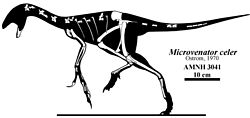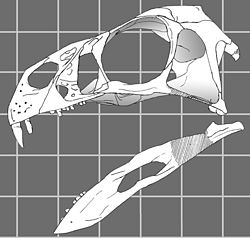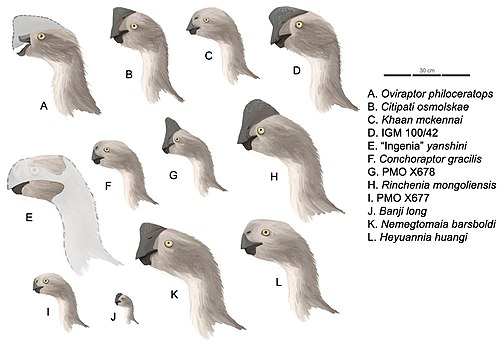
This timeline of oviraptorosaur research is a chronological listing of events in the history of paleontology focused on the oviraptorosaurs, a group of beaked, bird-like theropod dinosaurs. The early history of oviraptorosaur paleontology is characterized by taxonomic confusion due to the unusual characteristics of these dinosaurs. When initially described in 1924 Oviraptor itself was thought to be a member of the Ornithomimidae, popularly known as the "ostrich" dinosaurs, because both taxa share toothless beaks. [1] Early caenagnathid oviraptorosaur discoveries like Caenagnathus itself were also incorrectly classified at the time, having been misidentified as birds. [1]
Contents
- 20th century
- 1920s
- 1930s
- 1940s
- 1950s
- 1960s
- 1970s
- 1980s
- 1990s
- 21st century
- 2000s
- 2010s
- See also
- Footnotes
- References
- External links
The hypothesis that caenagnathids were birds was questioned as early as 1956 by Romer, but not corrected until Osmolska formally reclassified them as non-avian dinosaurs in 1976. Meanwhile, the classification of Oviraptor as an ornithomimid persisted unquestioned by researchers like Romer and Steel until the early 1970s when Dale Russell argued against the idea in 1972. In 1976 when Osmolska recognized Oviraptor's relationship with the Caenagnathids, she also recognized that it was not an ornithomimid and reclassified it as a member of the former family. [1] However, that same year Rinchen Barsbold argued that Oviraptor belonged to a distinct family he named the Oviraptoridae [1] and he also formally named the Oviraptorosauria later in the same year. [2]
Like their classification, the paleobiology of oviraptorosaurs has been subject to controversy and reinterpretation. The first scientifically documented Oviraptor skeleton was found lying on a nest of eggs. Because its powerful parrot-like beak appeared well-adapted to crushing hard food items and the eggs were thought to belonged to the neoceratopsian Protoceratops , oviraptorosaurs were thought to be nest-raiders that preyed on the eggs of other dinosaurs. In the 1980s, Barsbold proposed that oviraptorosaurs used their beaks to crack mollusk shells as well. In 1993, Currie and colleagues hypothesized that small vertebrate prey may have also been part of the oviraptorosaur diet. Not long after, fossil embryonic remains cast doubt on the popular reconstruction of oviraptorosaurs as egg thieves when it was discovered that the "Protoceratops" eggs that Oviraptor was thought to be "stealing" actually belonged to Oviraptor itself. The discovery of additional Oviraptor preserved on top of nests in lifelike brooding posture firmly established that oviraptorosaurs had been "framed" as egg thieves and were actually caring parents incubating their own nests. [3]