Related Research Articles

On 26 March 2015, Saudi Arabia, leading a coalition of nine countries from West Asia and North Africa, launched a military intervention in Yemen at the request of Yemeni president Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi, who had been ousted from the capital, Sanaa, in September 2014 by Houthi insurgents during the Yemeni Civil War. Efforts by the United Nations to facilitate a power sharing arrangement under a new transitional government collapsed, leading to escalating conflict between government forces, Houthi rebels, and other armed groups, which culminated in Hadi fleeing to Saudi Arabia shortly before it began military operations in the country.
International reactions to the Saudi-led intervention in Yemen of 2015 were mixed. Most other Arab League nations and several Western governments backed the Saudi Arabia-led military coalition, but other governments warned against an escalation in the violent situation in Yemen.

The siege of Taiz is an ongoing, protracted military confrontation between opposing Yemeni forces in the city of Taiz for control of the city and surrounding area. The battle began one month after the start of the Yemeni Civil War.
On 24 July 2015, between 9:30 and 10:00 p.m., the city of Mokha, Yemen, was bombed by the Saudi Arabian led coalition. The airstrikes struck two worker housing complexes for engineers and technicians at the Mokha steam power plant. The attack left between 65 and 120 dead, including at least 10 children.

The Houthi–Saudi Arabian conflict is an ongoing armed conflict between the Royal Saudi Armed Forces and Iran-backed Yemeni Houthi forces that has been taking place in the Arabian Peninsula, including the southern Saudi regions of Asir, Jizan, and Najran, and northern Yemeni governorates of Saada, Al Jawf, and Hajjah, since the onset of the Saudi Arabian-led intervention in Yemen in 2015.
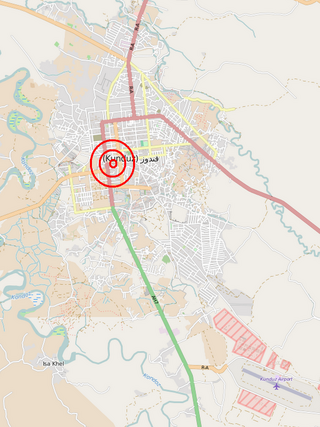
On 3 October 2015, a United States Air Force AC-130U gunship attacked the Kunduz Trauma Centre operated by Médecins Sans Frontières in the city of Kunduz, in the province of the same name in northern Afghanistan. 42 people were killed and over 30 were injured. Médecins Sans Frontières condemned the incident, calling it a deliberate breach of international humanitarian law and a war crime. It further stated that all warring parties had been notified about the hospital and its operations well in advance.

Almigdad Mojalli was a Yemeni freelance journalist working for the United States media service Voice of America. On 17 January 2016 Mojalli was killed by a Saudi airstrike in a village near Sana'a while attempting to report on the Saudi Arabian-led intervention in Yemen.
The Battle of Port Midi refers to a battle during the Yemeni Civil War between the Saudi coalition-backed Hadi loyalists and the Houthi government. Although Hadi loyalists seized the port, the Houthi fighters along with the popular committees managed to conduct some attacks around Midi. The conflict also had spillovers in the rest of the Hajjah Governorate. On 26 January 2017, Hadi loyalists extended their control to Harad District in Hajjah Governorate.

War crimes and human rights violations, committed by all warring parties, have been widespread throughout the Yemeni civil war. This includes the two main groups involved in the ongoing conflict: forces loyal to the current Yemeni president, Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi, and Houthis and other forces supporting Ali Abdullah Saleh, the former Yemeni president. Al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula and the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant have also carried out attacks in Yemen. The Saudi-led coalition, backed by the United States and other nations, has also been accused of violating human rights and breaking international law, especially in regards to airstrikes that repeatedly hit civilian targets.
The Aleppo bombings were intense bombardments on both rebel and government-held areas in the city of Aleppo, Syria starting in late April 2016. Some rebel shelling also hit a Kurdish-held part of the city. The bombings decreased in intensity after 55 days when a temporary truce was established. However, the bombings continued through July.
The following lists events that will happen in 2016 in Yemen.
The Sanaa funeral airstrike took place on the afternoon of 8 October 2016 when 155 people were killed and at least 525 more wounded when two airstrikes, about three to eight minutes apart, hit the packed Al Kubra hall in Sanaa, Yemen during a funeral. The attack was the deadliest single bombing in the then-two year long Yemeni civil war. The funeral was being held for the father of former interior minister Jalal al-Rowaishan. Sanaa mayor Abdel Qader Hilal was reportedly among those killed. The Saudi-led coalition initially denied responsibility but then took responsibility and put the blame on information given by the Yemeni government.
The following is a timeline of the Yemeni civil war, which began in September 2014.

