
5-HT receptors, 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors, or serotonin receptors, are a group of G protein-coupled receptor and ligand-gated ion channels found in the central and peripheral nervous systems. They mediate both excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission. The serotonin receptors are activated by the neurotransmitter serotonin, which acts as their natural ligand.

Ketanserin (INN, USAN, BAN) (brand name Sufrexal; former developmental code name R41468) is a drug used clinically as an antihypertensive agent and in scientific research to study the serotonergic system; specifically, the 5-HT2 receptor family. It was discovered at Janssen Pharmaceutica in 1980. It is not available in the United States.

Doxepin is a medication belonging to the tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) class of drugs used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic hives, and insomnia. For hives it is a less preferred alternative to antihistamines. It has a mild to moderate benefit for sleeping problems. It is used as a cream for itchiness due to atopic dermatitis or lichen simplex chronicus.
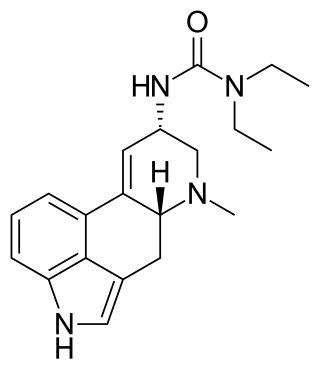
Lisuride, sold under the brand name Dopergin among others, is a monoaminergic medication of the ergoline class which is used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease, migraine, and high prolactin levels. It is taken by mouth.

The 5-HT2A receptor is a subtype of the 5-HT2 receptor that belongs to the serotonin receptor family and is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). The 5-HT2A receptor is a cell surface receptor, but has several intracellular locations.
The 5-HT2 receptors are a subfamily of 5-HT receptors that bind the endogenous neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT). The 5-HT2 subfamily consists of three G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) which are coupled to Gq/G11 and mediate excitatory neurotransmission, including 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, and 5-HT2C. For more information, please see the respective main articles of the individual subtypes:

meta-Chlorophenylpiperazine (mCPP) is a psychoactive drug of the phenylpiperazine class. It was initially developed in the late-1970s and used in scientific research before being sold as a designer drug in the mid-2000s. It has been detected in pills touted as legal alternatives to illicit stimulants in New Zealand and pills sold as "ecstasy" in Europe and the United States.
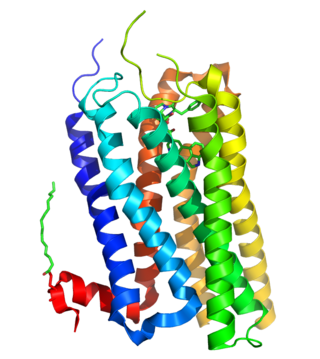
5-Hydroxytryptamine receptor 2B (5-HT2B) also known as serotonin receptor 2B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HTR2B gene. 5-HT2B is a member of the 5-HT2 receptor family that binds the neurotransmitter serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT). Like all 5-HT2 receptors, the 5-HT2B receptor is Gq/G11-protein coupled, leading to downstream activation of phospholipase C.

Setoperone is a compound that is a ligand to the 5-HT2A receptor. It can be radiolabeled with the radioisotope fluorine-18 and used as a radioligand with positron emission tomography (PET). Several research studies have used the radiolabeled setoperone in neuroimaging for the studying neuropsychiatric disorders, such as depression or schizophrenia.

Sarpogrelate is a drug which acts as an antagonist at the 5HT2A and 5-HT2B receptors. It blocks serotonin-induced platelet aggregation, and has applications in the treatment of many diseases including diabetes mellitus, Buerger's disease, Raynaud's disease, coronary artery disease, angina pectoris, and atherosclerosis.
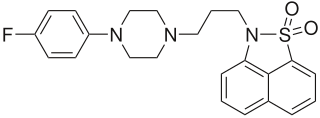
Fananserin (RP-62203) is a drug which acts as a potent antagonist at both the 5HT2A receptor, and the Dopamine D4 receptor, but without blocking other dopamine receptors such as D2. It has sedative and antipsychotic effects, and has been researched for the treatment of schizophrenia, although efficacy was less than expected and results were disappointing.

