Related Research Articles
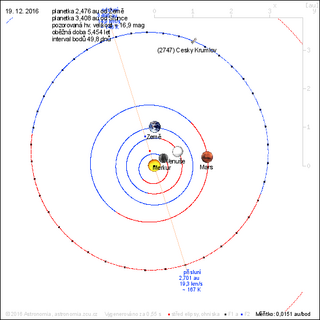
2747 Český Krumlov, provisional designation 1980 DW, is a carbonaceous asteroid and slow rotator from the outer regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 22 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered by Czech astronomer Antonín Mrkos at Kleť Observatory on 19 February 1980, and named for the Czech town of Český Krumlov.
4349 Tibúrcio, provisional designation 1989 LX, is a dark asteroid from the central region of the asteroid belt, approximately 29 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 5 June 1989, by German astronomer Werner Landgraf at ESO's La Silla Observatory in northern Chile.
2007 McCuskey, provisional designation 1963 SQ, is a carbonaceous asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 22 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 22 September 1963, by astronomers of the Indiana Asteroid Program at Goethe Link Observatory near Brooklyn, Indiana, United States. The asteroid was later named after American astronomer Sidney McCuskey.

1039 Sonneberga, provisional designation 1924 TL, is a dark background asteroid, approximately 34 kilometers in diameter, located in the central region of the asteroid belt. It was discovered on 24 November 1924, by German astronomer Max Wolf at Heidelberg Observatory in southwest Germany. The asteroid was named for the German city of Sonneberg, where the Sonneberg Observatory is located.

1214 Richilde, provisional designation 1932 AA, is a dark background asteroid from the central regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 35 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered by Max Wolf at Heidelberg Observatory in 1932. Any reference of the asteroid's name to a person is unknown.
1041 Asta, provisional designation 1925 FA, is a carbonaceous background asteroid from the outer regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 57 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 22 March 1925, by German astronomer Karl Reinmuth at the Heidelberg Observatory in southwest Germany. The asteroid was likely named after Danish actress Asta Nielsen.

1081 Reseda is a dark background asteroid from the outer regions of the asteroid belt. It was discovered on 31 August 1927, by astronomer Karl Reinmuth at the Heidelberg-Königstuhl State Observatory in southwest Germany. The asteroid has a rotation period of 7.3 hours and measures approximately 37 kilometers in diameter. It was named after the herbaceous plant Reseda.
6433 Enya, provisional designation 1978 WC, is a stony background asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 7 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 18 November 1978, by Czech astronomer Antonín Mrkos at the Kleť Observatory in the Czech Republic. It was named for Irish musician Enya.
1136 Mercedes, provisional designation 1929 UA, is a background asteroid from the central regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 26 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 30 October 1929, by Catalan astronomer Josep Comas i Solà at the Fabra Observatory in Barcelona, Spain. The asteroid was named for the sister-in-law of the discoverer.
1159 Granada, provisional designation 1929 RD, is a dark background asteroid and relatively slow rotator from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 30 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 2 September 1929, by astronomer Karl Reinmuth at the Heidelberg Observatory in southwest Germany. The asteroid was named for the Spanish city and province of Granada.
7167 Laupheim, provisional designation 1985 TD3, is a dark background asteroid from the outer regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 20 kilometers (12 miles) in diameter. It was discovered on 12 October 1985, by American astronomers Carolyn and Eugene Shoemaker at the Palomar Observatory in California. The presumed C-type asteroid has a rotation period of 7.04 hours and was named for Robert Clausen and his team at the public Laupheim Observatory in Germany.
11277 Ballard, provisional designation 1988 TW2, is a Phocaea asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 6.3 kilometers (3.9 miles) in diameter. It was discovered on 8 October 1988, by American astronomer couple Carolyn and Eugene Shoemaker at the Palomar Observatory in California. The assumed S-type asteroid has a rotation period of at least 10 hours. It was named for American marine scientist Robert Ballard.
