
Stylonurina is one of two suborders of eurypterids, a group of extinct arthropods commonly known as "sea scorpions". Members of the suborder are collectively and informally known as "stylonurine eurypterids" or "stylonurines". They are known from deposits primarily in Europe and North America, but also in Siberia.

Dolichopterus is a genus of prehistoric sea scorpions, arthropods in the order Eurypterida. Fossils of Dolichopterus have been discovered in deposits ranging from Silurian to Devonian, and have been referred to several different species, some of them of dubious affinity to this genus.

Mixopterus is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of Mixopterus have been discovered in deposits from Late Silurian age, and have been referred to several different species. Fossils have been recovered from two continents; Europe and North America.

Hughmilleria is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of Hughmilleria have been discovered in deposits of the Silurian age in China and the United States. Classified as part of the basal family Hughmilleriidae, the genus contains three species, H. shawangunk from the eastern United States, H. socialis from Pittsford, New York, and H. wangi from Hunan, China. The genus is named in honor of the Scottish geologist Hugh Miller.

Chasmataspidids, sometime referred to as chasmataspids, are a group of extinct chelicerate arthropods that form the order Chasmataspidida. Chasmataspidids are probably related to horseshoe crabs (Xiphosura) and/or sea scorpions (Eurypterida), with more recent studies suggest that they form a clade (Dekatriata) with Eurypterida and Arachnida. Chasmataspidids are known sporadically in the fossil record through to the mid-Devonian, with possible evidence suggesting that they were also present during the late Cambrian. Chasmataspidids are most easily recognised by having an opisthosoma divided into a wide forepart (preabdomen) and a narrow hindpart (postabdomen) each comprising 4 and 9 segments respectively. There is some debate about whether they form a natural group.

Brachyopterus is a genus of prehistoric eurypterid of the family Rhenopteridae. It is one of the earliest known eurypterids, having been recovered from Middle Ordovician deposits in Montgomeryshire, Wales. Though other species have been assigned to it in the past, Brachyopterus is today recognized as containing one valid species, B. stubblefieldi.

Drepanopterus is an extinct genus of eurypterid and the only member of the family Drepanopteridae within the Mycteropoidea superfamily. There are currently three species assigned to the genus. The genus has historically included more species, with nine species having been associated with the genus Drepanopterus. Five of these have since been proven to be synonyms of pre-existing species, assigned to their own genera, or found to be based on insubstantial fossil data. The holotype of one species proved to be a lithic clast.

Nanahughmilleria is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of Nanahughmilleria have been discovered in deposits of Devonian and Silurian age in the United States, Norway, Russia, England and Scotland, and have been referred to several different species.

Parastylonurus is a genus of prehistoric eurypterid. It is classified within the Parastylonuridae family and contains three species, P. hendersoni and P. ornatus from the Silurian of Scotland and P. sigmoidalis from the Silurian of England.

Stylonurella is a genus of prehistoric eurypterid. It is classified within the Parastylonuridae family and contains three species, S. arnoldi and S. beecheri from the Devonian of Pennsylvania, United States and S. spinipes from the Silurian of Kip Burn, Scotland.
Tarsopterella is a genus of prehistoric eurypterid classified within the family Hardieopteridae. It contains only one species, T. scotica from the Lower Devonian of Scotland.

Erettopterus is a genus of large predatory eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of Erettopterus have been discovered in deposits ranging from Early Silurian to the Early Devonian, and have been referred to several different species. Fossils have been recovered from two continents; Europe and North America. The genus name is composed by the Ancient Greek words ἐρέττω (eréttō), which means "rower", and πτερόν (pterón), which means "wing", and therefore, "rower wing".

Stylonurus is a genus of prehistoric eurypterid of the family Stylonuridae. The genus contains three species: Stylonurus powriensis from the Devonian of Scotland, Stylonurus shaffneri from the Devonian of Pennsylvania and Stylonurus perspicillum from the Devonian of Germany.

Ruedemannipterus is a genus of prehistoric eurypterid classified as part of the family Dolichopteridae. The genus contains one species, R. stylonuroides, known from the Silurian of New York.

Rhenopterus is an extinct prehistoric eurypterid. Fossils of Rhenopterus have been recovered from deposits of Lower Devonian age in Germany.

Parahughmilleria is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of Parahughmilleria have been discovered in deposits of the Devonian and Silurian age in the United States, Canada, Russia, Germany, Luxembourg and Great Britain, and have been referred to several different species. The first fossils of Parahughmilleria, discovered in the Shawangunk Mountains in 1907, were initially assigned to Eurypterus. It would not be until 54 years later when Parahughmilleria would be described.

Mycterops is a genus of prehistoric eurypterid of the family Mycteroptidae. Mycterops lived during the Carboniferous period in Europe and North America.

The Rhenopteridae are a family of eurypterids, an extinct group of chelicerate arthropods commonly known as "sea scorpions". The family is the only family currently contained in the superfamily Rhenopteroidea, one of four superfamilies classified as part of the suborder Stylonurina.
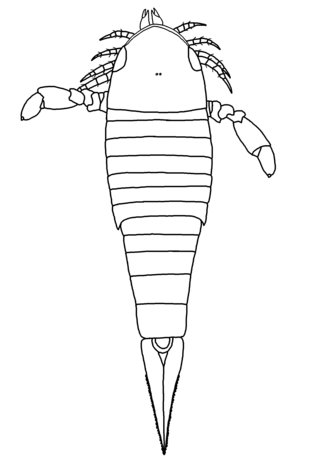
Herefordopterus is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Herefordopterus is classified as part of the family Hughmilleriidae, a basal family in the highly derived Pterygotioidea superfamily of eurypterids. Fossils of the single and type species, H. banksii, have been discovered in deposits of Silurian age in Herefordshire and Shropshire, England. The genus is named after Herefordshire, where most of the Herefordopterus fossils have been found. The specific epithet honors Richard Banks, who found several well-preserved specimens, including the first Herefordopterus fossils.

Eysyslopterus is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Eysyslopterus is classified as part of the family Adelophthalmidae, the only clade within the derived ("advanced") Adelophthalmoidea superfamily of eurypterids. One fossil of the single and type species, E. patteni, has been discovered in deposits of the Late Silurian period in Saaremaa, Estonia. The genus is named after Eysysla, the Viking name for Saaremaa, and opterus, a traditional suffix for the eurypterid genera, meaning "wing". The species name honors William Patten, an American biologist and zoologist who discovered the only known fossil of Eysyslopterus.


