Amperozide is an atypical antipsychotic of the diphenylbutylpiperazine class which acts as an antagonist at the 5-HT2A receptor. It does not block dopamine receptors as with most antipsychotic drugs, but does inhibit dopamine release, and alters the firing pattern of dopaminergic neurons. It was investigated for the treatment of schizophrenia in humans, but never adopted clinically. Its main use is instead in veterinary medicine, primarily in intensively farmed pigs, for decreasing aggression and stress and thereby increasing feeding and productivity.
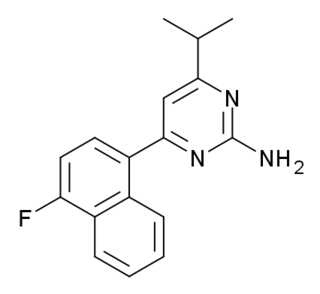
RS-127445 is a drug which acts as a potent and selective antagonist at the serotonin 5-HT2B receptor, with around 1000 times selectivity over the closely related 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors. The role of the 5-HT2B receptor in the body is still poorly understood, and RS-127445 has been a useful tool in unravelling the function of the various systems in which this receptor is expressed.

SB-204741 is a drug which acts as a potent and selective antagonist at the serotonin 5-HT2B receptor, with around 135x selectivity over the closely related 5-HT2C receptor, and even higher over the 5-HT2A receptor and other targets. It is used in scientific research for investigating the functions of the 5-HT2B receptor.
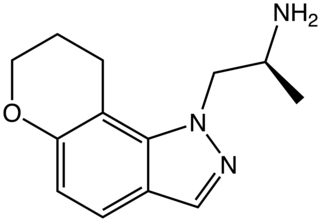
AL-38022A is an indazole derivative drug which is one of a range of similar drugs developed for scientific research and with some possible clinical applications. It acts as a potent and selective agonist for the 5-HT2 family of serotonin receptors, with highest binding affinity for the 5-HT2C subtype and around four times less affinity for 5-HT2A and 5-HT2B. In drug discrimination tests on animals, it fully substituted for both DOM and 5-MeO-DMT.
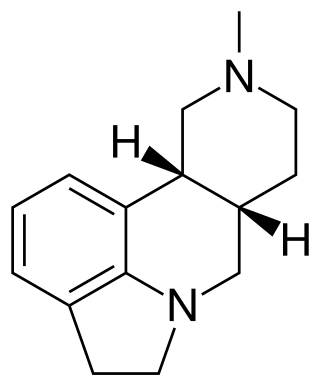
SDZ SER-082 is a drug which acts as a mixed antagonist for the 5-HT2B and 5-HT2C serotonin receptors, with good selectivity over other serotonin receptor subtypes and slight preference for 5-HT2C over 5-HT2B. It has been used in animal studies into the behavioural effects of the different 5-HT2 subtypes, and how they influence the effects of other drugs such as cocaine.
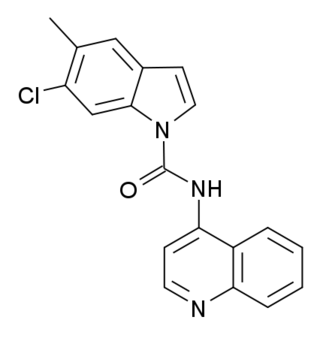
SB-215505 is a drug which acts as a potent and selective antagonist at the serotonin 5-HT2B receptor, with good selectivity over the related 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors. It is used in scientific research into the function of the 5-HT2 family of receptors, especially to study the role of 5-HT2B receptors in the heart, and to distinguish 5-HT2B-mediated responses from those produced by 5-HT2A or 5-HT2C.

Serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitors (SARIs) are a class of drugs used mainly as antidepressants, but also as anxiolytics and hypnotics. They act by antagonizing serotonin receptors such as 5-HT2A and inhibiting the reuptake of serotonin, norepinephrine, and/or dopamine. Additionally, most also antagonize α1-adrenergic receptors. The majority of the currently marketed SARIs belong to the phenylpiperazine class of compounds.

Pruvanserin is a selective 5-HT2A receptor antagonist which was under development by Eli Lilly and Company for the treatment of insomnia. It was in phase II clinical trials in 2008 but appears to have been discontinued as it is no longer in the company's development pipeline. In addition to its sleep-improving properties, pruvanserin has also been shown to have antidepressant, anxiolytic, and working memory-enhancing effects in animal studies.

25CN-NBOH is a compound indirectly derived from the phenethylamine series of hallucinogens, which was discovered in 2014 at the University of Copenhagen. This compound is notable as one of the most selective agonist ligands for the 5-HT2A receptor yet discovered, with a pKi of 8.88 at the human 5-HT2A receptor and with 100x selectivity for 5-HT2A over 5-HT2C, and 46x selectivity for 5-HT2A over 5-HT2B. A tritiated version of 25CN-NBOH has also been accessed and used for more detailed investigations of the binding to 5-HT2 receptors and autoradiography.




















