Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordered by Pakistan to the east and south, Iran to the west, Turkmenistan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, Tajikistan to the northeast, and China to the northeast and east. Occupying 652,864 square kilometres (252,072 sq mi) of land, the country is predominantly mountainous with plains in the north and the southwest, which are separated by the Hindu Kush mountain range. Kabul is the country's largest city and serves as its capital. As of 2021, Afghanistan's population is 40.2 million, composed of ethnic Pashtuns, Tajiks, Hazaras, Uzbeks, Turkmens, Qizilbash, Aimak, Pashayi, Baloch, Pamiris, Nuristanis, and others.

Ahmad Shāh Durrānī, also known as Ahmad Shāh Abdālī, was the founder of the Durrani Empire and is regarded as the founder of the modern Afghanistan. In July 1747, Ahmad Shah was appointed as King of the Afghans by a loya jirga in Kandahar, where he set up his capital. Primarily with the support of the Pashtun tribes, Ahmad Shah pushed east towards the Mughal and Maratha Empires of India, west towards the disintegrating Afsharid Empire of Iran, and north towards the Khanate of Bukhara of Turkestan. Within a few years, he extended his control from Khorasan in the west to North India in the east, and from the Amu Darya in the north to the Arabian Sea in the south.

The Amu Darya is a major river in Central Asia and Afghanistan. Rising in the Pamir Mountains, north of the Hindu Kush, the Amu Darya is formed by the confluence of the Vakhsh and Panj rivers, in the Tigrovaya Balka Nature Reserve on the border between Afghanistan and Tajikistan, and flows from there north-westwards into the southern remnants of the Aral Sea. In its upper course, the river forms part of Afghanistan's northern border with Tajikistan, Uzbekistan, and Turkmenistan. In ancient history, the river was regarded as the boundary of Greater Iran with "Turan", which roughly corresponded to present-day Central Asia. The Amu Darya has a flow of about 70 cubic kilometres per year on average.

The history of Afghanistan, preceding the establishment of the Emirate of Afghanistan in 1823 is shared with that of neighbouring Iran, central Asia and Indian subcontinent. The Sadozai monarchy ruled the Afghan Durrani Empire, considered the founding state of modern Afghanistan. The written recorded history of the land presently constituting Afghanistan can be traced back to around 500 BCE when the area was under the Achaemenid Empire, although evidence indicates that an advanced degree of urbanized culture has existed in the land since between 3000 and 2000 BCE. Bactria dates back to 2500 BCE. The Indus Valley civilisation stretched up to large parts of Afghanistan in the north. Alexander the Great and his Macedonian army arrived at what is now Afghanistan in 330 BCE after the fall of the Achaemenid Empire during the Battle of Gaugamela. Since then, many empires have established capitals in Afghanistan, including the Greco-Bactrians, Kushans, Indo-Sassanids, Kabul Shahi, Saffarids, Samanids, Ghaznavids, Ghurids, Kartids, Timurids, Hotakis and Durranis.

The Hazaras are an ethnic group and a principal component of the population of Afghanistan, native to, and primarily residing in the Hazaristan region in central Afghanistan and the northern regions of the Baluchistan province in Pakistan. They are one of the largest ethnic groups in Afghanistan, and a significant minority group in Pakistan, mostly in Quetta, and as well as in Iran. They speak the Dari and Hazaragi dialects of Persian. Dari, one of the two official languages in Afghanistan.

Kabul is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province; it is administratively divided into 22 municipal districts. According to 2023 estimates, the population of Kabul was 5 million people. In contemporary times, the city has served as Afghanistan's political, cultural, and economical center, and rapid urbanisation has made Kabul the 75th-largest city in the world and the country's primate city.

Kandahar is a city in Afghanistan, located in the south of the country on the Arghandab River, at an elevation of 1,010 m (3,310 ft). It is Afghanistan's second largest city after Kabul, with a population of about 614,118. It is the capital of Kandahar Province as well as the headquarters of the Taliban, formally known as the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan. It is also the centre of the larger cultural region called Loy Kandahar.

The Taliban, which also refers to itself by its state name, the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a Deobandi Islamic fundamentalist and Pashtun nationalist militant political movement in Afghanistan. It ruled approximately three-quarters of the country from 1996 to 2001, before being overthrown following the United States invasion. It recaptured Kabul on 15 August 2021 after nearly 20 years of insurgency, and currently controls all of the country, although its government has not yet been recognized by any country. The Taliban government has been criticized for restricting human rights in Afghanistan, including the right of women and girls to work and to have an education.

