sumba Regency. The population of East Sumba Regency was 227,732 at the 2010 Census and 244,820 at the 2020 Census, comprising 125,967 male and 118,853 female; the official estimate as at mid 2022 was 248,776.

Dompu Regency is a regency of the Indonesian Province of West Nusa Tenggara. It is located on the island of Sumbawa and the capital is Dompu. It is bordered to the north and to the east by two non-contiguous parts of Bima Regency, and to the west by Sumbawa Regency, as well as on its coasts by Saleh Bay, Sanggar Bay, and Cempi Bay. It covers an area of 2,324.55 km2, and the population at the 2010 Census was 218,984 and at the 2020 Census was 236,665; the official estimate as at mid 2022 was 239,781.

East Flores Regency is a regency in East Nusa Tenggara province of Indonesia. Established in 1958, the regency has its seat (capital) in Larantuka on Flores Island. It covers a land area of 1,812.85 km2, and it had a population of 232,605 as of the 2010 census and 276,896 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2022 was 288,897. The regency encompasses the eastern tip of the island of Flores, together with all of the adjacent islands of Adonara and Solor to the east of Flores, with some much smaller offshore islands. On 4 October 1999 the island of Lembata at the eastern end of the Solor Archipelago was separated out from the East Flores Regency to create its own Regency.

Kupang Regency is a regency in East Nusa Tenggara province of Indonesia. It occupies the far western end of Timor Island, together with the small offshore island of Semau. Other islands to the southwest and west which were formerly part of Kupang Regency have been separated administratively - the Rote Islands Group on 10 April 2002, and the Savu Islands on 29 October 2008. The capital of Kupang Regency is at Oelamasi.

Sabu Raijua Regency is one of the regencies in the province of East Nusa Tenggara, Indonesia. It comprises the three Savu Islands, lying between Sumba and Rote Island in the Savu Sea, with a land area of 459.58 km2. The regency was established by Indonesia's Minister of Home Affairs, Mardiyanto, on 29 October 2008, when it was partitioned from Kupang Regency. The population was 72,960 at the 2010 census, and 89,327 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2022 was 92,792.

North Penajam Paser Regency is a regency in the Indonesian province of East Kalimantan. Its administrative centre is the town of Penajam. The area which now forms North Penajam Paser was part of Paser Regency until its creation as a separate regency on 10 April 2002. It covers an area of 3,333.06 km2 and it had 142,922 inhabitants at the 2010 census and 178,681 at the 2020 census; the official estimate as at mid 2022 was 183,043. North Penajam Paser Regency has the smallest area among the seven regencies in East Kalimantan province.
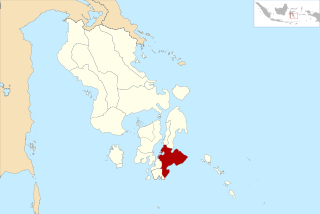
Buton Regency is a regency of Indonesia's Southeast Sulawesi Province, lying entirely on Buton Island. Until 2014 it had an area of 2,681.22 km2, and a population estimated at 276,944. However, in 2014 it was divided into three regencies, with two new regencies being cut out of it; the residual area now is 1,648.04 km2, and the districts in that area contained a population of 94,388 at the 2010 Census while the 2020 Census produced a total of 115,207; the official estimate as at mid 2022 was 119,353.

The Sangihe Islands Regency is a regency of North Sulawesi Province, Indonesia. It comprises a group of islands situated to the North of Sulawesi. It covers a land area of 736.98 km2, and had a population of 126,100 at the 2010 census and 139,262 at the 2020 census; the official estimate as at mid 2022 was 140,165. The principal island is also named Sangihe, on which lies the main town of Tahuna. Minor island groups within the Regency include the Marore group considerably to the north of Sangihe Island, the Tatoareng group to the south, and the Nusa Tabukan group off the northeast coast of Sangihe Island. It borders the Philippines in the north, making it one of Indonesia's border regions.

South Minahasa Regency is a regency in North Sulawesi, Indonesia. Its capital is the town of Amurang. It was originally part of the Minahasa Regency until it was established as a separate regency on 25 February 2003. In turn, a Southeast Minahasa Regency was established as a separate regency from part of the South Minahasa Regency on 2 January 2007. The residual Regency now covers an area of 1,456.46 km2, and had a population of 195,553 at the 2010 Census; this had risen to 236,463 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2022 was 241,680.
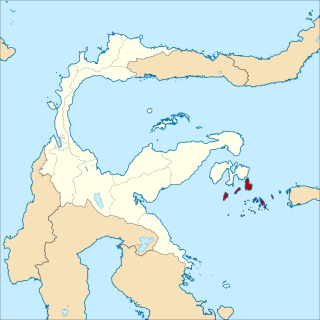
Banggai Sea Regency is a regency in the province of Central Sulawesi, Indonesia. The regency was established on 14 December 2012, partitioned from the Banggai Islands Regency. It comprises southern part of the Banggai Islands archipelago, including the main island of Banggai itself, the islands of Labobo and Bangkurung to the southwest of Banggai Island, and the numerous small Bokan Islands to the southeast. It covers a land area of 725.67 km2, and the districts now comprising the new Regency had a population of 62,183 at the 2010 Census and 70,435 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2022 was 71,350.

Ba'a is the capital of the Indonesian island of Rote and of the Rote Ndao Regency (kabupaten), in the province of East Nusa Tenggara. It lies in the district (kecamatan) of Lobalain, and constitutes a village (desa) with 1,263 inhabitants at the 2020 Census.