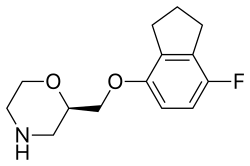
Mirtazapine, sold under the brand name Remeron among others, is an atypical tetracyclic antidepressant, and as such is used primarily to treat depression. Its effects may take up to four weeks, but can also manifest as early as one to two weeks. It is often used in cases of depression complicated by anxiety or insomnia. The effectiveness of mirtazapine is comparable to other commonly prescribed antidepressants. It is taken by mouth.

Serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) are a class of antidepressant medications used to treat major depressive disorder (MDD), anxiety disorders, social phobia, chronic neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS), and menopausal symptoms. Off-label uses include treatments for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD), and migraine prevention. SNRIs are monoamine reuptake inhibitors; specifically, they inhibit the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine. These neurotransmitters are thought to play an important role in mood regulation. SNRIs can be contrasted with the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (NRIs), which act upon single neurotransmitters.

Doxepin is a medication belonging to the tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) class of drugs used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic hives, and insomnia. For hives it is a less preferred alternative to antihistamines. It has a mild to moderate benefit for sleeping problems. It is used as a cream for itchiness due to atopic dermatitis or lichen simplex chronicus.

Trimipramine, sold under the brand name Surmontil among others, is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) which is used to treat depression. It has also been used for its sedative, anxiolytic, and weak antipsychotic effects in the treatment of insomnia, anxiety disorders, and psychosis, respectively. The drug is described as an atypical or "second-generation" TCA because, unlike other TCAs, it seems to be a fairly weak monoamine reuptake inhibitor. Similarly to other TCAs, however, trimipramine does have antihistamine, antiserotonergic, antiadrenergic, antidopaminergic, and anticholinergic activities.

Trazodone, sold under many brand names, is an antidepressant medication. It is used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, and insomnia. The medication is taken orally.

The 5-HT2A receptor is a subtype of the 5-HT2 receptor that belongs to the serotonin receptor family and is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). The 5-HT2A receptor is a cell surface receptor, but has several intracellular locations.

Etoperidone, associated with several brand names, is an atypical antidepressant which was developed in the 1970s and either is no longer marketed or was never marketed. It is a phenylpiperazine related to trazodone and nefazodone in chemical structure and is a serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitor (SARI) similarly to them.

A serotonin receptor agonist is an agonist of one or more serotonin receptors. They activate serotonin receptors in a manner similar to that of serotonin, a neurotransmitter and hormone and the endogenous ligand of the serotonin receptors.
A serotonin–norepinephrine–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (SNDRI), also known as a triple reuptake inhibitor (TRI), is a type of drug that acts as a combined reuptake inhibitor of the monoamine neurotransmitters serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine. It does this by concomitantly inhibiting the serotonin transporter (SERT), norepinephrine transporter (NET), and dopamine transporter (DAT), respectively. Inhibition of the reuptake of these neurotransmitters increases their extracellular concentrations and, therefore, results in an increase in serotonergic, adrenergic, and dopaminergic neurotransmission. The naturally-occurring and potent SNDRI cocaine is widely used recreationally and often illegally for the euphoric effects it produces.

Medifoxamine, previously sold under the brand names Clédial and Gerdaxyl, is an atypical antidepressant with additional anxiolytic properties acting via dopaminergic and serotonergic mechanisms which was formerly marketed in France and Spain, as well as Morocco. The drug was first introduced in France sometime around 1990. It was withdrawn from the market in 1999 (Morocco) and 2000 (France) following incidences of hepatotoxicity.

Pimavanserin, sold under the brand name Nuplazid, is an atypical antipsychotic which is approved for the treatment of Parkinson's disease psychosis and is also being studied for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease psychosis, schizophrenia, agitation, and major depressive disorder. Unlike other antipsychotics, pimavanserin is not a dopamine receptor antagonist.

Litoxetine (developmental code names SL 81-0385, IXA-001) is an antidepressant which was under clinical development for the treatment of depression in the early 1990s but was never marketed. It acts as a potent serotonin reuptake inhibitor (Ki for SERTTooltip serotonin transporter = 7 nM) and modest 5-HT3 receptor antagonist (Ki = 315 nM). It has antiemetic activity, and unlike the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), appears to have a negligible incidence of nausea and vomiting. The drug is structurally related to indalpine. Development of litoxetine for depression was apparently ceased in the late 1990s. However, as of March 2017, development of litoxetine has been reinitiated and the drug is now in the phase II stage for the treatment of urinary incontinence.

Serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitors (SARIs) are a class of drugs used mainly as antidepressants, but also as anxiolytics and hypnotics. They act by antagonizing serotonin receptors such as 5-HT2A and inhibiting the reuptake of serotonin, norepinephrine, and/or dopamine. Additionally, most also antagonize α1-adrenergic receptors. The majority of the currently marketed SARIs belong to the phenylpiperazine class of compounds.
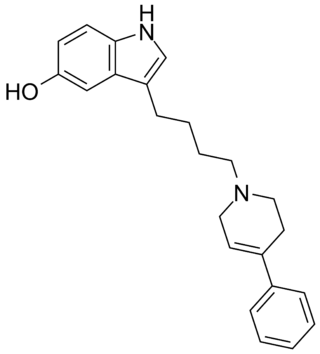
Roxindole (EMD-49,980) is a dopaminergic and serotonergic drug which was originally developed by Merck KGaA for the treatment of schizophrenia. In clinical trials its antipsychotic efficacy was only modest but it was unexpectedly found to produce potent and rapid antidepressant and anxiolytic effects. As a result, roxindole was further researched for the treatment of depression instead. It has also been investigated as a therapy for Parkinson's disease and prolactinoma.

A serotonin–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (SDRI) is a type of drug which acts as a reuptake inhibitor of the monoamine neurotransmitters serotonin and dopamine by blocking the actions of the serotonin transporter (SERT) and dopamine transporter (DAT), respectively. This in turn leads to increased extracellular concentrations of serotonin and dopamine, and, therefore, an increase in serotonergic and dopaminergic neurotransmission.
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, or serotonin-specific re-uptake inhibitor (SSRIs), are a class of chemical compounds that have application as antidepressants and in the treatment of depression and other psychiatric disorders. SSRIs are therapeutically useful in the treatment of panic disorder (PD), posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), social anxiety disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD), and anorexia. There is also clinical evidence of the value of SSRIs in the treatment of the symptoms of schizophrenia and their ability to prevent cardiovascular diseases.

Amesergide is a serotonin receptor antagonist of the ergoline and lysergamide families related to methysergide which was under development by Eli Lilly and Company for the treatment of a variety of conditions including depression, anxiety, schizophrenia, male sexual dysfunction, migraine, and thrombosis but was never marketed. It reached phase II clinical trials for the treatment of depression, erectile dysfunction, and premature ejaculation prior to the discontinuation of its development.