
The first indigenous peoples of Costa Rica were hunters and gatherers, and when the Spanish conquerors arrived, Costa Rica was divided in two distinct cultural areas due to its geographical location in the Intermediate Area, between Mesoamerican and the Andean cultures, with influences of both cultures.

Pedro de Alvarado was a Spanish conquistador and governor of Guatemala. He participated in the conquest of Cuba, in Juan de Grijalva's exploration of the coasts of the Yucatán Peninsula and the Gulf of Mexico, and in the conquest of the Aztec Empire led by Hernán Cortés. He is considered the conquistador of much of Central America, including Guatemala, Honduras and El Salvador.

Mestizo is a person of mixed European and indigenous non-European ancestry in the former Spanish Empire. In certain regions such as Latin America, it may also refer to people who are culturally European even though their ancestors are indigenous. The term was used as an ethno-racial exonym for mixed-race castas that evolved during the Spanish Empire. It was a formal label for individuals in official documents, such as censuses, parish registers, Inquisition trials, and others. Priests and royal officials might have classified persons as mestizos, but individuals also used the term in self-identification.

Tecun Uman was one of the last rulers of the K'iche' Maya people, in the Highlands of what is now Guatemala. According to the Kaqchikel annals, he was slain by Spanish conquistador Pedro de Alvarado while waging battle against the Spanish and their allies on the approach to Quetzaltenango on 12 February 1524. Tecun Uman was declared Guatemala's official national hero on March 22, 1960, and is commemorated on February 20, the popular anniversary of his death. Tecun Uman has inspired a wide variety of activities ranging from the production of statues and poetry to the retelling of the legend in the form of folkloric dances to prayers. Despite this, Tecun Uman's existence is not well documented, and it has proven to be difficult to separate the man from the legend.

Guatemalans are people connected to the country of Guatemala. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Guatemalans, several of these connections exist.

The Kaqchikel are one of the indigenous Maya peoples of the midwestern highlands of Guatemala and of southern Mexico. They constitute Guatemala's third largest Maya group. The name was formerly spelled in various other ways, including Cakchiquel, Kakchiquel, Caqchikel, and Cachiquel.

In a protracted conflict during the Spanish colonization of the Americas, Spanish colonisers gradually incorporated the territory that became the modern country of Guatemala into the colonial Viceroyalty of New Spain. Before the conquest, this territory contained a number of competing Mesoamerican kingdoms, the majority of which were Maya. Many conquistadors viewed the Maya as "infidels" who needed to be forcefully converted and pacified, disregarding the achievements of their civilization. The first contact between the Maya and European explorers came in the early 16th century when a Spanish ship sailing from Panama to Santo Domingo was wrecked on the east coast of the Yucatán Peninsula in 1511. Several Spanish expeditions followed in 1517 and 1519, making landfall on various parts of the Yucatán coast. The Spanish conquest of the Maya was a prolonged affair; the Maya kingdoms resisted integration into the Spanish Empire with such tenacity that their defeat took almost two centuries.

The Captaincy General of Guatemala, also known as the Kingdom of Guatemala, was an administrative division of the Spanish Empire, under the viceroyalty of New Spain in Central America, including the present-day nations of Costa Rica, Nicaragua, Honduras, El Salvador, and Guatemala, and the Mexican state of Chiapas. The governor-captain general was also president of the Royal Audiencia of Guatemala, the superior court.

The Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, also known as the Conquest of Mexico, the Spanish-Aztec War (1519–1521), or the Conquest of Tenochtitlan was one of the primary events in the Spanish colonization of the Americas. There are multiple 16th-century narratives of the events by Spanish conquistadors, their indigenous allies, and the defeated Aztecs. It was not solely a small contingent of Spaniards defeating the Aztec Empire but a coalition of Spanish invaders with tributaries to the Aztecs, and most especially the Aztecs' indigenous enemies and rivals. They combined forces to defeat the Mexica of Tenochtitlan over a two-year period. For the Spanish, Mexico was part of a project of Spanish colonization of the New World after 25 years of permanent Spanish settlement and further exploration in the Caribbean.
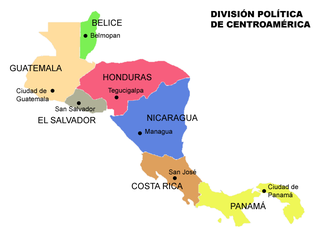
Central America is a subregion of the Americas formed by six Latin American countries and one (officially) Anglo-American country, Belize. As an isthmus it connects South America with the remainder of mainland North America, and comprises the following countries : Belize, Guatemala, Honduras, El Salvador, Nicaragua, Costa Rica, and Panama.
Jorge de Alvarado y Contreras was a Spanish conquistador, brother of the more famous Pedro de Alvarado.
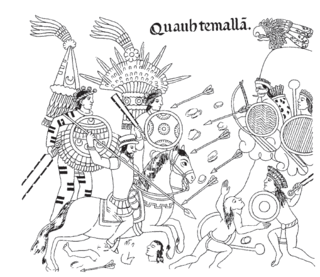
Indian auxiliaries were those indigenous peoples of the Americas who allied with Spain and fought alongside the conquistadors during the Spanish colonization of the Americas. These auxiliaries acted as guides, translators and porters, and in these roles were also referred to as yanakuna, particularly during the Spanish conquest of the Inca Empire. The term was also used for formations composed of indigenous warriors which were used by the Spanish for reconnaissance and combat duties. Indian auxiliaries continued to be used by the Spanish to maintain control over their colonies in the Americas; frequently stationed on the frontier, they were often used to suppress anti-colonial revolts such as Arauco War.

