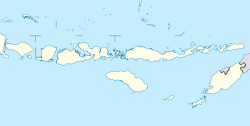
Alor is the largest island in the Alor Archipelago and is one of the 92 officially listed outlying islands of Indonesia. It is located at the eastern end of the Lesser Sunda Islands chain that runs through southeastern Indonesia, which from the west include such islands as Bali, Lombok, Sumbawa, Komodo, and Flores.

Anambas Islands Regency is an island regency in the Riau Islands Province, Indonesia, located in the Natuna Sea. The regency consists of 255 islands, including five outer islands that are important for Indonesia's sovereignty boundaries, namely: Tokong Berlayar Island, Tokong Nanas Island, Mangkai Island, Damar Island, and Malangbiru Island. Anambas Islands Regency located 150 nautical miles northeast of Batam Island in the Natuna Sea between the Malaysian Peninsula to the west and the island of Borneo to the east. Geographically part of the Tudjuh Archipelago. This island regency covers a land area of approximately 661.47 square kilometres (255.39 sq mi) spread over an area of approximately 46,664 km² of water. The regency had a population of around 37,411 at the 2010 Census. and 47,402 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 50,140. The administrative centre is at Tarempa on Siantan Island.

The Lingga Regency is a group of 600 islands in Indonesia, located south of Singapore and along both sides of the equator, off the eastern coast of Riau Province on Sumatra island. They are due south of the populated Riau Archipelago, known for the industrial island of Batam and the tourist-frequented island of Bintan, although the Lingga Islands themselves are rarely visited due to the infrequent local transportation. The equator goes through the northern tip of Lingga Island, the main island in the archipelago.

Ende Regency is a regency on the island of Flores, within East Nusa Tenggara Province of Indonesia. The regency covers an area of 2,091.19 km2, and it had a population of 260,605 at the 2010 Census and 270,763 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 280,328. It is bordered to the west by Nagekeo Regency and to the east by Sikka Regency, while the Flores Sea lies to the north and the Savu Sea to the south.

Ende is the seat capital of the Ende Regency, East Nusa Tenggara province of Indonesia. Ende is located on the southern coast of Flores Island. The town had a population of 87,269 residents at the 2020 census, divided administratively between four districts (kecamatan) of the regency – Ende Selatan, Ende Timur, Ende Tengah, and Ende Utara. Note that this does not include Ende District or Pulau Ende District. The official estimate as at mid 2023 was 87,723.

Bintan Regency is an administrative area in the Riau Islands Province of Indonesia. Bintan Regency includes all of Bintan Island and also includes many outlying islands including the Tambelan Archipelago and Badas Islands situated between Bintan and West Kalimantan; altogether there are 273 islands comprising the regency.

Alor Regency is a regency in East Nusa Tenggara (NTT) province of Indonesia. Established in 1958, Alor Regency administers the Alor Archipelago with its seat (capital) in Kalabahi on Alor Island.

Belu Regency is a regency in East Nusa Tenggara province of Indonesia. Situated on the north side of Timor island, it originally stretched to the south coast, but in December 2012 its southern half was detached to form the new Malaka Regency. It now adjoins the North Central Timor Regency to the west, the new Malaka Regency to the south, and the separate nation of East Timor to the east, while to the north lies the Sawu Sea. Established on 20 December 1958, Belu Regency has its seat (capital) in the large town of Atambua, which lies inland from the coastal port of Atapupu.

Central Sumba Regency is a regency in East Nusa Tenggara of Indonesia. The new Central Sumba Regency was established on the island of Sumba when West Sumba Regency was split into two regencies on 22 May 2007 and a further Regency was created in Central Sumba from parts of both West Sumba and East Sumba Regencies. The new Regency covers 1,845.28 km2 and had a population of 62,485 at the 2010 Census and 85,482 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 91,531. The seat (capital) of its government is located at Waibakul.

The Karimun Regency is located in the Riau Islands Province, Indonesia. Besides the central island of Great Karimun, the regency also includes the island of Kundur and over 240 lesser islands. The district covers a land area of 1,339.9 km2 and a sea area of 6,460 km2, and its population was 212,561 at the 2010 census and 253,457 at the 2020 census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 270,121.

East Sumba Regency is geographically the largest of the four regencies which divide the island of Sumba, within East Nusa Tenggara Province of Indonesia. It occupies 62% of the entire island, being much less densely populated than the western third. The town of Waingapu is the capital of East Sumba Regency. The population of East Sumba Regency was 227,732 at the 2010 Census and 244,820 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2022 was 255,498.

