A total lunar eclipse occurred from 5:27 to 11:06 UTC on 21 December 2010, coinciding with the date of the Winter solstice in the Northern Hemisphere and Summer solstice in the Southern Hemisphere. It was visible in its entirety as a total lunar eclipse in North and South America, Iceland, Ireland, Britain and northern Scandinavia.

The total solar eclipse of July 11, 2010 occurred over the southern Pacific Ocean. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.

A total lunar eclipse took place on Sunday 9 November 2003, the second of two total lunar eclipses in 2003, the first being on 16 May 2003. It is the first total lunar eclipse of 21st century which happened on a micromoon day. The Moon barely edged into total eclipse for 21 minutes and 58 seconds. With the Moon just 1.78% of its diameter into the Earth's umbral shadow, the Moon may have been quite bright, but even so, this should have been worth seeing. The partial eclipse lasted for 3 hours, 31 minutes and 25 seconds. Occurring only 1.4 days before apogee, the Moon's apparent diameter was 6.4% smaller than average.

Saros cycle series 121 for lunar eclipses occurs at the moon's descending node. It began in 1029 and will end in 2526. It contains 84 member lunar eclipses, each separated by 18 years 11 and 1/3 days, and will last 1496.5 years.
A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on 23 March 2016, the first of three lunar eclipses in 2016. The Moon was just 2.1 days before apogee, making it very small, so this was a "Micromoon" penumbral lunar eclipse.
A total lunar eclipse took place on Monday, October 28, 1985, the second of two total lunar eclipses in 1985, the first being on May 4, 1985.

A partial lunar eclipse took place on Monday, June 15, 1992, the first of two lunar eclipses in 1992, the second being with a total lunar eclipse on Wednesday, December 9.

A partial lunar eclipse occurred on 19 November 2021. The eclipse occurred towards a micromoon. This was the longest partial lunar eclipse since 18 February 1440, and the longest until 8 February, 2669; however, many eclipses, including the November 2022 lunar eclipse, have a longer period of umbral contact at next to 3 hours 40 minutes. It was often referred to as a "Beaver Blood Moon" although not technically fulfilling the criteria for a true blood moon (totality).
A partial lunar eclipse took place on Tuesday, March 13, 1979, the first of two lunar eclipses in 1979. The Moon was strikingly shadowed in this deep partial eclipse which lasted 3 hours, 17 minutes and 40.6 seconds, with 85.377% of the Moon in darkness at maximum.

A partial lunar eclipse will take place on November 30, 2039. At 3 hours 26 minutes, it is the longest partial lunar eclipse since November 19, 2021, which is the previous member of Lunar Saros 126.

A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on Friday, June 15, 1973, the second of four lunar eclipses in 1973, the first was a penumbral lunar eclipse on Thursday, January 18, the third being with a penumbral lunar eclipse on Sunday, July 15, and the last being with a partial lunar eclipse on Monday, December 10.

A total lunar eclipse took place on Wednesday, October 18, 1967, the second of two total lunar eclipses in 1967, the first being on April 24, 1967.

A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on Wednesday, January 9, 1963, the first of three lunar eclipses in 1963.
A total lunar eclipse took place on Monday, September 15, 1913. The moon passed through the center of the Earth's shadow.

A total solar eclipse took place on Saturday, December 4, 2021, when the Moon passed between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. This eclipse was unusual as the path of the total eclipse moved from east to west across West Antarctica, while most eclipse paths move from west to east. This reversal is only possible in polar regions. Its path across Antarctica crossed near Berkner Island, traversed an arc over the continent and passed over Shepard Island.
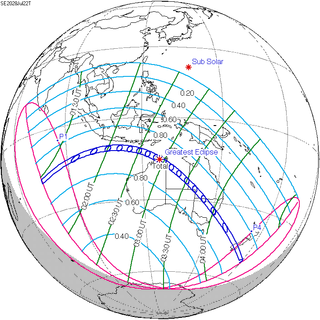
A total solar eclipse will occur on Saturday, July 22, 2028. The central line of the path of the eclipse will cross the Australian continent from the Kimberley region in the north west and continue in a south-easterly direction through Western Australia, the Northern Territory, south-west Queensland and New South Wales, close to the towns of Wyndham, Kununurra, Tennant Creek, Birdsville, Bourke and Dubbo, and continuing on through the centre of Sydney, where the eclipse will have a duration of over three minutes. It will also cross Queenstown and Dunedin, New Zealand. Totality will also be viewable from two of Australia's external territories: Christmas Island and Cocos (Keeling) Island.
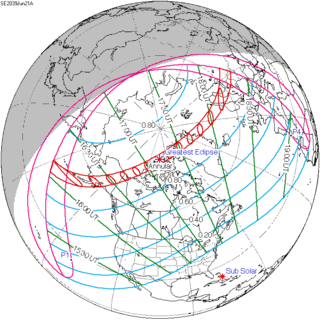
An annular solar eclipse will occur on Tuesday, June 21, 2039. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. An annular solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is smaller than the Sun's, blocking most of the Sun's light and causing the Sun to look like an annulus (ring). An annular eclipse appears as a partial eclipse over a region of the Earth thousands of kilometres wide. This eclipse will start only a few hours after the northern solstice and most of the path will go across areas with midnight sun. For mainland Norway, Sweden and Belarus it will be the first central solar eclipse since June 1954.
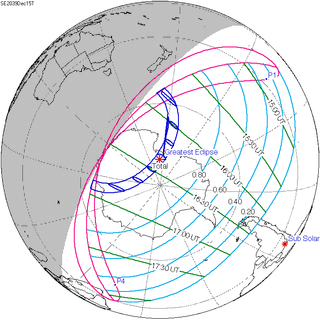
A total solar eclipse will occur on December 15, 2039. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide.

A total lunar eclipse took place on Friday, October 7, 1949, the second of two lunar eclipses in 1949.

A total lunar eclipse took place on Saturday, September 26, 1931. The Moon passed through the central of the Earth's shadow. This was the last central lunar eclipse of Saros cycle 126.