Azapirones are a class of drugs used as anxiolytics, antidepressants, and antipsychotics. [1] [2] [3] [4] They are commonly used as add-ons to other antidepressants, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10]

Azapirones are a class of drugs used as anxiolytics, antidepressants, and antipsychotics. [1] [2] [3] [4] They are commonly used as add-ons to other antidepressants, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs). [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10]
The azapirones include the following agents: [11]
Azapirones have shown benefit in general anxiety [14] and augmenting SSRIs in social anxiety [15] and depression. [16] Evidence is not clear for panic disorder [17] and functional gastrointestinal disorders. [18]
Tandospirone has also been used to augment antipsychotics in Japan as it improves cognitive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia. [19] Buspirone is being investigated for this purpose as well. [20] [21]
Side effects of azapirones may include dizziness, headaches, restlessness, nausea, and diarrhea. [4] [22]
Azapirones have more tolerable adverse effects than many other available anxiolytics, such as benzodiazepines or SSRIs. Unlike benzodiazepines, azapirones lack abuse potential and are not addictive, do not cause cognitive/memory impairment or sedation, and do not appear to induce appreciable tolerance or physical dependence. However, azapirones are considered less effective with slow onset in controlling symptoms. [23]
Buspirone was originally classified as an azaspirodecanedione, shortened to azapirone or azaspirone due to the fact that its chemical structure contained this moiety, and other drugs with similar structures were labeled as such as well. However, despite all being called azapirones, not all of them actually contain the azapirodecanedione component, and most in fact do not or contain a variation of it. Additionally, many azapirones are also pyrimidinylpiperazines, though again this does not apply to them all.
Drugs classed as azapirones can be identified by their -spirone or -pirone suffix. [24]
On a pharmacological level, azapirones varyingly possess activity at the following receptors: [25] [26] [27] [28] [29] [30] [31] [32]
Actions at D4, 5-HT2C, 5-HT7, and sigma receptors have also been shown for some azapirones. [33] [34] [35] [36]
While some of the listed properties such as 5-HT2A and D2 blockade may be useful in certain indications such as in the treatment of schizophrenia (as with perospirone and tiospirone), all of them except 5-HT1A agonism are generally undesirable in anxiolytics and only contribute to side effects. As a result, further development has commenced to bring more selective of anxiolytic agents to the market. An example of this initiative is gepirone, which was recently approved after completing clinical trials in the United States for the treatment of major depression and generalized anxiety disorder. Another example is tandospirone which has been licensed in Japan for the treatment of anxiety and as an augmentation to antidepressants for depression.
5-HT1A receptor partial agonists have demonstrated efficacy against depression in rodent studies and human clinical trials. [37] [38] [39] [40] Unfortunately, however, their efficacy is limited and they are only relatively mild antidepressants. Instead of being used as monotherapy treatments, they are more commonly employed as augmentations to serotonergic antidepressants like the SSRIs. [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] It has been proposed that high intrinsic activity at 5-HT1A postsynaptic receptors is necessary for maximal therapeutic benefits to come to prominence, and as a result, investigation has commenced in azapirones which act as 5-HT1A receptor full agonists such as alnespirone and eptapirone. [41] [42] [43] [44] Indeed, in preclinical studies, eptapirone produces robust antidepressant effects which surpass those of even high doses of imipramine and paroxetine. [41] [42] [43] [44]
| Binding site | Buspirone | Gepirone | Ipsapirone | Tandospirone |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-HT1A | 20 ± 3 | 70 ± 10 | 7.9 ± 2 | 27 ± 5 |
| 5-HT1B | > 100,000 | > 100,000 | > 100,000 | > 100,000 |
| 5-HT1D | > 100,000 | > 100,000 | 33,000 ± 8,000 | > 100,000 |
| 5-HT2A | 1,300 ± 400 | 3,000 ± 50 | 6,400 ± 4,000 | 1,300 ± 200 |
| 5-HT2C | 1,100 ± 200 | 5,000 ± 700 | 5,000 ± 1,000 | 2,600 ± 60 |
| SERT | – | – | – | > 100,000 |
| D1 | 33,000 ± 1,000 | > 100,000 | 15,000 ± 2,000 | 41,000 ± 10,000 |
| D2 | 240 ± 50 | 2,200 ± 200 | 1,900 ± 200 | 1,700 ± 300 |
| α1-Adrenergic | 1,000 ± 400 | 2,300 ± 300 | 40 ± 7 | 1,600 ± 80 |
| α2-Adrenergic | 6,000 ± 700 | 1,600 ± 200 | 1,900 ± 500 | 1,900 ± 400 |
| β-Adrenergic | 8,800 ± 1,000 | > 100,000 | > 100,000 | > 100,000 |
| mACh | 38,000 ± 5,000 | > 100,000 | 49,000 ± 5,000 | > 100,000 |
| GABAA/BDZ | > 100,000 | > 100,000 | > 100,000 | > 100,000 |
Azapirones are poorly but nonetheless appreciably absorbed and have a rapid onset of action, but have only very short half-lives ranging from 1–3 hours. As a result, they must be administered 2–3 times a day. The only exception to this rule is umespirone, which has a very long duration with a single dose lasting as long as 23 hours. [45] Unfortunately, umespirone has not been commercialized. Although never commercially produced, Bristol-Myers Squibb applied for a patent on October 28, 1993, and received the patent on July 11, 1995, for an extended release formulation of buspirone. [46] An extended release formulation of gepirone is currently under development and if approved, should help to improve this issue.
Metabolism of azapirones occurs in the liver and they are excreted in urine and feces. A common metabolite of several azapirones including buspirone, gepirone, ipsapirone, revospirone, and tandospirone is 1-(2-pyrimidinyl)piperazine (1-PP). [47] [48] [49] 1-PP possesses 5-HT1A partial agonist and α2-adrenergic antagonist actions and likely contributes overall mostly to side effects. [47] [48] [50]
An anxiolytic is a medication or other intervention that reduces anxiety. This effect is in contrast to anxiogenic agents which increase anxiety. Anxiolytic medications are used for the treatment of anxiety disorders and their related psychological and physical symptoms.
Aripiprazole, sold under the brand names Abilify and Aristada, among others, is an atypical antipsychotic. It is primarily used in the treatment of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder; other uses include as an add-on treatment in major depressive disorder and obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD), tic disorders, and irritability associated with autism. Aripiprazole is taken by mouth or via injection into a muscle. A Cochrane review found low-quality evidence of effectiveness in treating schizophrenia.

