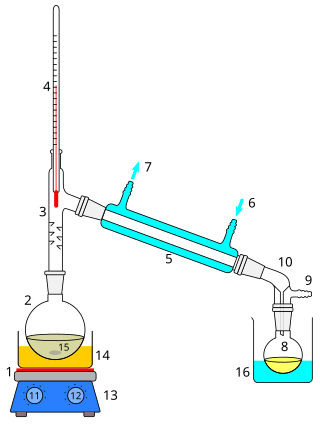
Distillation, also classical distillation, is the process of separating the component substances of a liquid mixture of two or more chemically discrete substances; the separation process is realized by way of the selective boiling of the mixture and the condensation of the vapors in a still.

Brandy is a liquor produced by distilling wine. Brandy generally contains 35–60% alcohol by volume and is typically consumed as an after-dinner digestif. Some brandies are aged in wooden casks. Others are coloured with caramel colouring to imitate the effect of ageing, and some are produced using a combination of ageing and colouring. Varieties of wine brandy can be found across the winemaking world. Among the most renowned are Cognac and Armagnac from south-western France.

Moonshine is high-proof liquor, traditionally made or distributed illegally. The name was derived from a tradition of distilling the alcohol at night to avoid detection. In the first decades of the 21st century, commercial distilleries have adopted the term for its outlaw cachet and have begun producing their own legal "moonshine", including many novelty flavored varieties, that are said to continue the tradition by using a similar method and/or locale of production.

Irish whiskey is whiskey made on the island of Ireland. The word 'whiskey' comes from the Irish uisce beatha, meaning water of life. Irish whiskey was once the most popular spirit in the world, though a long period of decline from the late 19th century onwards greatly damaged the industry, so much so that although Ireland boasted at least 28 distilleries in the 1890s, by 1966 this number had fallen to just two, and by 1972 the remaining distilleries, Bushmills Distillery and Old Midleton Distillery, were owned by just one company, Irish Distillers.
Fractional distillation is the separation of a mixture into its component parts, or fractions. Chemical compounds are separated by heating them to a temperature at which one or more fractions of the mixture will vaporize. It uses distillation to fractionate. Generally the component parts have boiling points that differ by less than 25 °C (45 °F) from each other under a pressure of one atmosphere. If the difference in boiling points is greater than 25 °C, a simple distillation is typically used.

Single malt whisky is malt whisky from a single distillery.

A still is an apparatus used to distill liquid mixtures by heating to selectively boil and then cooling to condense the vapor. A still uses the same concepts as a basic distillation apparatus, but on a much larger scale. Stills have been used to produce perfume and medicine, water for injection (WFI) for pharmaceutical use, generally to separate and purify different chemicals, and to produce distilled beverages containing ethanol.

A pot still is a type of distillation apparatus or still used to distill liquors such as whisky or brandy. In modern (post-1850s) practice, they are not used to produce rectified spirit, because they do not separate congeners from ethanol as effectively as other distillation methods. Pot stills operate on a batch distillation basis. Traditionally constructed from copper, pot stills are made in a range of shapes and sizes depending on the quantity and style of spirit desired.

A column still, also called a continuous still, patent still or Coffey still, is a variety of still consisting of two columns. Column stills can produce rectified spirit.

Pálinka is a traditional fruit spirit with origins in the medieval Hungary, known under several names. Protected as a geographical indication of the European Union, only fruit spirits mashed, distilled, matured and bottled in Hungary and similar apricot spirits from four provinces of Austria can be called "pálinka", while "Tótpálinka" refers to wheat-derived beverages. Törkölypálinka, a different product in the legal sense, is a similarly protected pomace spirit that is commonly included with pálinka. While pálinka may be made of any locally grown fruit, the most common ones are plums, apricots, apples, pears, and cherries.

Continuous distillation, a form of distillation, is an ongoing separation in which a mixture is continuously fed into the process and separated fractions are removed continuously as output streams. Distillation is the separation or partial separation of a liquid feed mixture into components or fractions by selective boiling and condensation. The process produces at least two output fractions. These fractions include at least one volatile distillate fraction, which has boiled and been separately captured as a vapor condensed to a liquid, and practically always a bottoms fraction, which is the least volatile residue that has not been separately captured as a condensed vapor.

A microdistillery is a small, often boutique-style distillery established to produce beverage grade spirit alcohol in relatively small quantities, usually done in single batches. While the term is most commonly used in the United States, micro-distilleries have been established in Europe for many years, either as small cognac distilleries supplying the larger cognac houses, or as distilleries of single malt whisky originally produced for the blended Scotch whisky market, but whose products are now sold as niche single malt brands. The more recent development of micro-distilleries can now also be seen in locations as diverse as London, Switzerland, and South Africa.

J.P. Wiser's Whisky is a Canadian whisky producer and one of the oldest in the country, established in 1857. Since 1935, it has held a majority stake in Corby Spirit and Wine. In 2005 the international Liquor company Pernod Ricard took ownership of both companies. Hiram Walker & Sons Limited currently produce J.P. Wiser's Whisky at their Windsor, Ontario, distillery.
Aeneas Coffey (1780–1839) was an Irish inventor and distiller.
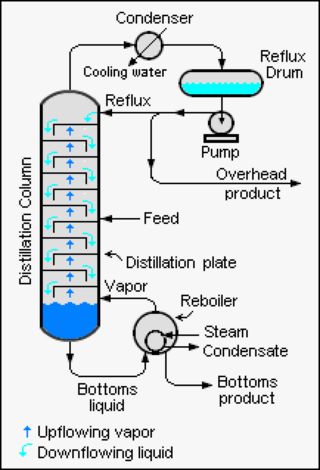
Reflux is a technique involving the condensation of vapors and the return of this condensate to the system from which it originated. It is used in industrial and laboratory distillations. It is also used in chemistry to supply energy to reactions over a long period of time.

Downslope Distilling is a craft beverage distillery in Centennial, Colorado, United States.
Chase Vodka is a brand of vodka owned and produced by the British company Diageo. The Chase brand began as a single estate potato vodka made in Herefordshire, England, UK by William Chase, who is also known for founding Tyrrells crisps.

Hangar 1 Vodka is a vodka brand produced by The Hangar 1 Distillery in Alameda, California. In addition to vodka, the distillery also produces spirits, some of which were formerly produced by St. George Spirits. The brand is owned and distributed by Proximo Spirits of Jersey City, New Jersey, and is available as a straight vodka as well as in a variety of flavors.

Willett Pot Still Reserve Bourbon is brand of a bourbon whiskey produced in Bardstown, Kentucky by the Willett Distillery.
















