
Noradrenergic and specific serotonergic antidepressants (NaSSAs) are a class of psychiatric drugs used primarily as antidepressants. They act by antagonizing the α2-adrenergic receptor and certain serotonin receptors such as 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C, but also 5-HT3, 5-HT6, and/or 5-HT7 in some cases. By blocking α2-adrenergic autoreceptors and heteroreceptors, NaSSAs enhance adrenergic and serotonergic neurotransmission in the brain involved in mood regulation, notably 5-HT1A-mediated transmission. In addition, due to their blockade of certain serotonin receptors, serotonergic neurotransmission is not facilitated in unwanted areas, which prevents the incidence of many side effects often associated with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressants; hence, in part, the "specific serotonergic" label of NaSSAs.

Trazodone, sold under many brand names, is an antidepressant medication. It is used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, and insomnia. The medication is taken orally.

Nefazodone, sold formerly under the brand names Serzone, Dutonin, and Nefadar among others, is an atypical antidepressant medication which is used in the treatment of depression and for other uses. Nefazodone is still available in the United States, but was withdrawn from other countries due to rare liver toxicity. The medication is taken by mouth.

Methylergometrine, also known as methylergonovine and sold under the brand name Methergine, is a medication of the ergoline and lysergamide groups which is used as an oxytocic in obstetrics and in the treatment of migraine. It reportedly produces psychedelic effects similar to those of lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) at high doses.
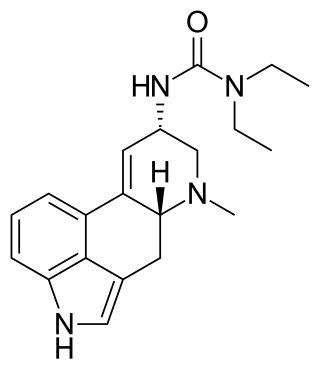
Lisuride, sold under the brand name Dopergin among others, is a monoaminergic medication of the ergoline class which is used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease, migraine, and high prolactin levels. It is taken by mouth.

Etoperidone, associated with several brand names, is an atypical antidepressant which was developed in the 1970s and either is no longer marketed or was never marketed. It is a phenylpiperazine related to trazodone and nefazodone in chemical structure and is a serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitor (SARI) similarly to them.

A serotonin receptor agonist is an agonist of one or more serotonin receptors. They activate serotonin receptors in a manner similar to that of serotonin, a neurotransmitter and hormone and the endogenous ligand of the serotonin receptors.

meta-Chlorophenylpiperazine (mCPP) is a psychoactive drug of the phenylpiperazine class. It was initially developed in the late-1970s and used in scientific research before being sold as a designer drug in the mid-2000s. It has been detected in pills touted as legal alternatives to illicit stimulants in New Zealand and pills sold as "ecstasy" in Europe and the United States.

A serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SRI) is a type of drug which acts as a reuptake inhibitor of the neurotransmitter serotonin by blocking the action of the serotonin transporter (SERT). This in turn leads to increased extracellular concentrations of serotonin and, therefore, an increase in serotonergic neurotransmission. It is a type of monoamine reuptake inhibitor (MRI); other types of MRIs include dopamine reuptake inhibitors and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors.

Medifoxamine, previously sold under the brand names Clédial and Gerdaxyl, is an atypical antidepressant with additional anxiolytic properties acting via dopaminergic and serotonergic mechanisms which was formerly marketed in France and Spain, as well as Morocco. The drug was first introduced in France sometime around 1990. It was withdrawn from the market in 1999 (Morocco) and 2000 (France) following incidences of hepatotoxicity.

Vilazodone, sold under the brand name Viibryd among others, is a medication used to treat major depressive disorder. It is classified as a serotonin modulator and is taken by mouth.

Lubazodone is an experimental antidepressant which was under development by Yamanouchi for the treatment for major depressive disorder in the late 1990s and early 2000s but was never marketed. It acts as a serotonin reuptake inhibitor and 5-HT2A receptor antagonist, and hence has the profile of a serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitor (SARI). The drug has good selectivity against a range of other monoamine receptors, with its next highest affinities being for the α1-adrenergic receptor and the 5-HT2C receptor. Lubazodone is structurally related to trazodone and nefazodone, but is a stronger serotonin reuptake inhibitor and weaker as a 5-HT2A receptor antagonist in comparison to them and is more balanced in its actions as a SARI. It reached phase II clinical trials for depression, but development was discontinued in 2001 reportedly due to the "erosion of the SSRITooltip selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor market in the United States".

Norepinephrine and dopamine disinhibitors (NDDIs) are a class of drugs which act at specific sites to disinhibit downstream norepinephrine and dopamine release in the brain.

Mepiprazole is an anxiolytic drug of the phenylpiperazine group with additional antidepressant properties that is marketed in Spain. It acts as a 5-HT2A and α1-adrenergic receptor antagonist and inhibits the reuptake and induces the release of serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine to varying extents, and has been described as a serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitor (SARI). Controlled clinical trials of mepiprazole in patients with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) were also carried out and suggested some benefits of the drug in relieving symptoms of IBS in some patients. Similarly to other phenylpiperazines like trazodone, nefazodone, and etoperidone, mepiprazole produces mCPP as an active metabolite.
A serotonin modulator and stimulator (SMS), sometimes referred to more simply as a serotonin modulator, is a type of drug with a multimodal action specific to the serotonin neurotransmitter system. To be precise, SMSs simultaneously modulate one or more serotonin receptors and inhibit the reuptake of serotonin. The term was created to describe the mechanism of action of the serotonergic antidepressant vortioxetine, which acts as a serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SRI), agonist of the 5-HT1A receptor, and antagonist of the 5-HT3 and 5-HT7 receptors. However, it can also technically be applied to vilazodone, which is an antidepressant as well and acts as an SRI and 5-HT1A receptor partial agonist.

Triazoledione is a phenylpiperazine compound and a major metabolite of the antidepressant nefazodone. It is active, but with substantially reduced potency compared to nefazodone. As such, it has been suggested that it is unlikely that triazoledione contributes significantly to the pharmacology of nefazodone. However, triazoledione may reach concentrations as great as 10 times those of nefazodone, and hence could still be a significant contributor to its therapeutic effects.
















