
A samosa is a fried South Asian pastry with a savoury filling, including ingredients such as spiced potatoes, onions, peas, meat or fish. It may take different forms, including triangular, cone, or half-moon shapes, depending on the region. Samosas are often accompanied by chutney, and have origins in medieval times or earlier. Sweet versions are also made. Samosas are a popular entrée, appetizer, or snack in the cuisines of South Asia, the Middle East, Central Asia, East Africa and their South Asian diasporas.

Russian cuisine is a collection of the different dishes and cooking traditions of the Russian people as well as a list of culinary products popular in Russia, with most names being known since pre-Soviet times, coming from all kinds of social circles.
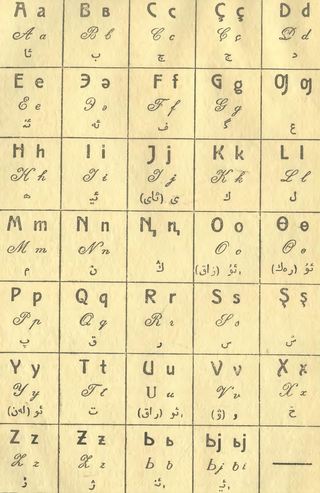
Jaꞑalif, Yangalif or Yañalif is the first Latin alphabet used during the latinisation in the Soviet Union in the 1930s for the Turkic languages. It replaced the Yaña imlâ Arabic script-based alphabet in 1928, and was replaced by the Cyrillic alphabet in 1938–1940. After their respective independence in 1991, several former Soviet states in Central Asia switched back to Latin script, with slight modifications to the original Jaꞑalif.

Jewish cuisine refers to the worldwide cooking traditions of the Jewish people. During its evolution over the course of many centuries, it has been shaped by Jewish dietary laws (kashrut), Jewish festivals and holidays, and traditions centred around Shabbat. Jewish cuisine is influenced by the economics, agriculture, and culinary traditions of the many countries where Jewish communities have settled and varies widely throughout the entire world.

Pennsylvania Dutch cuisine is the typical and traditional fare of the Pennsylvania Dutch. According to one writer, "If you had to make a short list of regions in the United States where regional food is actually consumed on a daily basis, the land of the Pennsylvania Dutch—in and around Lancaster County, Pennsylvania—would be at or near the top of that list," mainly because the area is a cultural enclave of Pennsylvania Dutch culture.

Kalduny or kolduny are potato pancakes with meat or, nowadays much less often, pelmeni made in Belarusian, Lithuanian, and Polish cuisines, akin to the Polish pierogi, Russian pelmeni and the Ukrainian varenyky.

Traditional Kazakh cuisine is the traditional food of the Kazakh people. It is focused on mutton and horse meat, as well as various milk products. For hundreds of years, Kazakhs were herders who raised fat-tailed sheep, Bactrian camels, and horses, relying on these animals for transportation, clothing, and food. The cooking techniques and major ingredients have been strongly influenced by the nation's nomadic way of life. For example, most cooking techniques are aimed at long-term preservation of food. There is a large practice of salting and drying meat so that it will last, and there is a preference for sour milk, as it is easier to save in a nomadic lifestyle.

Soviet cuisine, the common cuisine of the Soviet Union, was formed by the integration of the various national cuisines of the Soviet Union, in the course of the formation of the Soviet people. It is characterized by a limited number of ingredients and simplified cooking. This type of cuisine was prevalent in canteens everywhere in the Soviet Union. It became an integral part of household cuisine and was used in parallel with national dishes, particularly in large cities. Generally, Soviet cuisine was shaped by Soviet eating habits and a very limited availability of ingredients in most parts of the USSR. Most dishes were simplifications of French, Russian, Austro-Hungarian cuisines, and cuisines from other Eastern Bloc nations. Caucasian cuisines, particularly Georgian cuisine, contributed as well. Canteens run by the government were called stolovaya.

Tatar cuisine is primarily the cuisine of the Volga Tatars, who live in Tatarstan, Russia, and surrounding areas.

Yemeni cuisine is distinct from the wider Middle Eastern cuisines, but with a degree of regional variation. Although some foreign influences are evident in some regions of the country, the Yemeni kitchen is based on similar foundations across the country.

Uzbek cuisine shares the culinary traditions of peoples across Central Asia. There is a great deal of grain farming in Uzbekistan, so breads and noodles are of importance, and Uzbek cuisine has been characterized as "noodle-rich". Mutton is a popular variety of meat due to the abundance of sheep in the country and it is a part of various Uzbek dishes.
Azerbaijani cuisine refers to the cooking styles and dishes of the Republic of Azerbaijan. The cuisine developed significantly due to its diversity of agriculture, from abundant grasslands which historically allowed for a culture of pastoralism to develop, as well as to the unique geographical location of Azerbaijan, which is situated on the crossroads of Europe and Asia with an access to the Caspian Sea. The location has enabled the people to develop a varied diet rich in produce, milk products, and meat, including beef, mutton, fish and game. The location, which was contended over by many historical kingdoms, khanates, and empires, also meant that Azerbaijani cuisine was influenced by the culinary traditions of multiple different cultures, such as Turkic, Iranian, and Eastern European.

Tajik cuisine is a traditional cuisine of Tajikistan, and has much in common with Russian, Afghan, Iranian and Uzbek cuisines. Plov (pilaf), also called osh, is the national dish in Tajikistan, as in other countries in the region. Green tea is the national drink.

Chicken and dumplings is a soup that consists of a chicken cooked in water, with the resulting chicken broth being used to cook the dumplings by boiling. A dumpling—in this context—is a biscuit dough, which is a mixture of flour, shortening, and liquid. The dumplings are either rolled out flat, dropped, or formed into a ball.

Speķrauši or speķa pīrādziņi, sometimes also colloquially known simply as pīrāgi or pīrādziņi, are Latvian oblong or crescent-shaped baked bread rolls or pastries filled with finely chopped fatty bacon cubes and onions. They range from five to thirteen centimetres in length, depending on if they are intended as a snack or a more substantial meal. Smaller speķrauši are often prized for their daintiness and are considered the work of a skilled cook.

Mordovian cuisine is the traditional cuisine of the Mordovians, who now live in Mordovia and surrounding areas. It consists of a variety of dishes, based on geographical, cultural and climate features of the region, with fish traditionally featured heavily.

Peremech is an individual-sized fried dough pastry common for Volga Tatar and Bashkir cuisines. It is made from unleavened or leavened dough and usually filled with ground meat and chopped onion. Originally, finely chopped pre-cooked meat was used as a filling, but later raw ground meat became more common. Alternatively, peremech can be filled with potato or quark.

Ashkenazi Jewish cuisine is an assortment of cooking traditions that was developed by the Ashkenazi Jews of Central, Eastern and Northern Europe, and their descendants, particularly in the United States and other Western countries.
















