| Stomatosuchus Temporal range: Late Cretaceous, Cenomanian | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Life restoration of a Stomatosuchus in its environment | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Clade: | Archosauria |
| Clade: | Pseudosuchia |
| Clade: | Crocodylomorpha |
| Family: | † Stomatosuchidae |
| Genus: | † Stomatosuchus Stromer, 1925 |
| Type species | |
| †Stomatosuchus inermis Stromer, 1925 | |
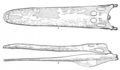
Stomatosuchus (meaning "mouth crocodile") is an extinct stomatosuchid neosuchian from the Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian) Bahariya Formation of Egypt. The type and only species is S. inermis. Much of what is known about Stomatosuchus has been inferred from the related genus Laganosuchus .