Related Research Articles

CD30, also known as TNFRSF8, is a cell membrane protein of the tumor necrosis factor receptor family and tumor marker.

Cluster of differentiation 40, CD40 is a costimulatory protein found on antigen-presenting cells and is required for their activation. The binding of CD154 (CD40L) on TH cells to CD40 activates antigen presenting cells and induces a variety of downstream effects.
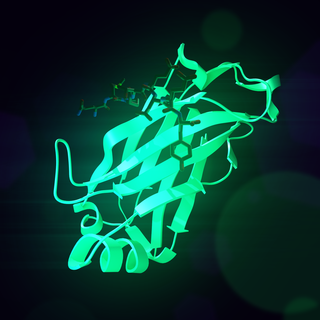
Receptor activator of nuclear factor κ B (RANK), also known as TRANCE receptor or TNFRSF11A, is a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNFR) molecular sub-family. RANK is the receptor for RANK-Ligand (RANKL) and part of the RANK/RANKL/OPG signaling pathway that regulates osteoclast differentiation and activation. It is associated with bone remodeling and repair, immune cell function, lymph node development, thermal regulation, and mammary gland development. Osteoprotegerin (OPG) is a decoy receptor for RANKL, and regulates the stimulation of the RANK signaling pathway by competing for RANKL. The cytoplasmic domain of RANK binds TRAFs 1, 2, 3, 5, and 6 which transmit signals to downstream targets such as NF-κB and JNK.

Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 4 (TNFRSF4), also known as CD134 and OX40 receptor, is a member of the TNFR-superfamily of receptors which is not constitutively expressed on resting naïve T cells, unlike CD28. OX40 is a secondary co-stimulatory immune checkpoint molecule, expressed after 24 to 72 hours following activation; its ligand, OX40L, is also not expressed on resting antigen presenting cells, but is following their activation. Expression of OX40 is dependent on full activation of the T cell; without CD28, expression of OX40 is delayed and of fourfold lower levels.

CD137 is a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor family. Its alternative names are tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 9 (TNFRSF9), 4-1BB and induced by lymphocyte activation (ILA). It is of interest to immunologists as a co-stimulatory immune checkpoint molecule.

TRAF6 is a TRAF human protein.

TNF receptor-associated factor 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRAF2 gene.
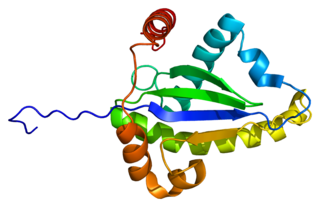
Tumor necrosis factor receptor type 1-associated DEATH domain protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRADD gene.

Lymphotoxin beta receptor (LTBR), also known as tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 3 (TNFRSF3), is a cell surface receptor for lymphotoxin involved in apoptosis and cytokine release. It is a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily.

CD27 is a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily. It is currently of interest to immunologists as a co-stimulatory immune checkpoint molecule.

Tumor necrosis factor receptor 1 (TNFR1), also known as tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 1A (TNFRSF1A) and CD120a, is a ubiquitous membrane receptor that binds tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFα).

TNF receptor-associated factor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRAF1 gene.

TNF receptor-associated factor 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRAF5 gene.

TNF receptor-associated factor (TRAF3) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRAF3 gene.

LIGHT, also known as tumor necrosis factor superfamily member 14 (TNFSF14), is a secreted protein of the TNF superfamily. It is recognized by herpesvirus entry mediator (HVEM), as well as decoy receptor 3.

Herpesvirus entry mediator (HVEM), also known as tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 14 (TNFRSF14), is a human cell surface receptor of the TNF-receptor superfamily.
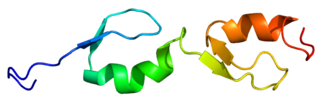
TNF receptor-associated factor 4 (TRAF4) also known as RING finger protein 83 (RNF83) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRAF4 gene.
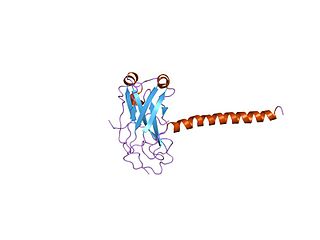
TRAF family member-associated NF-kappa-B activator is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TANK gene.

Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 19, also known as TNFRSF19 and TROY is a human gene.

Tumor necrosis factor receptor 2 (TNFR2), also known as tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 1B (TNFRSF1B) and CD120b, is a membrane receptor that binds tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFα).
References
- ↑ Inoue J, Ishida T, Tsukamoto N, Kobayashi N, Naito A, Azuma S, Yamamoto T (January 2000). "Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF) family: adapter proteins that mediate cytokine signaling". Exp. Cell Res. 254 (1): 14–24. doi:10.1006/excr.1999.4733. PMID 10623461.