5-HT receptors, 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors, or serotonin receptors, are a group of G protein-coupled receptor and ligand-gated ion channels found in the central and peripheral nervous systems. They mediate both excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission. The serotonin receptors are activated by the neurotransmitter serotonin, which acts as their natural ligand.

Buspirone, sold under the brand name Buspar, among others, is an anxiolytic, a medication primarily used to treat anxiety disorders, particularly generalized anxiety disorder. It is a serotonin 5-HT1A receptor agonist, increasing action at serotonin receptors in the brain. It is taken orally, and takes two to six weeks to be fully effective.

Clomipramine, sold under the brand name Anafranil among others, is a tricyclic antidepressant (TCA). It is used in the treatment of various conditions, most-notably obsessive–compulsive disorder but also many other disorders, including hyperacusis, panic disorder, major depressive disorder, trichotilomania, body dysmorphic disorder and chronic pain. It has also been notably used to treat premature ejaculation and the cataplexy associated with narcolepsy.

Trazodone, sold under many brand names, is an antidepressant medication. It is used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, and insomnia. The medication is taken orally.
An anxiogenic or panicogenic substance is one that causes anxiety. This effect is in contrast to anxiolytic agents, which inhibits anxiety. Together these categories of psychoactive compounds may be referred to as anxiotropic compounds.

Ipsapirone is a selective 5-HT1A receptor partial agonist of the piperazine and azapirone chemical classes. It has antidepressant and anxiolytic effects. Ipsapirone was studied in several placebo-controlled trials for depression and continues to be used in research.

A serotonin receptor agonist is an agonist of one or more serotonin receptors. They activate serotonin receptors in a manner similar to that of serotonin, a neurotransmitter and hormone and the endogenous ligand of the serotonin receptors.
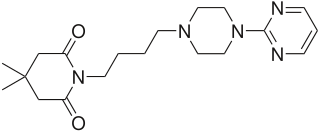
Gepirone, sold under the brand name Exxua, is a medication used for the treatment of major depressive disorder. It is taken orally.