On 22 April 2018, an airstrike by the Saudi Arabian-led coalition hit a wedding in the Bani Qa'is District of Hajjah Governorate, Yemen. Casualty estimates vary, with the Houthi-owned Al-Masirah reporting the toll later that day to be at least 33 civilians including the bride. Forty-five other people were injured.

The siege of Al Hudaydah, codenamed Operation Golden Victory, was a major Saudi-led coalition assault on the port city of Al Hudaydah in Yemen. It was spearheaded by the United Arab Emirates and Saudi Arabia and has been considered as the largest battle since the start of Saudi Arabian-led intervention in Yemen in 2015.
On 9 August 2018, Saudi Arabian expeditionary aircraft bombed a civilian school bus passing through a crowded market in Dahyan, Saada Governorate, Yemen, near the border with Saudi Arabia. At least 40 children were killed, all under 15 years old and most under age 10. Sources disagree on the exact number of deaths, but they estimate that the air strike killed about 51 people.
During the Yemeni civil war, Saudi Arabia led an Arab coalition of nine nations from the Middle East and parts of Africa in response to calls from the internationally recognized pro-Saudi president of Yemen Abdrabbuh Mansur Hadi for military support after he was ousted by the Houthi movement due to economic and political grievances, and fled to Saudi Arabia.

