
Diocletian, nicknamed Jovius, was Roman emperor from 284 until his abdication in 305. He was born Diocles to a family of low status in the Roman province of Dalmatia. Diocles rose through the ranks of the military early in his career, eventually becoming a cavalry commander for the army of Emperor Carus. After the deaths of Carus and his son Numerian on a campaign in Persia, Diocles was proclaimed emperor by the troops, taking the name Diocletianus. The title was also claimed by Carus's surviving son, Carinus, but Diocletian defeated him in the Battle of the Margus.

The Tetrarchy was the system instituted by Roman emperor Diocletian in 293 AD to govern the ancient Roman Empire by dividing it between two emperors, the augusti, and their junior colleagues and designated successors, the caesares.
The 300s decade ran from January 1, 300, to December 31, 309.
The 350s decade ran from January 1, 350, to December 31, 359.
The 290s decade ran from January 1, 290, to December 31, 299.
The 280's decade ran from January 1, 280, to December 31, 289.

Year 299 (CCXCIX) was a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Diocletian and Maximian. The denomination 299 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 302 (CCCII) was a common year starting on Thursday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Constantius and Valerius or, less frequently, year 1055 Ab urbe condita. The denomination 302 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 293 (CCXCIII) was a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Diocletian and Maximian. The denomination 293 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 288 (CCLXXXVIII) was a leap year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. In the Roman Empire, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Maximian and Ianuarianus. The denomination 288 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 306 (CCCVI) was a common year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Constantius and Valerius. The denomination 306 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Flavius Valerius Constantius, also called Constantius I, was a Roman emperor from 305 to 306. He was one of the four original members of the Tetrarchy established by Diocletian, first serving as caesar from 293 to 305 and then ruling as augustus until his death. Constantius was also father of Constantine the Great, the first Christian emperor of Rome. The nickname "Chlorus" was first popularized by Byzantine-era historians and not used during the emperor's lifetime.

Galerius Valerius Maximianus was Roman emperor from 305 to 311. While acting as Caesar under Emperor Diocletian, Galerius obtained victory warring against the Persian Sassanian Empire, defeating Narseh at the battle of Satala in 298 and possibly sacking the Sassanian capital of Ctesiphon in 299. He also campaigned across the Danube against the Carpi, defeating them in 297 and 300. Although he was a staunch opponent of Christianity, Galerius ended the Diocletianic Persecution when he issued the Edict of Toleration in Serdica (Sofia) in 311.

Maximian, nicknamed Herculius, was Roman emperor from 286 to 305. He was Caesar from 285 to 286, then Augustus from 286 to 305. He shared the latter title with his co-emperor and superior, Diocletian, whose political brain complemented Maximian's military brawn. Maximian established his residence at Trier but spent most of his time on campaign. In late 285, he suppressed rebels in Gaul known as the Bagaudae. From 285 to 288, he fought against Germanic tribes along the Rhine frontier. Together with Diocletian, he launched a scorched earth campaign deep into Alamannic territory in 288, refortifying the frontier.

Marcus Aurelius Mausaeus Carausius was a military commander of the Roman Empire in the 3rd century. He was a Menapian from Belgic Gaul, who usurped power in 286, during the Carausian Revolt, declaring himself emperor in Britain and northern Gaul. He did this only 13 years after the Gallic Empire of the Batavian Postumus was ended in 273. He held power for seven years, fashioning the name "Emperor of the North" for himself, before being assassinated by his finance minister Allectus.

Allectus was a Roman-Britannic usurper-emperor in Britain and northern Gaul from 293 to 296.
Julius Asclepiodotus was a Roman praetorian prefect who, according to the Historia Augusta, served under the emperors Aurelian, Probus and Diocletian, and was consul in 292. In 296, he assisted the western Caesar Constantius Chlorus in re-establishing Roman rule in Britain, following the illegal rules of Carausius and Allectus.

The Carausian revolt (AD 286–296) was an episode in Roman history during which a Roman naval commander, Carausius, declared himself emperor over Britain and northern Gaul. His Gallic territories were retaken by the western Caesar Constantius Chlorus in 293, after which Carausius was assassinated by his subordinate Allectus. Britain was regained by Constantius and his subordinate Asclepiodotus in 296.
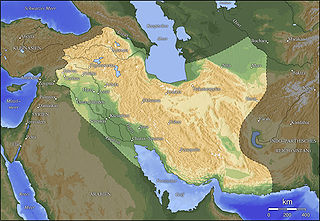
The Battle of Carrhae, also known as the Battle of Callinicum, took place in 296 or 297, after the invasion of Mesopotamia and Armenia by the Sasanian king Narseh. The battle took place between Carrhae (Harran) and Callinicum (al-Raqqah) and was a victory for the Sasanians. Narseh attacked with forces recruited from the Euphrates frontier. He managed to defeat his opponent by good timing.
The history of the Later Roman Empire covers the history of the Roman Empire from the beginning of the rule of Diocletian in 284 AD and the establishment of the Tetrarchy in 293 AD by Diocletian to the death of Heraclius in 641 AD.