The Spanish conquest of the Maya was a protracted conflict during the Spanish colonisation of the Americas, in which the Spanish conquistadores and their allies gradually incorporated the territory of the Late Postclassic Maya states and polities into the colonial Viceroyalty of New Spain. The Maya occupied the Maya Region, an area that is now part of the modern countries of Mexico, Guatemala, Belize, Honduras and El Salvador; the conquest began in the early 16th century and is generally considered to have ended in 1697.

Honduras has been inhabited by a number of indigenous peoples, the most powerful of which, until the ninth century CE, were the Maya. The western-central part of Honduras was inhabited by the Lenca while other indigenous peoples settled in the northeast and coastal regions. These peoples had their conflicts but maintained commercial relationships with each other and with other populations as distant as Panama and Mexico.

The Spanish diaspora consists of Spanish people and their descendants who emigrated from Spain. In the Americas, the term may refer to those of Spanish nationality living there; "Hispanic" is usually a more appropriate term to describe the general Spanish-speaking populations of the Americas together with those in Spain. The diaspora is concentrated in places that were part of the Spanish Empire. Countries with sizeable populations are Argentina, Bolivia, Chile, Colombia, Costa Rica, Cuba, Dominican Republic, Ecuador, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Panama, Paraguay, Peru, Uruguay, Venezuela, and, to a lesser extent, Brazil, Belize, Haiti, United States, Canada, the Philippines and the rest of Europe.
The Spanish conquest of Chiapas was the campaign undertaken by the Spanish conquistadores against the Late Postclassic Mesoamerican polities in the territory that is now incorporated into the modern Mexican state of Chiapas. The region is physically diverse, featuring a number of highland areas, including the Sierra Madre de Chiapas and the Montañas Centrales, a southern littoral plain known as Soconusco and a central depression formed by the drainage of the Grijalva River.

The Spanish conquest of Honduras was a 16th-century conflict during the Spanish colonization of the Americas in which the territory that now comprises the Republic of Honduras, one of the seven states of Central America, was incorporated into the Spanish Empire. In 1502, the territory was claimed for the king of Spain by Christopher Columbus on his fourth and final trip to the New World. The territory that now comprises Honduras was inhabited by a mix of indigenous peoples straddling a transitional cultural zone between Mesoamerica to the northwest, and the Intermediate Area to the southeast. Indigenous groups included Maya, Lenca, Pech, Miskitu, Mayangna (Sumu), Jicaque, Pipil and Chorotega. Two indigenous leaders are particularly notable for their resistance against the Spanish; the Maya leader Sicumba, and the Lenca ruler referred to as Lempira.

Pedro de Portocarrero was a Spanish conquistador who was active in the early 16th century in Guatemala, and Chiapas in southern Mexico. He was one of the few Spanish noblemen that took part in the early stages of the Spanish conquest of the Americas, and was distantly related to prominent conquistador Pedro de Alvarado, who appointed him as an official in early colonial Guatemala.

The Spanish conquest of El Salvador was the campaign undertaken by the Spanish conquistadores against the Late Postclassic Mesoamerican polities in the territory that is now incorporated into the modern Central American country of El Salvador. El Salvador is the smallest country in Central America, and is dominated by two mountain ranges running east–west. Its climate is tropical, and the year is divided into wet and dry seasons. Before the conquest the country formed a part of the Mesoamerican cultural region, and was inhabited by a number of indigenous peoples, including the Pipil, the Lenca, the Xinca, and Maya. Native weaponry consisted of spears, bows and arrows, and wooden swords with inset stone blades; they wore padded cotton armour.

Guatemala–Spain relations are the current and historical relations between Guatemala and Spain. Both nations are members of the Organization of Ibero-American States and the United Nations.


















