
N,N-Dimethyltryptamine is a substituted tryptamine that occurs in many plants and animals, including humans, and which is both a derivative and a structural analog of tryptamine. DMT is used as a psychedelic drug and prepared by various cultures for ritual purposes as an entheogen.

A serotonin receptor agonist is an agonist of one or more serotonin receptors. They activate serotonin receptors in a manner similar to that of serotonin, a neurotransmitter and hormone and the endogenous ligand of the serotonin receptors.

5,N,N-trimethyltryptamine is a tryptamine derivative that is a psychedelic drug. It was first made in 1958 by Edwin H. P. Young. In animal experiments it was found to be in between DMT and 5-MeO-DMT in potency which would suggest an active dosage for humans in the 20–60 mg range. Human psychoactivity for this compound has been claimed in reports on websites such as Erowid but has not been independently confirmed.
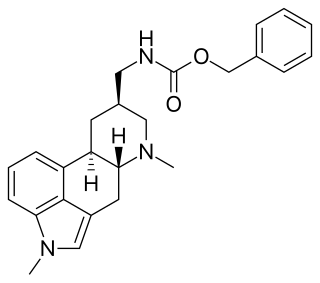
Metergoline, also known as methergoline and sold under the brand names Contralac (veterinary) and Liserdol (clinical), is a monoaminergic medication of the ergoline group which is used as a prolactin inhibitor in the treatment of hyperprolactinemia and to suppress lactation.

5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) receptor 1D, also known as HTR1D, is a 5-HT receptor, but also denotes the human gene encoding it. 5-HT1D acts on the central nervous system, and affects locomotion and anxiety. It also induces vasoconstriction in the brain.
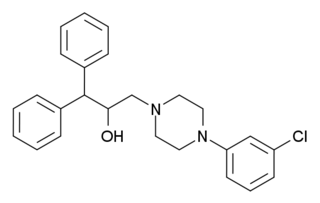
BRL-15,572 is a drug which acts as a selective antagonist for the serotonin receptor subtype 5-HT1D, with around 60x selectivity over other related receptors. The 5-HT1D receptor has a very similar pharmacology to the closely related 5-HT1B receptor, and most older ligands for these receptors bind to both subtypes with approximately equal affinity, so development of compounds such as BRL-15572 which are able to selectively block the 5-HT1D subtype while leaving 5-HT1B unaffected, have been a significant advance which has helped scientists in researching the function of these serotonin receptor subtypes. One function of the 5-HT1D receptor this research has revealed is its role in modulating release of the neurotransmitter glutamate in the brain, as well as functions in regulation of cerebral blood pressure which are important in the pathogenesis of migraine headaches.

AL-37350A (4,5-DHP-AMT) is a tricyclic tryptamine derivative which acts as a potent and selective agonist for the serotonin receptor 5-HT2A, with a Ki of 2.0 nM, and moderate selectivity over the related 5-HT2B and 5-HT2C receptors. It has been shown to have ocular hypotensive activity in animal models, suggesting it may be useful for the treatment of glaucoma.
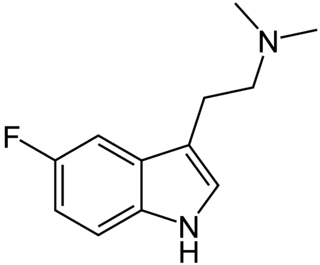
5-Fluoro-N,N-dimethyltryptamine is a tryptamine derivative related to compounds such as 5-bromo-DMT and 5-MeO-DMT. Fluorination of psychedelic tryptamines either reduces or has little effect on 5-HT2A/C receptor affinity or intrinsic activity, although 6-fluoro-DET is inactive as a psychedelic despite acting as a 5-HT2A agonist, while 4-fluoro-5-methoxy-DMT is a much stronger agonist at 5-HT1A than 5-HT2A.

Dimemebfe (5-MeO-BFE) is a recreational drug and research chemical. It acts as an agonist for the 5-HT1A and 5-HT2 family of serotonin receptors. It is related in structure to the psychedelic tryptamine derivative 5-MeO-DMT, but with the indole nitrogen replaced by oxygen, making dimemebfe a benzofuran derivative. It is several times less potent as a serotonin agonist than 5-MeO-DMT and with relatively more activity at 5-HT1A, but still shows strongest effects at the 5-HT2 family of receptors.
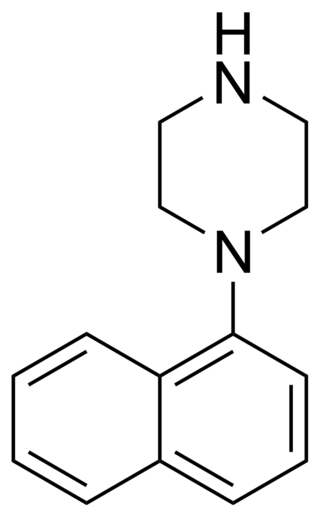
1-(1-Naphthyl)piperazine (1-NP) is a drug which is a phenylpiperazine derivative. It acts as a non-selective, mixed serotonergic agent, exerting partial agonism at the 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B, 5-HT1D, 5-HT1E, and 5-HT1F receptors, while antagonizing the 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, and 5-HT2C receptors. It has also been shown to possess high affinity for the 5-HT3, 5-HT5A, 5-HT6, and 5-HT7 receptors, and may bind to 5-HT4 and the SERT as well. In animals it produces effects including hyperphagia, hyperactivity, and anxiolysis, of which are all likely mediated predominantly or fully by blockade of the 5-HT2C receptor.

