Related Research Articles
MIPS is a family of reduced instruction set computer (RISC) instruction set architectures (ISA) developed by MIPS Computer Systems, now MIPS Technologies, based in the United States.

In electronics and computer science, a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) is a computer architecture designed to simplify the individual instructions given to the computer to accomplish tasks. Compared to the instructions given to a complex instruction set computer (CISC), a RISC computer might require more instructions in order to accomplish a task because the individual instructions are written in simpler code. The goal is to offset the need to process more instructions by increasing the speed of each instruction, in particular by implementing an instruction pipeline, which may be simpler to achieve given simpler instructions.
ARM is a family of RISC instruction set architectures (ISAs) for computer processors. Arm Holdings develops the ISAs and licenses them to other companies, who build the physical devices that use the instruction set. It also designs and licenses cores that implement these ISAs.
IA-64 is the instruction set architecture (ISA) of the discontinued Itanium family of 64-bit Intel microprocessors. The basic ISA specification originated at Hewlett-Packard (HP), and was subsequently implemented by Intel in collaboration with HP. The first Itanium processor, codenamed Merced, was released in 2001.
SuperH is a 32-bit reduced instruction set computing (RISC) instruction set architecture (ISA) developed by Hitachi and currently produced by Renesas. It is implemented by microcontrollers and microprocessors for embedded systems.
OpenRISC is a project to develop a series of open-source hardware based central processing units (CPUs) on established reduced instruction set computer (RISC) principles. It includes an instruction set architecture (ISA) using an open-source license. It is the original flagship project of the OpenCores community.

Blackfin is a family of 16-/32-bit microprocessors developed, manufactured and marketed by Analog Devices. The processors have built-in, fixed-point digital signal processor (DSP) functionality performed by 16-bit multiply–accumulates (MACs), accompanied on-chip by a microcontroller. It was designed for a unified low-power processor architecture that can run operating systems while simultaneously handling complex numeric tasks such as real-time H.264 video encoding.
Nios II is a 32-bit embedded processor architecture designed specifically for the Altera family of field-programmable gate array (FPGA) integrated circuits. Nios II incorporates many enhancements over the original Nios architecture, making it more suitable for a wider range of embedded computing applications, from digital signal processing (DSP) to system-control.
The MicroBlaze is a soft microprocessor core designed for Xilinx field-programmable gate arrays (FPGA). As a soft-core processor, MicroBlaze is implemented entirely in the general-purpose memory and logic fabric of Xilinx FPGAs.
PicoBlaze is the designation of a series of three free soft processor cores from Xilinx for use in their FPGA and CPLD products. They are based on an 8-bit RISC architecture and can reach speeds up to 100 MIPS on the Virtex 4 FPGA's family. The processors have an 8-bit address and data port for access to a wide range of peripherals. The license of the cores allows their free use, albeit only on Xilinx devices, and they come with development tools. Third-party tools are available from Mediatronix and others. Also PacoBlaze, a behavioral and device independent implementation of the cores exists and is released under the BSD License. The PauloBlaze is an open source VHDL implementation under the Apache License.

AVR32 is a 32-bit RISC microcontroller architecture produced by Atmel. The microcontroller architecture was designed by a handful of people educated at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology, including lead designer Øyvind Strøm and CPU architect Erik Renno in Atmel's Norwegian design center.
LatticeMico32 is a 32-bit microprocessor reduced instruction set computer (RISC) soft core from Lattice Semiconductor optimized for field-programmable gate arrays (FPGAs). It uses a Harvard architecture, which means the instruction and data buses are separate. Bus arbitration logic can be used to combine the two buses, if desired.
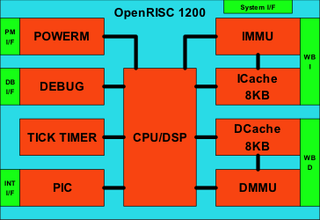
The OpenRISC 1200 (OR1200) is an implementation of the open source OpenRISC 1000 RISC architecture.
The R2000 is a 32-bit microprocessor chip set developed by MIPS Computer Systems that implemented the MIPS I instruction set architecture (ISA). Introduced in January 1986, it was, by a few months, the first commercial implementation of the RISC architecture. The R2000 competed with Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) VAX minicomputers and with Motorola 68000 and Intel Corporation 80386 microprocessors. R2000 users included Ardent Computer, DEC, Silicon Graphics, Northern Telecom and MIPS's own Unix workstations.
IBM Power microprocessors are designed and sold by IBM for servers and supercomputers. The name "POWER" was originally presented as an acronym for "Performance Optimization With Enhanced RISC". The Power line of microprocessors has been used in IBM's RS/6000, AS/400, pSeries, iSeries, System p, System i, and Power Systems lines of servers and supercomputers. They have also been used in data storage devices and workstations by IBM and by other server manufacturers like Bull and Hitachi.
RISC-V is an open standard instruction set architecture (ISA) based on established reduced instruction set computer (RISC) principles. The project began in 2010 at the University of California, Berkeley, transferred to the RISC-V Foundation in 2015, and on to RISC-V International, a Swiss non-profit entity, in November 2019. Like several other RISC ISAs, e.g. Amber (ARMv2) or OpenRISC, RISC-V is offered under royalty-free open-source licenses. The documents defining the RISC-V instruction set architecture (ISA) are offered under a Creative Commons license or a BSD License.
The ZPU is a microprocessor stack machine designed by Norwegian company Zylin AS to run supervisory code in electronic systems that include a field-programmable gate array (FPGA).
Microwatt is an open source soft processor core originally written in VHDL by Anton Blanchard at IBM, announced at the OpenPOWER Summit NA 2019 and published on GitHub in August 2019. It adheres to the Power ISA 3.0 instruction set and can be run on FPGA boards, booting Linux, MicroPython and Zephyr.
References
- ↑ Spooner, John G. (January 2, 2002). "Open-source credo moves to chip design". Tech Industry. CNET . Retrieved 2018-05-15.
- ↑ "Amber RISC Core". Soft Processor. 32bit micro. Archived from the original on 2015-02-02.
- ↑ van Someren, Alex; van Someren, Nic (February 1989). Archimedes Operating System: A Dabhand Guide (PDF). Dabs Press. ISBN 1-870336-48-8 . Retrieved 2018-05-15..
- ↑ VLSI Technology (1990). Acorn RISC Machine (ARM) Data Manual (PDF). Prentice Hall. ISBN 0-13-781618-9 . Retrieved 2018-05-15..