
Jujuy is a province of Argentina, located in the extreme northwest of the country, at the borders with Chile and Bolivia. The only neighboring Argentine province is Salta to the east and south.

Cerro Galán is a caldera in the Catamarca Province of Argentina. It is one of the largest exposed calderas in the world and forms part of the Central Volcanic Zone of the Andes, one of the three volcanic belts found in South America. One of several major caldera systems in the Central Volcanic Zone, the mountain is grouped into the Altiplano–Puna volcanic complex.

Salar de Atacama, located 55 km (34 mi) south of San Pedro de Atacama, is the largest salt flat in Chile. It is surrounded by mountains and lacks drainage outlets. To the east, it is enclosed by the main chain of the Andes, while to the west lies a secondary mountain range called Cordillera de Domeyko. The landscape is dominated by imposing volcanoes such as Licancabur, Acamarachi, Aguas Calientes, and Láscar, the latter being one of Chile's most active volcanoes. These volcanoes are situated along the eastern side of the Salar de Atacama, forming a north–south trending line that separates it from smaller endorheic basins.
Allkem Limited, known as Orocobre Limited until 30 November 2021, is an Australian mining company that is a wholly-owned subsidiary of Arcadium Lithium. Allkem's portfolio includes lithium brine operations in Argentina, a hard-rock lithium operation in Australia and a lithium hydroxide conversion facility in Japan. Allkem is dual listed on the Australian Securities Exchange and Toronto Stock Exchange. In May 2023, Allkem agreed terms to merge with Livent. In January 2024, Allkem and Livent merged to form the NYSE-listed Arcadium Lithium.
Salar de Pedernales is a large salt flat in the Atacama Region of Chile. It lies east of the Cordillera Domeyko at an elevation of 3,370 metres (11,060 ft). The salt flat has an irregular shape and consists mostly of gypsum and rock salt, with an area of 0.6 square kilometres (0.23 sq mi)-1.1 square kilometres (0.42 sq mi) covered by open water. During the late Pleistocene, the climate was wetter and thus open water covered a much larger area of Salar de Pedernales.

La Pacana is a Miocene age caldera in northern Chile's Antofagasta Region. Part of the Central Volcanic Zone of the Andes, it is part of the Altiplano-Puna volcanic complex, a major caldera and silicic ignimbrite volcanic field. This volcanic field is located in remote regions at the Zapaleri tripoint between Chile, Bolivia and Argentina.

Salar de Arizaro is a large salt flat of the Andes in north-western Argentina. It is located between the villages of Tolar Grande and Caipe and near Mina La Casualidad, in Los Andes Department, Salta Province.

Tuyajto Lake is a salt lake located in the Antofagasta Region, northern Chile. Located at an elevation of about 4,010 metres (13,160 ft), its surface area presently fluctuates between 1.7–2.7 square kilometres (0.66–1.04 sq mi) but in the past it was considerably larger; this led to humans going to the lake and creating archeological sites there. Presently, the lake is groundwater-fed and has no surface outlet but water might seep out underground. It is part of the Los Flamencos Natural Reserve.
Salta Basin or Salta Rift Basin is a sedimentary basin located in the Argentine Northwest. The basin started to accumulate sediments in the Early Cretaceous (Neocomian) and at present it has sedimentary deposits reaching thicknesses of 5,000 metres (16,000 ft). The basin contains seven sub-basins: Tres Cruces, Lomas de Olmedo, Metán, Alemanía, Salfity, El Rey, Sey and Brealito. The basin environment has variously been described as a "foreland rift" and an "intra-continental rift". The basin developed under conditions of extensional tectonics and rift-associated volcanism.