Turki bin Saleh Al-Maliki is a Saudi Arabian military officer and member of the Department of Plans and Operations at the command of the Royal Saudi Air Force. He is the spokesperson for the Saudi-led Coalition in Yemen since 2017, succeeding Major General Ahmad Asiri, who was the head of the mission since the start of the military intervention led by the Saudi Armed Forces, Operation Decisive Storm, and then Operation Restoring Hope in Yemen.
On 21 January 2022, according to news sources a Saudi-led coalition carried out an airstrike on a prison in Saada, Yemen, killing at least 87 people. The coalition denied targeting the center.
The following is a timeline of the Yemeni humanitarian crisis, ongoing since the mid-2010s.
References
- ↑ "Yemen crisis: Why is there a war?". BBC News. 19 June 2020.
- ↑ "Saudi 'Decisive Storm' waged to save Yemen". english.alarabiya.net. 25 March 2015.
- ↑ "Report: Over 130 attacks on medical facilities in Yemen war". AP NEWS. 2019-11-14. Retrieved 2022-10-26.
- ↑ "Yemen - Doctors Without Borders - USA". www.doctorswithoutborders.org.
- ↑ "Saudi blacklist call over Yemen attacks". BBC News. 20 April 2017.
- ↑ "Yemen: Events of 2020". World Report 2021: Yemen | Human Rights Watch. 13 January 2021.
- ↑ "Bombing of schools by Saudi Arabia-led coalition a flagrant attack on future of Yemen's children". www.amnesty.org. 11 December 2015.
- ↑ Dehghan, Saeed Kamali (9 August 2018). "Dozens dead in Yemen as bus carrying children hit by airstrike". the Guardian.
- ↑ Hubbard, Ben (14 November 2016). "U.S. Fingerprints on Attacks Obliterating Yemen's Economy". The New York Times.
- ↑ "Saudi-led coalition air strikes 'hit Yemen school'" . Independent.co.uk . 22 January 2017. Archived from the original on 2017-01-24.
- ↑ Ratcliffe, Rebecca (19 July 2017). "UN warned not to whitewash 'grave violations against children' in Yemen". the Guardian.
- ↑ "The UN just accused Saudi Arabia led coalition of war crimes" . Independent.co.uk . 21 October 2016. Archived from the original on 2016-10-22.
- ↑ "Death toll from Saudi airstrike on Yemeni wedding rises to 88: report". 23 April 2018. Archived from the original on 1 April 2019. Retrieved 30 April 2018.
- ↑ Al-Batati, Saeed; Gladstone, Rick (2 April 2018). "Saudi Bombing Is Said to Kill Yemeni Civilians Seeking Relief From the Heat". The New York Times.
- ↑ Al Jazeera Staff. "War looms large as Yemeni children head back to school". www.aljazeera.com. Retrieved 2022-10-26.
- ↑ "Saudi-led air strikes in Yemen killed 68 civilians in one day, UN says" . Independent.co.uk . 28 December 2017. Archived from the original on 2017-12-28.
- ↑ "Exposed: British-made bombs used on civilian targets in Yemen | Amnesty International UK".
- ↑ "Yemen conflict: MSF hospital destroyed by air strikes". BBC News. 27 October 2015. Retrieved 3 February 2017.
- ↑ "MSF hospital in Yemen bombed by airstrike", Xinhua (2015-10-28)
- ↑ "Exclusive: Saudi Arabia Admits Bombing MSF Hospital in Yemen — But Faults MSF - VICE News". 27 October 2015. Retrieved 3 February 2017.
- ↑ Noah Browning, "Yemeni MSF hospital bombed, Saudi-led coalition denies responsibility", Reuters (October 27 2015)
- ↑ "Doctors Without Borders says Saudi-led airstrikes bomb Yemen hospital", Associated Press (October 28, 2015)
- ↑ "Yemen: Nine Wounded in Saudi-Led Coalition Airstrike on MSF Clinic in Taiz". 3 December 2015. Archived from the original on 30 January 2017. Retrieved 3 February 2017.
- ↑ "MSF-Supported Hospital Bombed in Northern Yemen", MSF (Update January 11 2016) Archived 2016-02-01 at the Wayback Machine .
- ↑ "Hospital Aided by Doctors Without Borders Is Bombed in Yemen". The New York Times. 11 January 2016. Retrieved 3 February 2017.
- ↑ Mark Tran, "Four patients among dead after explosion at hospital in Yemen", The Guardian (January 10, 2016).
- ↑ Adam Withnall, "Attacks on hospitals mean people in Yemen are now too scared to go for treatment, MSF says", The Independent (January 19, 2016).
- ↑ "Yemen: Even in War, Hospitals Should Be "Places of Refuge And Healing"". 19 January 2016. Archived from the original on 30 January 2017. Retrieved 3 February 2017.
- ↑ Devereaux, Ryan (2016-01-05). "Saudi Coalition Just Bombed a Center for the Blind in Yemen". The Intercept. Retrieved 2017-11-16.
- ↑ "Saudi blacklist call over Yemen attacks". BBC News. 2017-04-20. Retrieved 2017-11-16.
- ↑ Noah Browning and Tom Brown, "Airstrike Hits Doctors Without Borders Hospital in Yemen", Scientific American. On line, n.d.
- ↑ "Yemen: Death Toll Rises to 19 in Airstrike on MSF-Supported Hospital". 16 August 2016. Retrieved 3 February 2017.[ permanent dead link ]
- ↑ Gul Tuysuz; Steve Visser (15 August 2016). "Airstrike hits Yemen hospital, aid group says". CNN. Retrieved 3 February 2017.
- ↑ Bulos, Nabih (15 August 2016). "At least 11 dead as airstrike hits Doctors Without Borders hospital in northern Yemen". Los Angeles Times . Retrieved 3 February 2017.
- ↑ Dehghan, Saeed Kamali (15 August 2016). "At least 11 dead after Saudi-led coalition bombs Yemen hospital". The Guardian. Retrieved 3 February 2017.
- ↑ "MSF Evacuates Staff from Six Hospitals in Northern Yemen". 18 August 2016. Archived from the original on 11 February 2017. Retrieved 3 February 2017.
- ↑ "Bombing of Doctors Without Borders Hospital in Yemen Kills at Least 15". The New York Times. 16 August 2016. Retrieved 3 February 2017.
- ↑ "Yemen: Airstrike hits cholera treatment center in Abs". 12 June 2018. Retrieved 27 June 2018.
- ↑ "'It was a massacre': Dozens killed in Saudi air raids on Hodeidah". www.aljazeera.com.
- ↑ "Yemen war: Eight killed in air strike near Kitaf hospital - BBC News". BBC News. 26 March 2019.
- ↑ "Hospital hit in air strike as Yemenis mark four years of war". 27 March 2019.
- ↑ "Saudi-led air raids 'kill at least 11 civilians' in Yemen's Sanaa". aljazeera.com. Aljazeera. 7 April 2019. Retrieved 8 April 2019.
- ↑ "Explosion in Yemen Warehouse Kills at Least 13, Including 7 Children". The New York Times . Nytimes. 7 April 2019. Retrieved 8 April 2019.
- ↑ The Washington Post (6 November 2019). "Yemeni officials: Rebels missile, drone attack kills 8". Archived from the original on 7 November 2019.