
Burkittsville is a historic village in Frederick County, Maryland, United States. The village lies in the southern Middletown Valley along the eastern base of South Mountain.

Boonsboro is a town in Washington County, Maryland, United States, located at the foot of South Mountain. It nearly borders Frederick County and is proximate to the Antietam National Battlefield. The population was 3,336 at the 2010 census.

Sharpsburg is a town in Washington County, Maryland. The town is approximately 13 miles (21 km) south of Hagerstown. Its population was 705 at the 2010 census.

The Battle of South Mountain—known in several early Southern accounts as the Battle of Boonsboro Gap—was fought on September 14, 1862, as part of the Maryland campaign of the American Civil War. Three pitched battles were fought for possession of three South Mountain passes: Crampton's, Turner's, and Fox's Gaps. Maj. Gen. George B. McClellan, commanding the Union Army of the Potomac, needed to pass through these gaps in his pursuit of Confederate General Robert E. Lee's precariously divided Army of Northern Virginia. Although the delay bought at South Mountain would allow him to reunite his army and forestall defeat in detail, Lee considered termination of the Maryland Campaign at nightfall.

The Wilderness Road was one of two principal routes used by colonial and early national era settlers to reach Kentucky from the East. Although this road goes through the Cumberland Gap into southern Kentucky and northern Tennessee, the other is sometimes called the "Cumberland Road" because it started in Fort Cumberland in Maryland. Despite Kentucky Senator Henry Clay's advocacy of this route, early in the 19th century, the northern route was selected for the National Road, connecting near Washington, Pennsylvania into the Ohio Valley of northern Kentucky and Ohio.

The Cumberland Gap is a pass in the eastern United States through the long ridge of the Cumberland Mountains, within the Appalachian Mountains and near the tripoint of Kentucky, Virginia, and Tennessee. At an elevation of 1,631 feet (497 m) above sea level, it is famous in American colonial history for its role as a key passageway through the lower central Appalachians.

Washington Monument State Park is a public recreation area located approximately one mile (1.6 km) southeast of Boonsboro, Maryland. The park preserves the Washington Monument, a 40-foot-tall (12 m) tower honoring George Washington, the first President of the United States. The monument sits along the Appalachian Trail near the summit of South Mountain's Monument Knob. It was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1972. The park is managed by the Maryland Department of Natural Resources.

Pisgah National Forest is a National Forest in the Appalachian Mountains of western North Carolina. It is administered by the United States Forest Service, part of the United States Department of Agriculture. The Pisgah National Forest is completely contained within the state of North Carolina. The forest is managed together with the other three North Carolina National Forests from common headquarters in Asheville, North Carolina. There are local ranger district offices located in Pisgah Forest, Mars Hill, and Nebo.

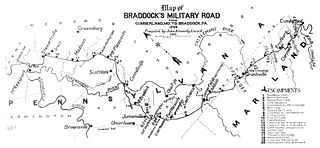
The Braddock Road was a military road built in 1755 in what was then British America and is now the United States. It was the first improved road to cross the barrier of the successive ridgelines of the Appalachian Mountains. It was constructed by troops of Virginia militia and British regulars commanded by General Edward Braddock of the Coldstream Guards, part of an expedition to conquer the Ohio Country from the French at the beginning of the French and Indian War, the North American portion of the Seven Years' War. George Washington was an aide-de-camp to General Braddock who accompanied the expedition. The expedition gave him his first field military experience along with other American military officers. A number of these men would profit from this experience during the Revolutionary War.

Cowans Gap State Park is a 1,085-acre (439 ha) Pennsylvania state park in Todd Township, Fulton County and Metal Township, Franklin County, Pennsylvania in the United States. The park is largely surrounded by Buchanan State Forest in Allens Valley just off Pennsylvania Route 75 near Fort Loudon.

South Mountain is the northern extension of the Blue Ridge Mountain range in Maryland and Pennsylvania. From the Potomac River near Knoxville, Maryland in the south to Dillsburg, Pennsylvania in York County, Pennsylvania in the north, the 70-mile-long (110 km) range separates the Hagerstown and Cumberland valleys from the Piedmont regions of the two states.

The Great Indian Warpath (GIW)—also known as the Great Indian War and Trading Path, or the Seneca Trail—was that part of the network of trails in eastern North America developed and used by Native Americans which ran through the Great Appalachian Valley. The system of footpaths extended from what is now upper New York to deep within Alabama. Various Native peoples traded and made war along the trails, including the Catawba, numerous Algonquian tribes, the Cherokee, and the Iroquois Confederacy. The British traders' name for the route was derived from combining its name among the northeastern Algonquian tribes, Mishimayagat or "Great Trail", with that of the Shawnee and Delaware, Athawominee or "Path where they go armed".

Fort Valley is a mountain valley located primarily in Shenandoah County, Virginia. It is often called "valley within a valley" as it lies between the two arms of the northern part of the Blue Ridge mountain range in the Shenandoah Valley in the Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians geological zone.
Nemacolin's Trail, or less often Nemacolin's Path, was an ancient Native American trail that crossed the great barrier of the Allegheny Mountains via the Cumberland Narrows Mountain pass, connecting the watersheds of the Potomac River and the Monongahela River in the present-day United States of America. Nemacolin's Trail connected what are now Cumberland, Maryland and Brownsville, Pennsylvania.
Colonel Thomas Cresap (c.1702—c.1790) was an English-born settler and trader in the states of Maryland and Pennsylvania. Cresap served Lord Baltimore as an agent in the Maryland–Pennsylvania boundary dispute that became known as Cresap's War. Later, together with the Native American chief Nemacolin, Cresap improved a Native American path to the Ohio Valley, and ultimately settled and became a large landowner near Cumberland, Maryland, where he was involved in further disputes near Brownsville, Pennsylvania, including in the French and Indian War and Lord Dunmore's War.

Lambs Knoll is a peak of South Mountain on the border of Washington County and Frederick County in the state of Maryland. The 1,758 feet (536 m) peak is the second tallest on South Mountain in Maryland behind Quirauk Mountain.

Fox's Gap, also known as Fox Gap, is a wind gap in the South Mountain Range of the Blue Ridge Mountains, located in Frederick County and Washington County, Maryland. The gap is traversed by Reno Monument Road. The Appalachian Trail also crosses the gap along the ridgeline.
Park Hall is an unincorporated community in Washington County, Maryland, United States. Park Hall is located 3.5 miles (5.6 km) southeast of Keedysville.

U.S. Route 40 Alternate (US 40 Alternate) is an alternate route of US 40 in the U.S. state of Maryland. The highway runs 22.97 miles (36.97 km) from Potomac Street in Hagerstown east to US 40 in Frederick. US 40 Alternate parallels US 40 and much of Interstate 70 (I-70) to the south through eastern Washington County and western Frederick County. The alternate route connects Hagerstown and Frederick with Funkstown, Boonsboro, Middletown, and Braddock Heights. US 40 Alternate crosses two major north–south components of the Blue Ridge Mountains that separate the Great Appalachian Valley and the Piedmont: South Mountain between Boonsboro and Middletown and Catoctin Mountain, which is locally known as Braddock Mountain, at Braddock Heights.
Johns Creek Mountain, a wildland in the George Washington and Jefferson National Forests of western Virginia, has been recognized by the Wilderness Society as a special place worthy of protection from logging and road construction. The Wilderness Society has designated the area as a "Mountain Treasure".


