Llullaillaco is a dormant stratovolcano on the border between Argentina and Chile. It lies in the Puna de Atacama, a region of tall volcanic peaks on a high plateau close to the Atacama Desert, one of the driest places in the world. Its maximum elevation is most commonly given as 6723 m, making it the second- or third-highest volcano in the world. Despite its height, it is not clear whether the volcano has any glaciers or merely patches of perennial snow and ice. Between 3700 m and 5000 m elevation there is a sparse plant cover, while at lower altitudes the climate is too dry for plants to grow. A species of mouse on Llullaillaco is the highest-living known vertebrate species.
Pairique volcanic complex is a volcanic complex in the Jujuy Province, Argentina.
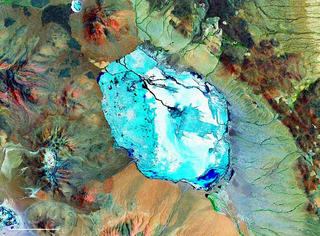
Pastos Grandes is the name of a caldera and its crater lake in Bolivia. The caldera is part of the Altiplano-Puna volcanic complex, a large ignimbrite province that is part of the Central Volcanic Zone of the Andes. Pastos Grandes has erupted a number of ignimbrites through its history, some of which exceeded a volume of 1,000 cubic kilometres (240 cu mi). After the ignimbrite phase, the lava domes of the Cerro Chascon-Runtu Jarita complex were erupted close to the caldera and along faults.

Antofalla is a Miocene-Pliocene volcano in Argentina's Catamarca Province. It is part of the volcanic segment of the Andes in Argentina, and it is considered to be part of the Central Volcanic Zone, one of the volcanic zones of the Andes. Antofalla forms a group of volcanoes that are aligned on and behind the main volcanic arc. Antofalla itself is a remote volcano.

Ojos de Mar is a group of 3–6 small water bodies close to the town of Tolar Grande in Argentina and an important tourist attraction there. They are inhabited by extremophile microorganisms of interest to biotechnology; stromatolites have also been found there.

Laguna Socompa is a small lake in the Salta Province of Argentina, at the foot of Socompa volcano. It covers an area of about 200 hectares and has an average depth of about 0.45–0.62 metres. The lake is fed by arroyos and springs, some of which are hot springs. Its waters are very rich in arsenic and otherwise salty and slightly alkaline; these properties and the regionally high UV radiation give Laguna Socompa extreme environmental conditions.
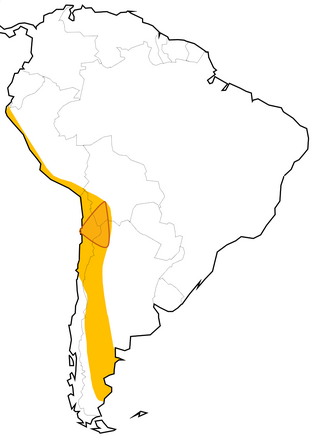
The Lithium Triangle is a region of the Andes that is rich in lithium reserves, encompassed by the borders of Argentina, Bolivia, and Chile. The lithium in the triangle is concentrated in various salt pans that exist along the Atacama Desert and neighboring arid areas. The largest areas three main salt pans that define its vertices are the Salar de Uyuni in Bolivia, Salar de Atacama in Chile, and Salar del Hombre Muerto in Argentina. Of these, the core of Salar de Atacama in Chile has the highest concentration of lithium among all world's brine sources.
The Geste Formation is a fossiliferous geologic formation of the Puna Plateau in the western Salta Province and northern Catamarca Province of the Argentine Northwest, northwestern Argentina.

Salar Ignorado is a salar in the Andes of Chile's Atacama Region at 4,250 metres (13,940 ft) elevation. Located just south of Cerro Bayo volcano, it comprises 0.7 square kilometres (0.27 sq mi) of salt flats, sand dunes and numerous pools of open water. The waters of Salar Ignorado, unlike these of other salt flats in the central Andes, are acidic owing to the input of sulfuric acid from hydrothermal water and the weathering of volcanic rocks.

Salar de Gorbea is a salt flat just south of the border between the Antofagasta and Atacama regions, within Chile but close to the border with Argentina.

Carachipampa is a Pleistocene volcanic cone in Argentina. Part of a wider, regional volcanic field, it has produced lava flows consisting of andesite. It is surrounded by a lake and a salt flat, the former of which features an ecosystem formed by microbes.


