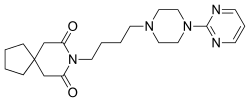
Tandospirone, sold under the brand name Sediel, is an anxiolytic and antidepressant medication used in Japan and China, where it is marketed by Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma. It is a member of the azapirone class of drugs and is closely related to other azapirones like buspirone and gepirone.

The serotonin 1A receptor is a subtype of serotonin receptors, or 5-HT receptors, that binds serotonin, also known as 5-HT, a neurotransmitter. 5-HT1A is expressed in the brain, spleen, and neonatal kidney. It is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR), coupled to the Gi protein, and its activation in the brain mediates hyperpolarization and reduction of firing rate of the postsynaptic neuron. In humans, the serotonin 1A receptor is encoded by the HTR1A gene.

8-OH-DPAT is a research chemical of the aminotetralin chemical class which was developed in the 1980s and has been widely used to study the function of the 5-HT1A receptor. It was one of the first major 5-HT1A receptor full agonists to have been discovered.

Flesinoxan (DU-29,373) is a potent and selective 5-HT1A receptor partial/near-full agonist of the phenylpiperazine class. Originally developed as a potential antihypertensive drug, flesinoxan was later found to possess antidepressant and anxiolytic effects in animal tests. As a result, it was investigated in several small human pilot studies for the treatment of major depressive disorder, and was found to have robust effectiveness and very good tolerability. However, due to "management decisions", the development of flesinoxan was stopped and it was not pursued any further.

Zalospirone (WY-47,846) is a selective 5-HT1A partial agonist of the azapirone chemical class. It was found to be effective in the treatment of anxiety and depression in clinical trials, but a high proportion of subjects dropped out due to side effects and development was subsequently never completed.

Eptapirone (F-11,440) is a very potent and highly selective 5-HT1A receptor full agonist of the azapirone family. Its affinity for the 5-HT1A receptor was reported to be 4.8 nM (Ki), and its intrinsic activity approximately equal to that of serotonin.

Umespirone (KC-9172) is a drug of the azapirone class which possesses anxiolytic and antipsychotic properties. It behaves as a 5-HT1A receptor partial agonist (Ki = 15 nM), D2 receptor partial agonist (Ki = 23 nM), and α1-adrenoceptor receptor antagonist (Ki = 14 nM), and also has weak affinity for the sigma receptor (Ki = 558 nM). Unlike many other anxiolytics and antipsychotics, umespirone produces minimal sedation, cognitive/memory impairment, catalepsy, and extrapyramidal symptoms.
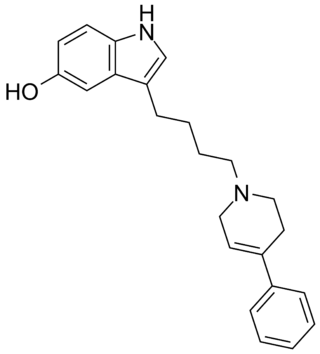
Roxindole (EMD-49,980) is a dopaminergic and serotonergic drug which was originally developed by Merck KGaA for the treatment of schizophrenia. In clinical trials its antipsychotic efficacy was only modest but it was unexpectedly found to produce potent and rapid antidepressant and anxiolytic effects. As a result, roxindole was further researched for the treatment of depression instead. It has also been investigated as a therapy for Parkinson's disease and prolactinoma.

Osemozotan (MKC-242) is a selective 5-HT1A receptor agonist with some functional selectivity, acting as a full agonist at presynaptic and a partial agonist at postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptors. 5-HT1A receptor stimulation influences the release of various neurotransmitters including serotonin, dopamine, norepinephrine, and acetylcholine. 5-HT1A receptors are inhibitory G protein-coupled receptor. Osemozotan has antidepressant, anxiolytic, antiobsessional, serenic, and analgesic effects in animal studies, and is used to investigate the role of 5-HT1A receptors in modulating the release of dopamine and serotonin in the brain, and their involvement in addiction to abused stimulants such as cocaine and methamphetamine.