1267 Geertruida, provisional designation 1930 HD, is a carbonaceous background asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 20 kilometers in diameter. Discovered by astronomer Hendrik van Gent at Johannesburg Observatory in 1930, the asteroid was later named after Geertruid Pels, sister of Dutch astronomer Gerrit Pels.
5385 Kamenka, provisional designation 1975 TS3, is a background asteroid from the outer regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 16 kilometers (10 miles) in diameter. It was discovered on 3 October 1975, by Soviet astronomer Lyudmila Chernykh at the Crimean Astrophysical Observatory in Nauchnij, on the Crimean peninsula. The presumed C-type asteroid has a rotation period of 6.68 hours. It was named for the Ukrainian town of Kamianka.
1383 Limburgia, provisional designation 1934 RV, is a carbonaceous asteroid from the outer region of the asteroid belt, approximately 23 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 9 September 1934, by Dutch astronomer Hendrik van Gent at the Leiden Southern Station, annex to the Johannesburg Observatory in South Africa. It is named for the Dutch province Limburg.
1428 Mombasa, provisional designation 1937 NO, is a dark asteroid from the middle region of the asteroid belt, approximately 56 kilometers in diameter.
1692 Subbotina, provisional designation 1936 QD, is a dark background asteroid from the central region of the asteroid belt, approximately 37 kilometers in diameter. The carbonaceous Cg-type asteroid has a rotation period of 9.2 hours. It was discovered by Grigory Neujmin at the Crimean Simeiz Observatory in 1936, and later named after Soviet mathematician and astronomer Mikhail Subbotin.
4962 Vecherka, provisional designation 1973 TP, is a Eunomian asteroid and slow rotator from the central regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 10 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 1 October 1973, by Soviet astronomer Tamara Smirnova at the Crimean Astrophysical Observatory in Nauchnij, on the Crimean peninsula. The asteroid was named after Vechernij Petersburg, a newspaper that also publishes astronomical information.
11441 Anadiego, provisional designation 1975 YD, is a stony background asteroid from the central region of the asteroid belt, approximately 7 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 31 December 1975, by Argentine astronomer Mario R. Cesco at the El Leoncito Complex in western Argentina. It was named in memory of Argentine political activist Ana Diego.
(7563) 1988 BC, provisional designation 1988 BC, is a background asteroid from the central region of the asteroid belt, approximately 16 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 16 January 1988, by Japanese amateur astronomer Takuo Kojima at the YGCO Chiyoda Station in the Kantō region of Japan. The asteroid has a rotation period of 6.5 hours.
References
- 1 2 3 4 "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: 6349 Acapulco (1995 CN1)" (2017-06-03 last obs.). Jet Propulsion Laboratory . Retrieved 21 June 2017.
- 1 2 3 4 Schmadel, Lutz D. (2007). "(6349) Acapulco". Dictionary of Minor Planet Names – (6349) Acapulco. Springer Berlin Heidelberg. p. 526. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-29925-7_5810. ISBN 978-3-540-00238-3.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "LCDB Data for (6349) Acapulco". Asteroid Lightcurve Database (LCDB). Retrieved 27 April 2016.
- 1 2 "Asteroid 6349 Acapulco – Nesvorny HCM Asteroid Families V3.0". Small Bodies Data Ferret. Retrieved 27 October 2019.
- 1 2 3 4 Nugent, C. R.; Mainzer, A.; Masiero, J.; Bauer, J.; Cutri, R. M.; Grav, T.; et al. (December 2015). "NEOWISE Reactivation Mission Year One: Preliminary Asteroid Diameters and Albedos". The Astrophysical Journal. 814 (2): 13. arXiv: 1509.02522 . Bibcode:2015ApJ...814..117N. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/814/2/117. S2CID 9341381 . Retrieved 21 June 2017.