Pashtuns, also known as Pakhtuns or Pathans, are an Eastern Iranian ethnic group primarily residing in southern and eastern Afghanistan and northwestern Pakistan. They historically were also referred to as Afghans until the 1970s, after the term's meaning had become a demonym for members of all ethnic groups in Afghanistan.

Tajiks are a Persian-speaking Iranian ethnic group native to Central Asia, living primarily in Afghanistan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan. Tajiks are the largest ethnicity in Tajikistan, and the second-largest in Afghanistan and Uzbekistan. They speak varieties of Persian, a Western Iranian language. In Tajikistan, since the 1939 Soviet census, its small Pamiri and Yaghnobi ethnic groups are included as Tajiks. In China, the term is used to refer to its Pamiri ethnic groups, the Tajiks of Xinjiang, who speak the Eastern Iranian Pamiri languages. In Afghanistan, the Pamiris are counted as a separate ethnic group.

Dari, also known as Dari Persian, is the variety of the Persian language spoken in Afghanistan. Dari is the term officially recognised and promoted since 1964 by the Afghan government for the Persian language, hence it is known as Afghan Persian or Eastern Persian in many Western sources. As Professor Nile Green remarks "the impulses behind renaming of Afghan Persian as Dari were more nationalistic than linguistic" in order to create an Afghan state narrative. Apart from a few basics of vocabulary, there is little difference between formal written Persian of Afghanistan and Iran. The term "Dari" is officially used for the characteristic spoken Persian of Afghanistan, but is best restricted to formal spoken registers. Persian-speakers in Afghanistan still prefer to call their language “Farsi,” while Pashto-speakers may sometimes refer to it as "Parsi." Farsi Dari serves as the lingua franca for interethnic communications in Afghanistan.
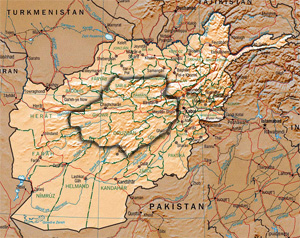
Hazaristan, or Hazarajat is a mostly mountainous region in the central highlands of Afghanistan, among the Koh-i-Baba mountains in the western extremities of the Hindu Kush. It is the homeland of the Hazara people who make up the majority of its population. Hazarajat denotes an ethnic and religious zone.

Kunduz is a city in northern Afghanistan, the capital of Kunduz Province. The city has an estimated population of about 268,893 as of 2015, making it about the 7th-largest city of Afghanistan, and the largest city in northeastern Afghanistan. Kunduz is in the historical Tokharistan region of Bactria, near the confluence of the Kunduz River with the Khanabad River. Kunduz is linked by highways with Kabul to the south, Mazar-i-Sharif to the west, and Badakhshan to the east. Kunduz is also linked with Dushanbe in Tajikistan to the north, via the Afghan dry port of Sherkhan Bandar. This city is famous in Afghanistan for its watermelon.

Nimruz or Nimroz is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan, located in the southwestern part of the country. It lies to the east of the Sistan and Baluchestan Province of Iran and north of Balochistan, Pakistan, also bordering the Afghan provinces of Farah and Helmand. It has a population of about 186,963 people. The province is divided into five districts, encompassing about 649 villages.

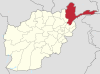
Nuristan, also spelled as Nurestan or Nooristan, is one of the 34 provinces of Afghanistan, located in the eastern part of the country. It is divided into seven districts and is Afghanistan's least populous province, with a population of around 167,000. Parun serves as the provincial capital. Nuristan is bordered on the south by Laghman and Kunar provinces, on the north by Badakhshan province, on the west by Panjshir province.

Buddhism, an Indian religion founded by Gautama Buddha, first arrived in modern-day Afghanistan through the conquests of Ashoka, the third emperor of the Maurya Empire. Among the earliest notable sites of Buddhist influence in the country is a bilingual mountainside inscription in Greek and Aramaic that dates back to 260 BCE and was found on the rocky outcrop of Chil Zena near Kandahar.

The Emirate of Afghanistan, known as the Emirate of Kabul until 1855, was an emirate in Central Asia and South Asia that encompassed present-day Afghanistan and parts of present-day Pakistan. The emirate emerged from the Durrani Empire, when Dost Mohammad Khan, the founder of the Barakzai dynasty in Kabul, prevailed.

The Kingdom of Afghanistan was a constitutional monarchy in Central Asia established in 1926 as a successor state to the Emirate of Afghanistan. It was proclaimed by its first king, Amanullah Khan, seven years after he acceded to the throne. The monarchy ended in the 1973 Afghan coup d'état.
Bagram is a district of Parwan province, Afghanistan. Its seat lies at Bagram, which lies about 60 kilometers north of the capital of Kabul. It borders Kabul District to the south, Shinwari District to the east, and Chaharikar District to the north.