East Flores Regency is a regency in East Nusa Tenggara province of Indonesia. Established in 1958, the regency has its seat (capital) in Larantuka on Flores Island. It covers a land area of 1,812.65 km2, and it had a population of 232,605 as of the 2010 census and 276,896 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as of mid-2023 was 289,376. The regency encompasses the eastern tip of the island of Flores, together with all of the adjacent islands of Adonara and Solor to the east of Flores, with some much smaller offshore islands. On 4 October 1999, the island of Lembata at the eastern end of the Solor Archipelago was separated from the East Flores Regency to create its own Regency.

Manggarai Regency is a regency in East Nusa Tenggara province of Indonesia, situated on the island of Flores. Established in 1958 to encompass the 6,924.18 km2 area of the lands of the indigenous Manggarai people, the regency was reduced in area and in population by the separation of the more western districts to form West Manggarai Regency on 25 February 2003 and of the more eastern districts to form East Manggarai Regency on 17 July 2007.

Kupang Regency is a regency in East Nusa Tenggara province of Indonesia. It occupies the far western end of Timor Island, together with the smaller island of Semau and other minor offshore islands. Other islands further to the southwest and west which were formerly part of Kupang Regency have been separated administratively - the Rote Islands Group on 10 April 2002, and the Savu Islands Group on 29 October 2008.
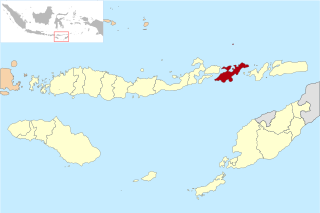
Lembata Regency is a regency in East Nusa Tenggara province of Indonesia. Established on 4 October 1999 from the most easterly part of East Flores Regency, the regency covers the island of Lembata, together with three small offshore islands together forming the eastern part of the Solor Archipelago, and has its administrative seat (capital) in Lewoleba. The population of the Regency was 117,829 at the 2010 decennial census and at the 2020 census was 135,930; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 137,812.
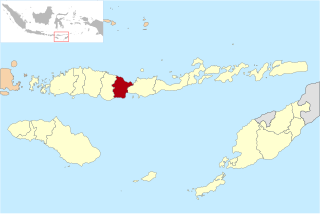
Nagekeo Regency is a regency on the island of Flores in East Nusa Tenggara province of Indonesia, comprising the Nage people in the south and the Keo in the north. It covers an area of 1,377.04 km2 and had a population of 130,120 at the 2010 Census, and 159,732 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 166,968. The regency was established on 2 January 2007 by separation of the former eastern districts from Ngada Regency; it has its administrative seat (capital) in the town of Mbay on the north coast of Flores. It is bordered to the west by the residual Ngada Regency and to the east by Ende Regency, while to the north is the Flores Sea and to the south is the Savu Sea.
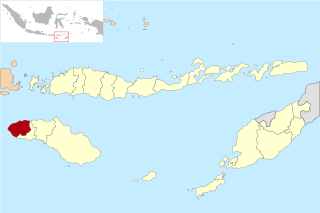
Southwest Sumba Regency is a regency on Sumba Island in East Nusa Tenggara province of Indonesia. Established on 2 January 2007 out of parts of West Sumba Regency, the regency has its seat (capital) in Tambolaka. Its population was 283,818 in the 2010 decennial census and had risen to 303,650 at the 2020 census; the official estimate as at mid 2022 was 322,073 (comprising 164,825 males and 157,248 females

East Manggarai Regency is a regency in East Nusa Tenggara province of Indonesia. Established on 17 July 2007, the regency has its seat (capital) in the town of Borong. It covers a land area of 2,438.68 km2. The population at the 2010 Census was 252,754, and at the 2020 Census was 275,603; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 310,822.

Katingan Regency is one of the thirteen regencies which comprise the Central Kalimantan Province on the island of Kalimantan (Borneo), Indonesia. It was created on 10 April 2002 from what were previously the eastern districts of East Kotawaringin Regency. The town of Kasongan is the capital of the Regency, which covers an area of 20,382.26 km2. The population of Katingan Regency was 146,439 at the 2010 Census and 162,222 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 177,106.

West Kotawaringin Regency is one of the thirteen regencies which comprise the Central Kalimantan Province on the island of Kalimantan (Borneo), Indonesia. It originally comprised the whole western part of the province, having been split from a single Kotawaringin Regency on 26 June 1959 into separate regencies for West and East Kotawaringin, but on 10 April 2002 the most westerly districts of West Kotawaringin were split off to form the new Lamandau Regency and Sukamara Regency. The residual West Kotawaringin Regency has a land area of about 10,816.56 km2, and its population was 235,803 at the 2010 Census and 270,388 at the 2020 Census; the official estimate as at mid 2023 was 280,812. The large town of Pangkalan Bun in Arut Selatan District is the capital of West Kotawaringin Regency.