- 1 2 3 Tedesco, E. F.; Noah, P. V.; Noah, M.; Price, S. D. (October 2004). "IRAS Minor Planet Survey V6.0". NASA Planetary Data System. 12: IRAS-A-FPA-3-RDR-IMPS-V6.0. Bibcode:2004PDSS...12.....T . Retrieved 22 October 2019.
- 1 2 3 4 Mainzer, A.; Grav, T.; Masiero, J.; Hand, E.; Bauer, J.; Tholen, D.; et al. (November 2011). "NEOWISE Studies of Spectrophotometrically Classified Asteroids: Preliminary Results". The Astrophysical Journal. 741 (2): 25. arXiv: 1109.6407 . Bibcode:2011ApJ...741...90M. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/741/2/90. S2CID 118700974 . Retrieved 27 April 2016.
- 1 2 Masiero, Joseph R.; Mainzer, A. K.; Grav, T.; Bauer, J. M.; Cutri, R. M.; Dailey, J.; et al. (November 2011). "Main Belt Asteroids with WISE/NEOWISE. I. Preliminary Albedos and Diameters". The Astrophysical Journal. 741 (2): 20. arXiv: 1109.4096 . Bibcode:2011ApJ...741...68M. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/741/2/68. S2CID 118745497 . Retrieved 5 December 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 Usui, Fumihiko; Kuroda, Daisuke; Müller, Thomas G.; Hasegawa, Sunao; Ishiguro, Masateru; Ootsubo, Takafumi; et al. (October 2011). "Asteroid Catalog Using Akari: AKARI/IRC Mid-Infrared Asteroid Survey". Publications of the Astronomical Society of Japan. 63 (5): 1117–1138. Bibcode:2011PASJ...63.1117U. doi:10.1093/pasj/63.5.1117. (online, AcuA catalog p. 153)
- 1 2 3 4 Masiero, Joseph R.; Mainzer, A. K.; Grav, T.; Bauer, J. M.; Cutri, R. M.; Nugent, C.; et al. (November 2012). "Preliminary Analysis of WISE/NEOWISE 3-Band Cryogenic and Post-cryogenic Observations of Main Belt Asteroids". The Astrophysical Journal Letters. 759 (1): 5. arXiv: 1209.5794 . Bibcode:2012ApJ...759L...8M. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/759/1/L8. S2CID 46350317 . Retrieved 11 January 2016.
- 1 2 3 4 Nugent, C. R.; Mainzer, A.; Bauer, J.; Cutri, R. M.; Kramer, E. A.; Grav, T.; et al. (September 2016). "NEOWISE Reactivation Mission Year Two: Asteroid Diameters and Albedos". The Astronomical Journal. 152 (3): 12. arXiv: 1606.08923 . Bibcode:2016AJ....152...63N. doi: 10.3847/0004-6256/152/3/63 . S2CID 119289027.
- 1 2 3 Waszczak, Adam; Chang, Chan-Kao; Ofek, Eran O.; Laher, Russ; Masci, Frank; Levitan, David; et al. (September 2015). "Asteroid Light Curves from the Palomar Transient Factory Survey: Rotation Periods and Phase Functions from Sparse Photometry". The Astronomical Journal. 150 (3): 35. arXiv: 1504.04041 . Bibcode:2015AJ....150...75W. doi:10.1088/0004-6256/150/3/75. S2CID 8342929 . Retrieved 27 April 2016.
- ↑ Veres, Peter; Jedicke, Robert; Fitzsimmons, Alan; Denneau, Larry; Granvik, Mikael; Bolin, Bryce; et al. (November 2015). "Absolute magnitudes and slope parameters for 250,000 asteroids observed by Pan-STARRS PS1 - Preliminary results". Icarus. 261: 34–47. arXiv: 1506.00762 . Bibcode:2015Icar..261...34V. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2015.08.007. S2CID 53493339 . Retrieved 27 April 2016.
- 1 2 "6349 Acapulco (1995 CN1)". Minor Planet Center. Retrieved 27 April 2016.
- ↑ "MPC/MPO/MPS Archive". Minor Planet Center. Retrieved 27 April 2016.