Related Research Articles
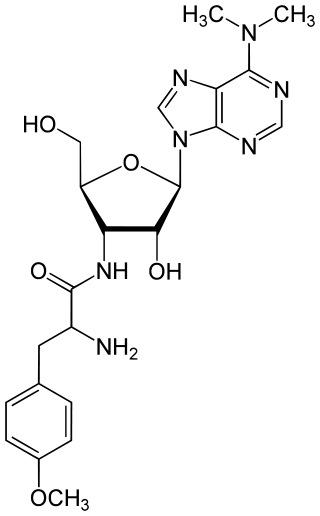
Puromycin is an antibiotic protein synthesis inhibitor which causes premature chain termination during translation.

Membrane alanyl aminopeptidase also known as alanyl aminopeptidase (AAP) or aminopeptidase N (AP-N) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ANPEP gene.
An exopeptidase is any peptidase that catalyzes the cleavage of the terminal peptide bond; the process releases a single amino acid, dipeptide or a tripeptide from the peptide chain. Depending on whether the amino acid is released from the amino or the carboxy terminal, an exopeptidase is further classified as an aminopeptidase or a carboxypeptidase, respectively. Thus, an aminopeptidase, an enzyme in the brush border of the small intestine, will cleave a single amino acid from the amino terminal, whereas carboxypeptidase, which is a digestive enzyme present in pancreatic juice, will cleave a single amino acid from the carboxylic end of the peptide.
Aminopeptidases are enzymes that catalyze the cleavage of amino acids from the amino terminus (N-terminus) of proteins or peptides (exopeptidases). They are widely distributed throughout the animal and plant kingdoms and are found in many subcellular organelles, in cytosol, and as membrane components. Aminopeptidases are used in essential cellular functions. Many, but not all, of these peptidases are zinc metalloenzymes.
Cytosol alanyl aminopeptidase is an enzyme.
Glutamyl aminopeptidase (EC 3.4.11.7, aminopeptidase A, aspartate aminopeptidase, angiotensinase A, glutamyl peptidase, Ca2+-activated glutamate aminopeptidase, membrane aminopeptidase II, antigen BP-1/6C3 of mouse B lymphocytes, L-aspartate aminopeptidase, angiotensinase A2) is an enzyme encoded by the ENPEP gene. Glutamyl aminopeptidase has also recently been designated CD249 (cluster of differentiation 249).

Leucyl aminopeptidases are enzymes that preferentially catalyze the hydrolysis of leucine residues at the N-terminus of peptides and proteins. Other N-terminal residues can also be cleaved, however. LAPs have been found across superkingdoms. Identified LAPs include human LAP, bovine lens LAP, porcine LAP, Escherichia coli LAP, and the solanaceous-specific acidic LAP (LAP-A) in tomato.

Aminopeptidase B is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RNPEP gene.

Dipeptidyl peptidase I is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Dipeptidyl-peptidase III is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Prolyl aminopeptidase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Aminopeptidase B is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Xaa-Pro aminopeptidase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
PepB aminopeptidase is an enzyme which catalyses the following chemical reaction:
Aminopeptidase S is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Dipeptidyl-peptidase II is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction:
Xaa-Xaa-Pro tripeptidyl-peptidase is an enzyme. It catalyses the following chemical reaction
Pyroglutamyl-peptidase I (EC 3.4.19.3, also known as Pyrrolidonyl peptidase, is an enzyme found in bacteria, plants and animals.
Pyroglutamyl-peptidase II is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
N-formylmethionyl-peptidase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
References
- ↑ Doumeng C, Maroux S (March 1979). "Aminotripeptidase, a cytosol enzyme from rabbit intestinal mucosa". The Biochemical Journal. 177 (3): 801–8. doi:10.1042/bj1770801. PMC 1186443 . PMID 109082.
- ↑ Sachs L, Marks N (September 1982). "A highly specific aminotripeptidase of rat brain cytosol. Substrate specificity and effects of inhibitors". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 706 (2): 229–38. doi:10.1016/0167-4838(82)90491-5. PMID 7126601.