Related Research Articles

Proteolysis is the breakdown of proteins into smaller polypeptides or amino acids. Uncatalysed, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds is extremely slow, taking hundreds of years. Proteolysis is typically catalysed by cellular enzymes called proteases, but may also occur by intra-molecular digestion.

Ubiquitin is a small regulatory protein found in most tissues of eukaryotic organisms, i.e., it is found ubiquitously. It was discovered in 1975 by Gideon Goldstein and further characterized throughout the late 1970s and 1980s. Four genes in the human genome code for ubiquitin: UBB, UBC, UBA52 and RPS27A.

Ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase L1 is a deubiquitinating enzyme.

Irwin Allan Rose was an American biologist. Along with Aaron Ciechanover and Avram Hershko, he was awarded the 2004 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for the discovery of ubiquitin-mediated protein degradation.

Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs), also known as deubiquitinating peptidases, deubiquitinating isopeptidases, deubiquitinases, ubiquitin proteases, ubiquitin hydrolases, ubiquitin isopeptidases, are a large group of proteases that cleave ubiquitin from proteins. Ubiquitin is attached to proteins in order to regulate the degradation of proteins via the proteasome and lysosome; coordinate the cellular localisation of proteins; activate and inactivate proteins; and modulate protein-protein interactions. DUBs can reverse these effects by cleaving the peptide or isopeptide bond between ubiquitin and its substrate protein. In humans there are nearly 100 DUB genes, which can be classified into two main classes: cysteine proteases and metalloproteases. The cysteine proteases comprise ubiquitin-specific proteases (USPs), ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolases (UCHs), Machado-Josephin domain proteases (MJDs) and ovarian tumour proteases (OTU). The metalloprotease group contains only the Jab1/Mov34/Mpr1 Pad1 N-terminal+ (MPN+) (JAMM) domain proteases.
An esterase is a hydrolase enzyme that splits esters into an acid and an alcohol in a chemical reaction with water called hydrolysis.

SUMO-conjugating enzyme UBC9 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the UBE2I gene. It is also sometimes referred to as "ubiquitin conjugating enzyme E2I" or "ubiquitin carrier protein 9", even though these names do not accurately describe its function.

Ubiquitin specific peptidase 5 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the USP5 gene.

Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 G1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UBE2G1 gene.
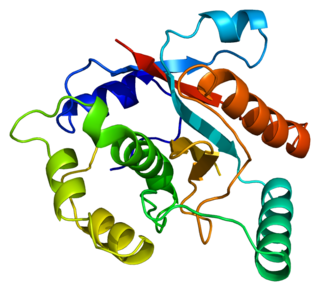
Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase isozyme L3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the UCHL3 gene.

BRCA1 associated protein-1 is a deubiquitinating enzyme that in humans is encoded by the BAP1 gene. BAP1 encodes an 80.4 kDa nuclear-localizing protein with a ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase (UCH) domain that gives BAP1 its deubiquitinase activity. Recent studies have shown that BAP1 and its fruit fly homolog, Calypso, are members of the polycomb-group proteins (PcG) of highly conserved transcriptional repressors required for long-term silencing of genes that regulate cell fate determination, stem cell pluripotency, and other developmental processes.

Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 48 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the USP48 gene.

Ubiquitin-specific protease 14 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the USP14 gene.

Sentrin-specific protease 8 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SENP8 gene.

Chromosome 9 open reading frame 3 (C9ORF3) also known as aminopeptidase O (APO) is an enzyme which in humans is encoded by the C9ORF3 gene. The protein encoded by this gene is an aminopeptidase which is most closely related in sequence to leukotriene A4 hydrolase (LTA4H). APO is a member of the M1 metalloproteinase family.
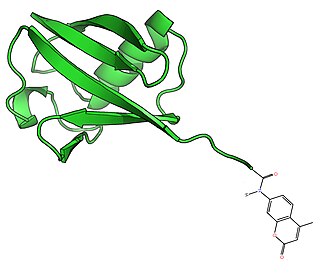
Ubiquitin-AMC is a fluorogenic substrate for a wide range of deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs), including ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolases (UCHs) and ubiquitin specific proteases (USPs). It is a particularly useful reagent for the study of deubiquitinating activity where detection sensitivity or continuous monitoring of activity is essential.
Lysine carboxypeptidase is an enzyme. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction:
Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase may refer to:
An isopeptidase is a protease enzyme that hydrolyzes isopeptide bonds, or amide bonds that occur outside the main chain in a polypeptide chain.

The ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 27, also known as deubiquitinating enzyme 27, ubiquitin thioesterase 27 and USP27X, is a deubiquitinating enzyme which is mainly characterized for cleaving ubiquitin (Ub) from proteins and other molecules. Ubiquitin binds to proteins so as to regulate the degradation of them via the proteasome and lysosome among many other functions.
References
- ↑ Johnston SC, Larsen CN, Cook WJ, Wilkinson KD, Hill CP (July 1997). "Crystal structure of a deubiquitinating enzyme (human UCH-L3) at 1.8 A resolution". The EMBO Journal. 16 (13): 3787–96. doi:10.1093/emboj/16.13.3787. PMC 1170002 . PMID 9233788.
- ↑ Wilkinson, K.D.; Rawlings, N.D.; Woessner, J.F. (1998). "Ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase". In Barrett, A.J. (ed.). Handbook of Proteolytic Enzymes. London: Academic Press. pp. 470–472.