7,N,N-trimethyltryptamine (7-methyl-DMT, 7-TMT), is a tryptamine derivative which acts as an agonist of 5-HT2 receptors. In animal tests, both 7-TMT and its 5-methoxy derivative 5-MeO-7-TMT produced behavioural responses similar to those of psychedelic drugs such as DMT, but the larger 7-ethyl and 7-bromo derivatives of DMT did not produce psychedelic responses despite having higher 5-HT2 receptor affinity in vitro (cf. DOBU, DOAM). 7-TMT also weakly inhibits reuptake of serotonin but with little effect on dopamine or noradrenaline reuptake.
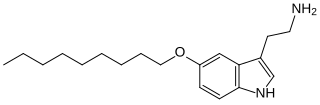
5-(Nonyloxy)tryptamine is a tryptamine derivative which acts as a selective agonist at the 5-HT1B receptor. Increasing the O-alkoxy chain length in this series gives generally increasing potency and selectivity for 5-HT1B, with highest activity found for the nonyloxy derivative, having a 5-HT1B binding affinity of 1.0 nM, and around 300-fold selectivity over the related 5-HT1A receptor.
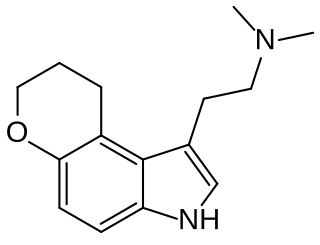
1-(2-Dimethylaminoethyl)dihydropyrano(3,2-e)indole (4,5-DHP-DMT) is a tricyclic tryptamine derivative which acts as a potent and reasonably selective partial agonist for the serotonin receptor 5-HT2A, with a Ki of 17.0 nM, and moderate selectivity over related serotonin receptors. It has lower 5-HT2 affinity and efficacy than the related compound AL-37350A, but higher lipophilicity.
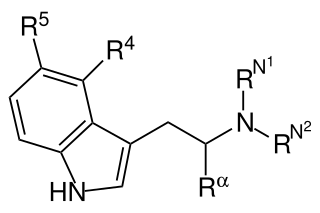
Substituted tryptamines, or serotonin analogues, are organic compounds which may be thought of as being derived from tryptamine itself. The molecular structures of all tryptamines contain an indole ring, joined to an amino (NH2) group via an ethyl (−CH2–CH2−) sidechain. In substituted tryptamines, the indole ring, sidechain, and/or amino group are modified by substituting another group for one of the hydrogen (H) atoms.

Donitriptan (INN) is a triptan drug which was investigated as an antimigraine agent but ultimately was never marketed. It acts as a high-affinity, high-efficacy/near-full agonist of the 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D receptors, and is among the most potent of the triptan series of drugs. Donitriptan was being developed in France by bioMérieux-Pierre Fabre and made it to phase II clinical trials in Europe before development was discontinued.

Acetryptine (INN), also known as 5-acetyltryptamine (5-AT), is a drug described as an antihypertensive agent which was never marketed. Structurally, acetryptine is a substituted tryptamine, and is closely related to other substituted tryptamines like serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine). It was developed in the early 1960s. The binding of acetryptine to serotonin receptors does not seem to have been well-investigated, although it was assessed at the 5-HT1A and 5-HT1D receptors and found to bind to them with high affinity. The drug may also act as a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI); specifically, as an inhibitor of MAO-A.

Amesergide is a serotonin receptor antagonist of the ergoline and lysergamide families related to methysergide which was under development by Eli Lilly and Company for the treatment of a variety of conditions including depression, anxiety, schizophrenia, male sexual dysfunction, migraine, and thrombosis but was never marketed. It reached phase II clinical trials for the treatment of depression, erectile dysfunction, and premature ejaculation prior to the discontinuation of its development.
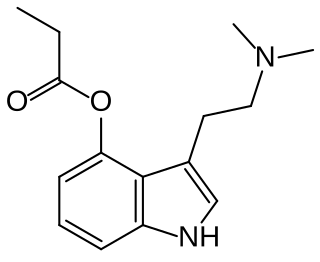
4-Propionoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine is a synthetic psychedelic drug from the tryptamine family with psychedelic effects, and is believed to act as a prodrug for psilocin. It produces a head-twitch response in mice. It has been sold online as a designer drug since May 2019. It was first identified as a new psychoactive substance in Sweden, in July 2019. A number of related derivatives have been synthesised as prodrugs of psilocin for medical applications.
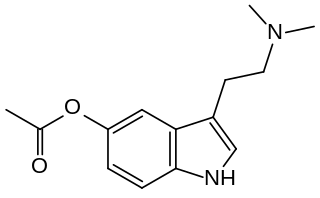
O-Acetylbufotenine is a tryptamine derivative which produces psychedelic-appropriate responding in animal studies. It is an acylated derivative of bufotenine with higher lipophilicity that allows it to cross the blood–brain barrier; once inside the brain, it is metabolised to bufotenine. It also acts directly as an agonist at 5-HT1A and 5-HT1D receptors.
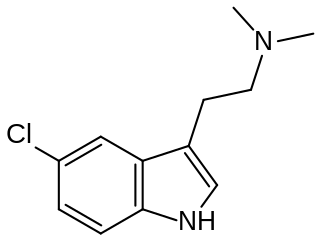
5-Chloro-N,N-dimethyltryptamine (5-chloro-DMT) is a tryptamine derivative related to compounds such as 5-bromo-DMT and 5-fluoro-DMT. It acts as a serotonin receptor agonist and has primarily sedative effects in animal studies. It has been sold as a designer drug.




















