A tax is a mandatory financial charge or levy imposed on a taxpayer by a governmental organization to support government spending and public expenditures collectively or to regulate and reduce negative externalities. Tax compliance refers to policy actions and individual behavior aimed at ensuring that taxpayers are paying the right amount of tax at the right time and securing the correct tax allowances and tax relief. The first known taxation occurred in Ancient Egypt around 3000–2800 BC. Taxes consist of direct or indirect taxes and may be paid in money or as labor equivalent.
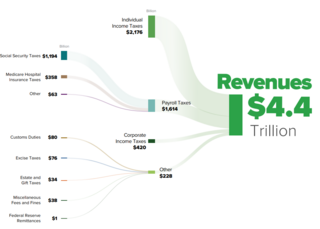
The United States has separate federal, state, and local governments with taxes imposed at each of these levels. Taxes are levied on income, payroll, property, sales, capital gains, dividends, imports, estates and gifts, as well as various fees. In 2020, taxes collected by federal, state, and local governments amounted to 25.5% of GDP, below the OECD average of 33.5% of GDP.
Tax noncompliance is a range of activities that are unfavorable to a government's tax system. This may include tax avoidance, which is tax reduction by legal means, and tax evasion which is the illegal non-payment of tax liabilities. The use of the term "noncompliance" is used differently by different authors. Its most general use describes non-compliant behaviors with respect to different institutional rules resulting in what Edgar L. Feige calls unobserved economies. Non-compliance with fiscal rules of taxation gives rise to unreported income and a tax gap that Feige estimates to be in the neighborhood of $500 billion annually for the United States.
Tax avoidance is the legal usage of the tax regime in a single territory to one's own advantage to reduce the amount of tax that is payable by means that are within the law. A tax shelter is one type of tax avoidance, and tax havens are jurisdictions that facilitate reduced taxes. Tax avoidance should not be confused with tax evasion, which is illegal. Both tax evasion and tax avoidance can be viewed as forms of tax noncompliance, as they describe a range of activities that intend to subvert a state's tax system.
Tax evasion or tax fraud is an illegal attempt to defeat the imposition of taxes by individuals, corporations, trusts, and others. Tax evasion often entails the deliberate misrepresentation of the taxpayer's affairs to the tax authorities to reduce the taxpayer's tax liability, and it includes dishonest tax reporting, declaring less income, profits or gains than the amounts actually earned, overstating deductions, bribing authorities and hiding money in secret locations.
A Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) is an identifying number used for tax purposes in the United States and in other countries under the Common Reporting Standard. In the United States it is also known as a Tax Identification Number (TIN) or Federal Taxpayer Identification Number (FTIN). A TIN may be assigned by the Social Security Administration (SSA) or by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS).

The United States federal government and most state governments impose an income tax. They are determined by applying a tax rate, which may increase as income increases, to taxable income, which is the total income less allowable deductions. Income is broadly defined. Individuals and corporations are directly taxable, and estates and trusts may be taxable on undistributed income. Partnerships are not taxed, but their partners are taxed on their shares of partnership income. Residents and citizens are taxed on worldwide income, while nonresidents are taxed only on income within the jurisdiction. Several types of credits reduce tax, and some types of credits may exceed tax before credits. Most business expenses are deductible. Individuals may deduct certain personal expenses, including home mortgage interest, state taxes, contributions to charity, and some other items. Some deductions are subject to limits, and an Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) applies at the federal and some state levels.
Gregory v. Helvering, 293 U.S. 465 (1935), was a landmark decision by the United States Supreme Court concerned with U.S. income tax law. The case is cited as part of the basis for two legal doctrines: the business purpose doctrine and the doctrine of substance over form. The business purpose doctrine is essentially that if a transaction has no substantial business purpose other than the avoidance or reduction of Federal tax, the tax law will not regard the transaction. The doctrine of substance over form is essentially that for Federal tax purposes, a taxpayer is bound by the economic substance of a transaction if the economic substance varies from its legal form.
A self-directed individual retirement account is an individual retirement account (IRA) which allows alternative investments for retirement savings. Some examples of these alternative investments are real estate, private mortgages, private company stock, oil and gas limited partnerships, precious metals, digital assets, horses and livestock, and intellectual property. The increased investment options available in self-directed IRAs prompted the SEC to issue a public notice in 2011 due an increased risk of fraud in alternative assets.
Cottage Savings Association v. Commissioner, 499 U.S. 554 (1991), was an income tax case before the Supreme Court of the United States.
Taxes in India are levied by the Central Government and the State Governments by virtue of powers conferred to them from the Constitution of India. Some minor taxes are also levied by the local authorities such as the Municipality.

