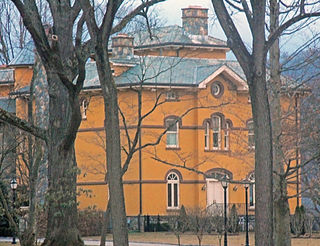The Eastbrook Baptist Church and Eastbrook Town House are a pair historic civic buildings on Maine State Route 200 in the center of Eastbrook, Maine. The church, built 1860, and the town house, built 1880, are both late examples of Greek Revival architecture, the latter apparently built in stylistic imitation of the former. The buildings were listed as a pair on the National Register of Historic Places in 1978.

The Guilford Memorial Library is the public library of Guilford, Maine, USA. It is located at the junction of Library and Water Streets, in a small architecturally distinguished Renaissance Revival structure designed by Frank A. Patterson and built in 1908 with funding assistance from Andrew Carnegie. The building was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1986. The library is one of the only libraries in Maine designated as a "Star Library" by Library Journal.

The Lower Sunday River School is an historic school on Sunday River Road, just north of its junction with Skiway Road, in Newry, Maine. Built in 1895 by the town, this is one of the best-preserved one-room schoolhouses in northern Oxford County. The school was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1978.
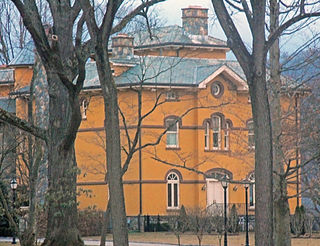
Rock Lawn is a historic house in Garrison, New York, United States. It was built in the mid-19th century from a design by architect Richard Upjohn. In 1982 it was listed on the National Register of Historic Places along with its carriage house, designed by Stanford White and built around 1880.

The North Grove Street Historic District is located along the north end of that street in Tarrytown, New York, United States. It consists of five mid-19th century residences, on both sides of the street, and a carriage barn. In 1979 it was listed on the National Register of Historic Places.

The Peterborough Main Post Office is located at 23 Grove Street in Peterborough, New Hampshire. Built in 1936, it is a well-preserved example of Georgian Revival architecture. It is further distinctive because it is virtually unaltered since its construction, and its interior features a WPA mural by Marguerite Zorach. The building was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1986.

The J.G. Deering House also known as the Dyer Library/Saco Museum is an historic house at 371 Main Street in Saco, Maine. Completed in 1870, it is a fine local example of Italianate style. Built for Joseph Godfrey Deering, it was given by his heirs to the city for use as a library. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1982.

The Durham House is a historic house on Ball Park Road in Goshen, New Hampshire. Built about 1860, it is one of a cluster of plank-frame houses built in the rural community in the 19th century. This one is further note for its Greek Revival features, and its construction is tentatively ascribed to James Chandler, a noted local builder. The house was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1985.
The Brown House is a historic house on High Street in Brownville, Maine, United States. This two-story wood-frame house was built in 1815 by Francis Brown, for whom the town is named. It is architecturally distinctive for a period suspended ceiling on the second floor. The house was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1985.
The Burgess House is a historic house on Burgess Road, just east of Austin Road in Sebec, Maine, United States. The oldest portion of this wood-frame house dates to about 1816, and was built by Ichabod Young, who erected the first fulling mill in Piscataquis County. The house is most remarkable for its high-quality interior woodwork, and for the artwork on the walls of several of its rooms, which includes paintings by Rufus Porter and stencilwork by Moses Eaton, Jr., two noted itinerant artists of the early-to-mid 19th century. The house was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1978.
The Chandler-Parsons Blacksmith Shop, now the Blacksmith Shop Museum, is a historic blacksmith shop at 107 Dawes Road in Dover-Foxcroft, Maine. Believed to be built in the early 1860s, it is one of a very small number of relatively unaltered rural 19th-century blacksmithies in the state. It is owned and operated by the local historical society as a museum, and was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1989.
The Harriman School is a historic one-room schoolhouse on North Road in rural Sebec, Maine. Built in 1860, it is the oldest of two surviving 19th-century district schoolhouses in the community. The vernacular Greek Revival building served as a public school until 1933, and was converted into a museum by the Sebec Historical Society after it acquired the property in 1966. The building was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1996.

The Observer Building is a historic commercial and residential building located at 128 Union Square in Dover-Foxcroft, Maine. Built in 1854, it is an architecturally unusual Greek Revival wood-frame "flatiron" triangular building with a variable-pitch gable roof. In addition to its architectural significance, it is also historically significant as the home for many years of The Piscataquis Observer, one of Maine's oldest weekly newspapers. The building is now owned by the Dover-Foxcroft Historical Society, which uses it as a museum and storage space.
Sangerville Town Hall is located at 1 Town Hall Lane in the village center of Sangerville, Maine. Built in 1902, it is one of the rural community's most sophisticated architectural buildings. It was designed and built by a local contractor, and has well-proportioned Colonial Revival features. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1991.
The Larsson–Noak Historic District encompasses a collection of buildings constructed by Swedish immigrants to northern Maine between about 1888 and 1930. The district is focused on a cluster of four buildings on Station Road, northeast of the center of New Sweden, Maine. Notable among these is the c. 1888 Larsson-Ostlund House, which is the only known two-story log house built using Swedish construction techniques in the state. Across the street is the c. 1900 Noak Blacksmith Shop, a virtually unaltered building housing original equipment. The district was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1989.
The A. B. Leavitt House is a historic house on Main Street in the Sherman Mills village of Sherman, Maine. Built in 1890, the house is a high-quality and well-preserved example of Gothic Revival mail-order architecture, being a nearly-intact and faithful rendition of a design pattern published by the architectural firm of Palliser, Palliser & Company, deviating only in the addition of a carriage house. The house was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1986.

The James Sullivan Wiley House is a historic house at 148 East Main Street in Dover-Foxcroft, Maine. A fine Greek Revival house with a temple front, it was built in 1849 by James Sullivan Wiley, a prominent local lawyer and teacher who also represented the area in the United States Congress for one term. The house was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1976. The building now houses offices of the Charlotte White Center, a social service agency.
The Norton's Corner School is a historic one-room schoolhouse at 2373 Elliotsville Road in Willimantic, Maine. Built about 1882, it was one of the small town's first public buildings, a role it continues to serve as it now houses the public library. The building was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1996.

Wallingford Hall is a historic house at 21 York Street in Kennebunk, Maine. Built in 1805–06, it is an unusually grand expression of Federal architecture in the town, built by the regionally architect and builder Thomas Eaton, and one of the oldest surviving examples in the state of a connected farmstead. In the late 19th and early 20th century it was also home to William Barry, an architectural historian who wrote extensively on the architecture of southern Maine, and was an early promoter of the Colonial Revival in the area. The house was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2004.

The Canal Street Schoolhouse is a historic school building on Canal Street in Brattleboro, Vermont. Built in 1892 out of locally quarried stone, it is a fine local example of Colonial Revival architecture. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1977.