Related Research Articles
The 4th century BCE started the first day of 400 BCE and ended the last day of 301 BCE. It is considered part of the Classical era, epoch, or historical period.

The 5th century BC started the first day of 500 BC and ended the last day of 401 BC.
The 6th century BC started on the first day of 600 BC and ended on the last day of 501 BC.
This article concerns the period 479 BC – 470 BC.
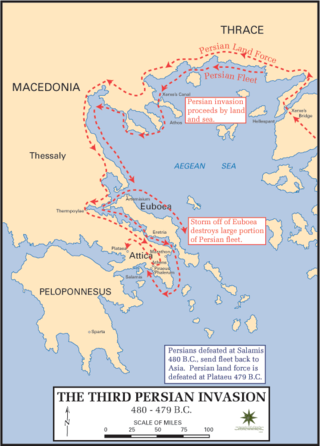
Year 480 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Vibulanus and Cincinnatus. The denomination 480 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
This article concerns the period 369 BC – 360 BC
This article concerns the period 339 BC – 330 BC.

This article concerns the period 329 BC – 320 BC.

This article concerns the period 309 BC – 300 BC.
This article concerns the period 269 BC – 260 BC.

Year 333 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Dictatorship of Rufinus. The denomination 333 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
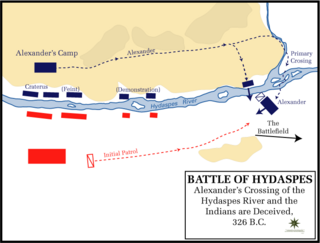
Year 326 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Visolus and Cursor. The denomination 326 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 278 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Luscinus and Papus. The denomination 278 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 281 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Barbula and Philippus. The denomination 281 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Nearchus or Nearchos was one of the Greek officers, a navarch, in the army of Alexander the Great. He is known for his celebrated expeditionary voyage starting from the Indus River, through the Persian Gulf and ending at the mouth of the Tigris River following the Indian campaign of Alexander the Great, in 326–324 BC.
King Huiwen of Qin, also known as Lord Huiwen of Qin, personal name Ying Si, was the ruler of the Qin state from 338 to 311 BC. He was the first ruler of Qin to style himself "King" (王) instead of "Duke" (公).

King Wuling of Zhao, personal name Zhao Yong, was a ruler of the Zhao state. His reign was famous for one important event: the reforms consisting of "Wearing the Hu (styled) Attire and Shooting from Horseback " (胡服騎射). He was credited for the implementation of protective outfit during military events and proceedings.
Peithon, son of Agenor (Αγήνωρ) was an officer in the expedition of Alexander the Great to India, who became satrap of the Indus from 325 to 316 BC, and then satrap of Babylon, from 316 to 312 BC, until he died at the Battle of Gaza in 312 BC.

The Indian campaign of Alexander the Great began in 327 BC and lasted until 325 BC. After conquering the Achaemenid Persian Empire, the Macedonian army undertook an expedition into the northwestern Indian subcontinent. Within two years, Alexander expanded the Macedonian Empire to include present-day Punjab and Sindh in what is modern-day Pakistan, surpassing the earlier frontiers that had been established by the Persian conquest of the Indus Valley.