
Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), also known as androstenolone, is an endogenous steroid hormone precursor. It is one of the most abundant circulating steroids in humans. DHEA is produced in the adrenal glands, the gonads, and the brain. It functions as a metabolic intermediate in the biosynthesis of the androgen and estrogen sex steroids both in the gonads and in various other tissues. However, DHEA also has a variety of potential biological effects in its own right, binding to an array of nuclear and cell surface receptors, and acting as a neurosteroid and modulator of neurotrophic factor receptors.
Steroid hormone receptors are found in the nucleus, cytosol, and also on the plasma membrane of target cells. They are generally intracellular receptors and initiate signal transduction for steroid hormones which lead to changes in gene expression over a time period of hours to days. The best studied steroid hormone receptors are members of the nuclear receptor subfamily 3 (NR3) that include receptors for estrogen and 3-ketosteroids. In addition to nuclear receptors, several G protein-coupled receptors and ion channels act as cell surface receptors for certain steroid hormones.

Selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs), also known as estrogen receptor agonists/antagonists (ERAAs), are a class of drugs that act on estrogen receptors (ERs). Compared to pure ER agonists–antagonists, SERMs are more tissue-specific, allowing them to selectively inhibit or stimulate estrogen-like action in various tissues.
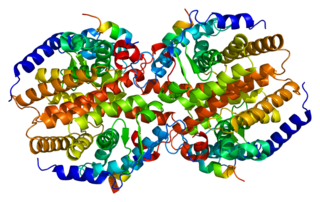
The constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) also known as nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group I, member 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NR1I3 gene. CAR is a member of the nuclear receptor superfamily and along with pregnane X receptor (PXR) functions as a sensor of endobiotic and xenobiotic substances. In response, expression of proteins responsible for the metabolism and excretion of these substances is upregulated. Hence, CAR and PXR play a major role in the detoxification of foreign substances such as drugs.
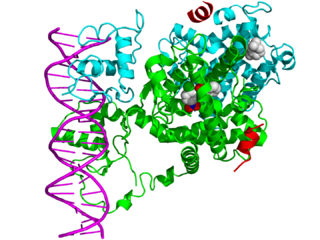
In the field of molecular biology, nuclear receptors are a class of proteins responsible for sensing steroids, thyroid hormones, vitamins, and certain other molecules. These intracellular receptors work with other proteins to regulate the expression of specific genes, thereby controlling the development, homeostasis, and metabolism of the organism.

Growth hormone receptor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GHR gene. GHR orthologs have been identified in most mammals.

Ohmefentanyl is an extremely potent opioid analgesic drug which selectively binds to the μ-opioid receptor.

The nuclear receptor 4A2 (NR4A2) also known as nuclear receptor related 1 protein (NURR1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NR4A2 gene. NR4A2 is a member of the nuclear receptor family of intracellular transcription factors.

RAR-related orphan receptor beta (ROR-beta), also known as NR1F2 is a nuclear receptor that in humans is encoded by the RORB gene.

RAR-related orphan receptor alpha (RORα), also known as NR1F1 is a nuclear receptor that in humans is encoded by the RORA gene. RORα participates in the transcriptional regulation of some genes involved in circadian rhythm. In mice, RORα is essential for development of cerebellum through direct regulation of genes expressed in Purkinje cells. It also plays an essential role in the development of type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2) and mutant animals are ILC2 deficient. In addition, although present in normal numbers, the ILC3 and Th17 cells from RORα deficient mice are defective for cytokine production.

Rev-Erb beta (Rev-Erbβ), also known as nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group D member 2 (NR1D2), is a member of the Rev-Erb protein family. Rev-Erbβ, like Rev-Erbα, belongs to the nuclear receptor superfamily of transcription factors and can modulate gene expression through binding to gene promoters. Together with Rev-Erbα, Rev-Erbβ functions as a major regulator of the circadian clock. These two proteins are partially redundant. Current research suggests that Rev-Erbβ is less important in maintaining the circadian clock than Rev-Erbα; knock-out studies of Rev-Erbα result in significant circadian disruption but the same has not been found with Rev-Erbβ. Rev-Erbβ compensation for Rev-Erbα varies across tissues, and further research is needed to elucidate the separate role of Rev-Erbβ.

Retinoid X receptor beta (RXR-beta), also known as NR2B2 is a nuclear receptor that in humans is encoded by the RXRB gene.

Thyroid hormone receptor beta (TR-beta) also known as nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group A, member 2 (NR1A2), is a nuclear receptor protein that in humans is encoded by the THRB gene.
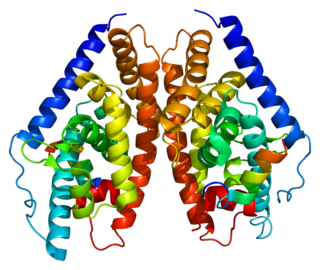
Liver X receptor beta (LXR-β) is a member of the nuclear receptor family of transcription factors. LXR-β is encoded by the NR1H2 gene.

Tripartite motif-containing 24 (TRIM24) also known as transcriptional intermediary factor 1α (TIF1α) is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the TRIM24 gene.

Altanserin is a compound that binds to the 5-HT2A receptor. Labeled with the isotope fluorine-18 it is used as a radioligand in positron emission tomography (PET) studies of the brain, i.e., studies of the 5-HT2A neuroreceptors. Besides human neuroimaging studies altanserin has also been used in the study of rats.

WAY-100635 is a piperazine drug and research chemical widely used in scientific studies. It was originally believed to act as a selective 5-HT1A receptor antagonist, but subsequent research showed that it also acts as potent full agonist at the D4 receptor. It is sometimes referred to as a silent antagonist at the former receptor. It is closely related to WAY-100135.

5-I-R91150 is a compound that acts as a potent and selective antagonist of 5-HT2A receptors. Its main application is as its iodine-123 radiolabeled form, in which it can be used in SPECT scanning in human neuroimaging studies, to examine the distribution of the 5-HT2A receptor subtype in the brain, e.g. with respect to sex and age and in adults with Asperger syndrome or Alzheimer's disease.

Mefway is a serotonin 5-HT1A receptor antagonist used in medical research, usually in the form of mefway (18F) as a positron emission tomography (PET) radiotracer.
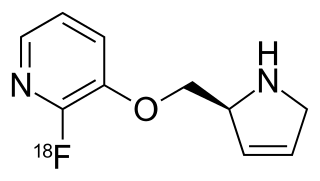
Nifene is a high affinity, selective nicotinic α4β2* receptor partial agonist used in medical research for nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, usually in the form of nifene (18F) as a positron emission tomography (PET) radiotracer.



















