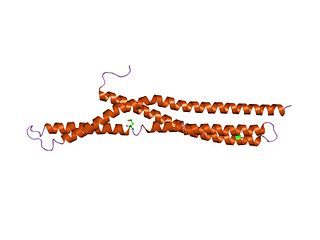
In molecular biology, BAR domains are highly conserved protein dimerisation domains that occur in many proteins involved in membrane dynamics in a cell. The BAR domain is banana-shaped and binds to membrane via its concave face. It is capable of sensing membrane curvature by binding preferentially to curved membranes. BAR domains are named after three proteins that they are found in: Bin, Amphiphysin and Rvs.

Sorting nexin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SNX1 gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a sorting nexin. SNX1 is a component of the retromer complex.

Myc box-dependent-interacting protein 1, also known as Bridging Integrator-1 and Amphiphysin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BIN1 gene.

Clathrin heavy chain 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CLTC gene.

Dynamin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DNM1 gene.

Sorting nexin-9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SNX9 gene.

Sorting nexin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SNX2 gene.

Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 26A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the VPS26A gene.

Sorting nexin-17 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SNX17 gene.

Sorting nexin-5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SNX5 gene.

TC10/CDC42 GTPase-activating protein is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SNX26 gene.

Sorting nexin-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SNX3 gene.

Sorting nexin family member 27, also known as SNX27, is a human gene.

Sorting nexin-13 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SNX13 gene.

Sorting nexin-15 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SNX15 gene.

Sorting nexin-21 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SNX21 gene.

Sorting nexin-18 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SNX18 gene.
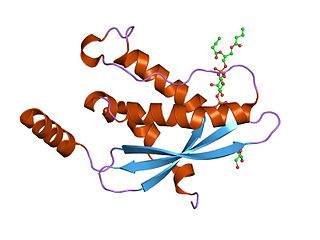
Sorting nexins are a large group of proteins that are localized in the cytoplasm and have the potential for membrane association either through their lipid-binding PX domain or through protein–protein interactions with membrane-associated protein complexes Some members of this family have been shown to facilitate protein sorting.

Sorting nexin 10 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SNX10 gene.

The SNX8 is a sorting nexin protein involved in intracellular molecular traffic from the early endosomes to the TGN. It is suggested that it acts as an adaptor protein in events related to immune response and cholesterol regulation, for example. As a protein of the SNXs family, the SNX8 is formed of 465 aminoacids and presents a BAR-domain and a PX-domain which are very relevant in relation to its functions. Furthermore, SNX8 study is motivated by its medical significance in relation to diseases such as Alzheimer's Disease, cancer, neurodevelopmental malformations and to its role in fighting against viral infections.