Corporate tax is imposed in the United States at the federal, most state, and some local levels on the income of entities treated for tax purposes as corporations. Since January 1, 2018, the nominal federal corporate tax rate in the United States of America is a flat 21% following the passage of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017. State and local taxes and rules vary by jurisdiction, though many are based on federal concepts and definitions. Taxable income may differ from book income both as to timing of income and tax deductions and as to what is taxable. The corporate Alternative Minimum Tax was also eliminated by the 2017 reform, but some states have alternative taxes. Like individuals, corporations must file tax returns every year. They must make quarterly estimated tax payments. Groups of corporations controlled by the same owners may file a consolidated return.
In the United States, individuals and corporations pay a tax on the net total of all their capital gains. The tax rate depends on both the investor's tax bracket and the amount of time the investment was held. Short-term capital gains are taxed at the investor's ordinary income tax rate and are defined as investments held for a year or less before being sold. Long-term capital gains, on dispositions of assets held for more than one year, are taxed at a lower rate.
Taxation in the British Virgin Islands is relatively simple by comparative standards; photocopies of all of the tax laws of the British Virgin Islands (BVI) would together amount to about 200 pages of paper.
A like-kind exchange under United States tax law, also known as a 1031 exchange, is a transaction or series of transactions that allows for the disposal of an asset and the acquisition of another replacement asset without generating a current tax liability from the sale of the first asset. A like-kind exchange can involve the exchange of one business for another business, one real estate investment property for another real estate investment property, livestock for qualifying livestock, and exchanges of other qualifying assets. Like-kind exchanges have been characterized as tax breaks or "tax loopholes".
The assignment of income doctrine is a judicial doctrine developed in United States case law by courts trying to limit tax evasion. The assignment of income doctrine seeks to "preserve the progressive rate structure of the Code by prohibiting the splitting of income among taxable entities."
Economic substance is a doctrine in the tax law of the United States under which a transaction must have both a substantial purpose aside from reduction of tax liability and an economic effect aside from the tax effect in order to qualify for any tax benefits. This doctrine is used by the Internal Revenue Service to determine whether tax shelters, or strategies used to reduce tax liability, are considered "abusive". Under the doctrine, for a transaction to be respected, the transaction must change the taxpayer's economic position in a "meaningful way" apart from the Federal income tax effects, and the taxpayer must have had a "substantial purpose" for entering into the transaction, apart from the Federal income tax effects.
For United States income tax purposes, a business entity may elect to be treated either as a corporation or as other than a corporation. This entity classification election is made by filing Internal Revenue Service Form 8832. Absent filing the form, a default classification applies. U.S. corporations of the type that can be publicly traded must be treated as corporations. There is a list of specific foreign entities that must be treated as corporations. The election is effective for Federal income tax purposes.

Taxation may involve payments to a minimum of two different levels of government: central government through SARS or to local government. Prior to 2001 the South African tax system was "source-based", where in income is taxed in the country where it originates. Since January 2001, the tax system was changed to "residence-based" wherein taxpayers residing in South Africa are taxed on their income irrespective of its source. Non residents are only subject to domestic taxes.
Taxation in Gibraltar is determined by the law of Gibraltar which is based on English law, but is separate from the UK legal system. Companies and non residents do not pay income tax unless the source of this income is or is deemed to be Gibraltar. Individuals pay tax on a worldwide basis on income from employment or self employment if they are ordinarily resident in Gibraltar. There is no tax on capital income.




