
A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on August 17, 1951. [1] The northern edges of the moon entered the southern edge of the earth's penumbral shadow, leading to visually minimal dimming.

A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on August 17, 1951. [1] The northern edges of the moon entered the southern edge of the earth's penumbral shadow, leading to visually minimal dimming.
| Center of moon | Lunar north pole |
|---|---|
 |  |
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saros | Date Viewing | Type Chart | Saros | Date Viewing | Type Chart | |
| 103 | 1951 Feb 21  | Penumbral | 108 | 1951 Aug 17  | Penumbral | |
| 113 | 1952 Feb 11  | Partial | 118 | 1952 Aug 5  | Partial | |
| 123 | 1953 Jan 29  | Total | 128 | 1953 Jul 26  | Total | |
| 133 | 1954 Jan 19  | Total | 138 | 1954 Jul 16  | Partial | |
| 143 | 1955 Jan 8  | Penumbral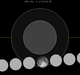 | ||||
| Last set | 1951 Mar 23 | Last set | 1951 Sep 15 | |||
| Next set | 1955 Nov 29 | Next set | 1955 Jun 5 | |||
This is the third of five Metonic lunar eclipses.
The Metonic cycle repeats nearly exactly every 19 years and represents a Saros cycle plus one lunar year. Because it occurs on the same calendar date, the earth's shadow will in nearly the same location relative to the background stars.
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saros | Date | Type | Saros | Date | Type | |
| 103 | 1951 Feb 21.88 | Penumbral | 108 | 1951 Aug 17.13 | Penumbral | |
 |  | |||||
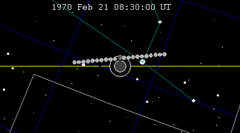
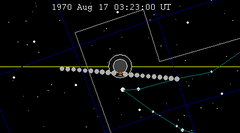
| 113 | 1970 Feb 21.35 | Partial | 118 | 1970 Aug 17.14 | Partial | |
 |  | |||||
| 123 | 1989 Feb 20.64 | Total | 128 | 1989 Aug 17.13 | Total | |
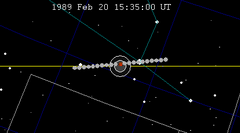 | 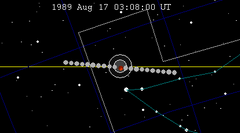 | |||||
| 133 | 2008 Feb 21.14 | Total | 138 | 2008 Aug 16.88 | Partial | |
 | 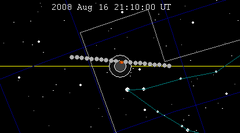 | |||||
| 143 | 2027 Feb 20.96 | Penumbral | 148 | 2027 Aug 17.30 | Penumbral | |
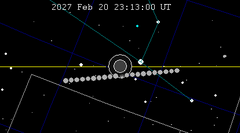 | 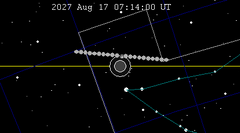 | |||||

A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on April 24, 2005, the first of two lunar eclipses in 2005. At maximum eclipse, 86.5% of the Moon's disc was partially shaded by the Earth, which caused a slight shadow gradient across its disc; this subtle effect may have been visible to careful observers. No part of the Moon was in complete shadow. The eclipse lasted 4 hours and 6 minutes overall, and was visible from east Asia, Australia, and the Americas.

A partial lunar eclipse took place on Monday, October 17, 2005, the second of two lunar eclipses in 2005. A tiny bite out of the Moon may have been visible at maximum, though just 6.25% of the Moon was shadowed in a partial eclipse which lasted for nearly 56 minutes and was visible over east Asia, Australasia, and most of the North America. A shading across the moon from the Earth's penumbral shadow should have been visible at maximum eclipse.

A partial lunar eclipse took place on Saturday, December 21, 1991, the last of four lunar eclipses in 1991. The moon grazed the northern edge of the umbral shadow.
A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on Thursday, March 3, 1988, the first of two lunar eclipses in 1988, the second being on August 27, 1988. Earlier sources compute this as a 0.3% partial eclipse lasting under 14 minutes, and newest calculations list it as a penumbral eclipse that never enters the umbral shadow. In a rare total penumbral eclipse, the entire Moon was partially shaded by the Earth, and the shading across the Moon should have been quite visible at maximum eclipse. The penumbral phase lasted for 4 hours, 53 minutes and 50.6 seconds in all, though for most of it, the eclipse was extremely difficult or impossible to see. The Moon was 2.2 days after apogee, making it 6.1% smaller than average.

A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on Thursday, June 27, 1991, the second of four lunar eclipses in 1991. The moon entered the Earth's penumbra for about 3 hours, and was difficult to see. This lunar eclipse is the predecessor of the Solar eclipse of July 11, 1991.
A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on Thursday, November 8, 1984, the last of three lunar eclipses in 1984. This subtle penumbral eclipse may have been visible to a skilled observer at maximum eclipse. 90% of the Moon's disc was partially shaded by the Earth, which caused a gentle shadow gradient across its disc at maximum; the eclipse as a whole lasted 4 hours and 28 minutes.
A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on Tuesday, May 15, 1984, the first of three lunar eclipses in 1984. This was a deep penumbral eclipse, with the southern limb of the Moon close to the Earth's shadow.

A penumbral lunar eclipse occurred on Friday, 5 May 2023, the first of two lunar eclipses in 2023. The moon's apparent diameter was 0.1% larger than average because it occurred 5.5 days before perigee. This was the deepest penumbral eclipse since February 2017 and until September 2042.
A partial lunar eclipse will take place on Saturday, 28 October 2023.

A penumbral lunar eclipse will take place on 20–21 February 2027.

A penumbral lunar eclipse will take place on Tuesday, August 17, 2027. It will cause a subtle dimming as 54.56% of the Moon will cross within Earth's penumbral shadow.
A partial lunar eclipse will take place on May 16, 2041.
A partial lunar eclipse will take place on November 8, 2041.

A penumbral lunar eclipse will take place on October 28, 2042, according to some sources. This will be 0.4 days after the Moon reached perigee. This event marks the beginning of lunar saros cycle 156 according to some sources, and will be visually imperceptible and other sources have this as a miss.
A partial lunar eclipse took place on Saturday, February 21, 1970. It was the first of two partial lunar eclipses in 1970, the other being on August 17 of the same year. A tiny bite out of the Moon may have been visible at maximum, though just 5% of the Moon was shadowed in a partial eclipse which lasted for 52 minutes and 42 seconds. A shading across the moon from the Earth's penumbral shadow should have been visible at maximum eclipse.

A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on Saturday, October 29, 1966, the second of two lunar eclipses in 1966. This was a deep penumbral eclipse, with over 90% within Penumbral Shadow.

A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on Wednesday, February 21, 1951. This was 6.4 days after the Moon reached apogee.

A penumbral lunar eclipse will take place on March 3, 2045.

A penumbral lunar eclipse will take place on December 20, 2048.

A penumbral lunar eclipse will occur on November 8, 2060. It will be too small to be visually perceptible.