The 470s decade ran from January 1, 470, to December 31, 479.
The 430s decade ran from January 1, 430, to December 31, 439.
The 500s decade ran from January 1, 500, to December 31, 509.
The 510s decade ran from January 1, 510, to December 31, 519.
The 520s decade ran from January 1, 520, to December 31, 529.
The 480s decade ran from January 1, 480, to December 31, 489.
The 450s decade ran from January 1, 450, to December 31, 459.

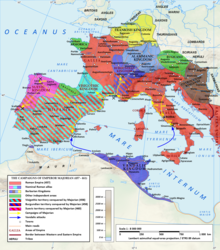
Year 451 (CDLI) was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Marcianus and Adelfius. The denomination 451 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
The 440s decade ran from January 1, 440, to December 31, 449.
The 460s decade ran from January 1, 460, to December 31, 469.

Year 456 (CDLVI) was a leap year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Avitus without colleague. The denomination 456 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Year 460 (CDLX) was a leap year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Magnus and Apollonius. The denomination 460 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Majorian was Western Roman emperor from 457 to 461. A prominent commander in the Western military, Majorian deposed Avitus in 457 with the aid of his ally Ricimer at the Battle of Placentia. Possessing little more than Italy and Dalmatia, as well as some territory in Hispania and northern Gaul, Majorian campaigned rigorously for three years against the Empire's enemies. In 461, he was murdered at Dertona in a conspiracy, and his successors until the fall of the Empire in 476 were puppets either of barbarian generals or the Eastern Roman court.

Eparchius Avitus was Roman emperor of the Western Empire from July 455 to October 456. He was a senator of Gallic extraction and a high-ranking officer both in the civil and military administration, as well as Bishop of Piacenza.
Gondioc, also called Gunderic and Gundowech, was a King of the Burgundians, succeeding his putative father Gunther in 436.
Nepotianus was a general of the Western Roman Empire.
The Battle of Arles was fought in 458 near Arelate (Arles) between Western Roman Emperor Majorian and Visigothic king Theodoric II. After the assassination of Flavius Aetius in 454, the Visigoths began to expand their kingdom at the expense of the crumbling Roman administration in Gaul and Hispania. When Majorian became emperor in 457, the Visigoths under king Theodoric II had just recently defeated the Suebic Kingdom in north-west Hispania and were consolidating their hold on the rest of the Iberian Peninsula.
The Battle of Toulouse was fought in the Gothic War between the Visigoths and the Western Roman Empire in 458. The battle was part of a great mid-winter expedition made across the alps by Emperor Majorian, taking a large army from Italy into Gaul with the goal of restoring the region to Roman rule after the disastrous reign of Avitus. Majorian and the Visigothic king Theodoric II fought a battle at Toulouse, in which the Visigoths were defeated. Majorian thereafter secured the cooperation of the Visigoths against the Suebi in Spain. However, fighting resumed, and Theodoric was finally defeated at Orléans in 463.

The Gothic War in Spain of 456 was a military operation of the Visigoths commissioned by the West Roman emperor Avitus. This operation consisted of an extensive campaign aimed at reclaiming the Spanish provinces of Lusitania and Betica that were in the hands of the Suebi and threatened Roman power in the provinces of Cartaginensis and Tarraconensis. The main players in this war were Theoderic II who led the army of the Visigoths and Rechiar the king of the Suebi. The Visigothic army was supported by Franks and Burgundian auxiliary troops.

The Gothic War of 457–458 was a military conflict between the Visigoths of Theoderic II against the Western Roman Empire of Emperor Majorian. The war began in 457 with a revolt of the Goths in Aquitania that pushed aside Roman authority, followed by an aggressive conquest in the adjacent Septimania aimed at area expansion. The war ended with a Roman victory over the Goths in the Battle of Arles in 458.