The Federated States of Micronesia or simply Micronesia, is an island country in Oceania associated with the United States. It consists of four states – from west to east, Yap, Chuuk, Pohnpei and Kosrae – that are spread across the western Pacific. Together, the states comprise around 607 islands that cover a longitudinal distance of almost 2,700 km (1,678 mi) just north of the equator. They lie northeast of Indonesia and Papua New Guinea, south of Guam and the Marianas, west of Nauru and the Marshall Islands, east of Palau and the Philippines, about 2,900 km (1,802 mi) north of eastern Australia, 3,400 km southeast of Japan, and some 4,000 km (2,485 mi) southwest of the main islands of the Hawaiian Islands.

Micronesia is a subregion of Oceania, comprising thousands of small islands in the western Pacific Ocean. It has a close shared cultural history with three other island regions—the Philippines to the west, Polynesia to the east, and Melanesia to the south—as well as with the wider community of Austronesian peoples.

Chuuk State is one of the four states of the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM). The other states are Kosrae State, Pohnpei State, and Yap State. It consists of several island groups:

Yap State is one of the four states of the Federated States of Micronesia (FSM). The other states are Kosrae State, Pohnpei State, and Chuuk State.

This is a list of the buildings, sites, districts, and objects listed on the National Register of Historic Places in the Federated States of Micronesia. There are currently 26 listed sites located in all 4 states of the Federated States of Micronesia.
Dinay is a village belonging to the municipality of Rull in the southern part of the island of Yap in the Federated States of Micronesia. The village was added to the United States National Register of Historic Places in 2004. It is unique in Micronesia as the site of an ancient pottery complex, and is probably one of the earliest settlements on the island. The ancient village complex includes more than a dozen family platforms (daf) of such age that local folklore has forgotten their lineages, normally a significant cultural feature of such sites. The period of occupation is estimated to have been between about 3000 BCE and 1600 CE.
The Micronesian Games are a quadrennial international multi-sport event within the Micronesian region. The Games were first held in 1969 in Saipan. The 2010 Micronesian Games were initially due to be held in Majuro, until the hosts withdrew. The 2010 Games were hosted by Palau. The Federated States of Micronesia won the bidding to host the 2014 Micronesian Games in Pohnpei State, and later won again against CNMI for the 2018 Micronesian Games to be held in Yap State.

The Rull Men's Meetinghouse is a historic meeting house in Rull, a village on the island of Yap in the Federated States of Micronesia. It is a large rectangular structure, set on a raised stone platform. The flooring consists of treated betelnut palm trunks, and has a steeply pitched roof made of bamboo supports with various types of tropical leaves tied in place using coconut fiber. The faluw, although not the first built on this platform, has historically occupied a central place in the civic life of the community, serving as a place where the men of the village could meet in seclusion, and as a place for social rites.

The Catholic Belltower is a historic tower at the Catholic Mission in Kolonia, on the island of Pohnpei in the Federated States of Micronesia. The belltower and adjoining masonry apse are all that remain of a church built in 1909 by German Capuchin missionaries, when Ponape and the other Caroline Islands were administered as part of German New Guinea. The rest of the church was destroyed during the fighting of World War II. The tower is 4.8 metres (16 ft) square, rising to a height of 20.7 metres (68 ft), and the shell of the apse is about 10 metres (33 ft) in height. The tower has a foundation of basalt rock and lime mortar, and is constructed out of concrete bricks.

Leluh is a major prehistoric and historic archaeological site, encompassing the remains of a city on Lelu Island, a satellite of the larger island of Kosrae in the Federated States of Micronesia. The remains are those of a civilization that peaked around the 14th and 15th centuries, with elements still visible at the time of European contact in the early 19th century.

The Chief Agriculturist House is a historic house in Kolonia, the capital of Pohnpei State in the Federated States of Micronesia. It is a steel and concrete structure, built in the mid-1920s when Pohnpei and the other Caroline Islands were part of the Japanese South Seas Mandate. It was one of the highest-quality buildings constructed on Pohnpei during the Japanese administration, and was the home of the Japanese weatherman and agricultural overseer, said to be the second most powerful figure in Japanese Micronesia.

The World War II Japanese Army Headquarters for the defense of Tonowas, an island in what is now Chuuk State in the Federated States of Micronesia, was located in an underground bunker in the village of Roro. The underground facilities, including an office, communications center, print shop, supply room, and health clinic, were built in response to American air raids against the facilities, which were associated with the major naval facility of the Imperial Japanese Navy in Chuuk Lagoon.

Tarang, also known as O'Keefe's Island is a small island in the main harbor of Yap Island in the Federated States of Micronesia. It is located roughly in the center of the harbor east of Colonia, the Yapese capital, between Pekel and Bi Islands. It is a low island with a maximum height of about 22 feet (6.7 m), and is overgrown with tropical vegetation. The island has local historical importance as the home of Captain David O'Keefe, an enterprising American who arrived on Yap in the 1870s, and was responsible for not only significant economic growth, but also for the depreciation of the distinctive Yapese currency, the large rai stones which became devalued after O'Keefe introduced iron tools that made manufacture of the stones easier. O'Keefe settled on Tarang, where he had a boat landing, coal warehouse, and house. Of these structures, only the boat landing has survived; only foundations survive of the others.

The German Cemetery is a historic cemetery in Kolonia, the capital of Pohnpei State in the Federated States of Micronesia. Pohnpei and the other Caroline Islands had become a German protectorate in 1899, after the Spanish–American War, and were administered as part of German New Guinea. This cemetery is a historical reminder of the period of German administration, although it was in deteriorated condition in 1976, accessible only by hiking through a mangrove swamp, with its wrought iron fence and gate in disrepair. Two German governors were buried here.

Tonnachau Mountain, is a mountain on Moen Island in Chuuk State of the Federated States of Micronesia. Rising to a height of 1,100 feet (340 m), it is not the highest peak of Moen, which is Mount Teroken to the south. Tonnachau is, however, a prominent landmark rising above Chuuk International Airport. The mountain also has an important place in Chuukese culture and prehistory, with archaeologically significant prehistoric middens and fortifications on its summit ridge which date back as far as 4,000 BCE. Chuukese tradition states that its hero Soukachou built a fort on Tonachau when he arrived from Kosrae and established rule over the lagoon. The mountain also has extensive remains of mainly Japanese fortifications erected during World War II.

The Tonotan Guns and Caves are a series of World War II-era military fortification on the island of Weno, the main island of Chuuk State in the Federated States of Micronesia. They consist of an excavation housing an English naval gun, and a series of caves used for housing and operations that provided shelter from aerial bombardment. The installations are located on the lower north flank of Mount Teroken, the island's highest peak.

The Japanese Artillery Road and Pohndolap Area are a historic area on Sokehs Island in the Federated States of Micronesia. Sokehs has a prominent north-south ridge (known locally as "Pohndolap", overlooking the state capital Kolonia, and was fortified by the Japanese during World War II. They built a road to the summit area and emplaced anti-aircraft guns on the ridge. The ridge was also a key site in the 1910 Sokehs Rebellion against Japanese rule, and the remnants of a Pohnpeian fort are also in the area. The surviving elements of these fortifications were listed on the United States National Register of Historic Places in 1976. The old road is now part of a hiking trail, leading up to the fortifications.

The Spanish Wall is the deteriorating remnant of Spanish Fort Alphonso XIII in Kolonia, the capital of Pohnpei State in the Federated States of Micronesia. When built, the wall was about 0.5 miles (0.80 km) in length and 8 feet (2.4 m) in height with a parapet that ranged in height from 2–3 feet (0.61–0.91 m). The wall was built by Spanish administrators of Pohnpei in 1887 after a local uprising drove the local Spanish authorities onto a ship in the harbor. Most of the wall was taken down by the German administration that took over in the early 20th century, after the Spanish–American War. The remains of the wall, about 700 feet (210 m) and two arches, are now part of a local park.

The Japanese Elementary School for Ponapean Children is a historic school building in Kolonia, the capital of Pohnpei State in the Federated States of Micronesia. The surviving building is one of two reinforced concrete buildings, constructed c. 1920-21 by the Japanese authorities of the South Seas Mandate, which included the island of Pohnpei, then known as "Ponape". These buildings were the sole educational facility on the island for native children, those of Japanese dependents attending a separate, segregated facility. They were heavily damaged by bombing during World War II, with one of them being demolished and the other restored for use as part of the island's hospital.
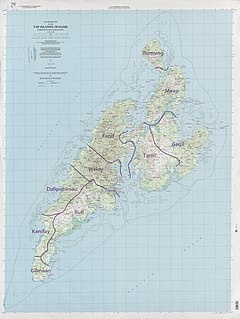
Bechiyal, also variously Bechiel or Bechyal, is a village in the municipality of Maap in the state of Yap, Federated States of Micronesia. When visited in the 1984 it had a population of about ten. The village was once larger, with a documented population of about 200 in the early 20th century. There are a significant number of stone platforms, sites where houses would have stood, and the village site is considered archaeologically sensitive. It was listed on the United States National Register of Historic Places in 1983.












