Visibility
It was completely visible over eastern Asia, Australia, Pacific, Americas, western Europe, seen rising over northwestern Pacific Ocean and setting over the north Atlantic Ocean.
| Partial eclipse | |||||||||||||
| Date | 21 February 1970 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gamma | 0.96198 | ||||||||||||
| Magnitude | 0.04639 | ||||||||||||
| Saros cycle | 113 (61 of 71) | ||||||||||||
| Partiality | 52 minutes, 42.4 seconds | ||||||||||||
| Penumbral | 298 minutes, 37.5 seconds | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
A partial lunar eclipse took place on Saturday, February 21, 1970. It was the first of two partial lunar eclipses in 1970, the other being on August 17 of the same year. A tiny bite out of the Moon may have been visible at maximum, though just 5% of the Moon was shadowed in a partial eclipse which lasted for 52 minutes and 42 seconds. A shading across the moon from the Earth's penumbral shadow should have been visible at maximum eclipse.
Occurring only 2.4 days after apogee (Apogee on Wednesday, February 18, 1970), the Moon's apparent diameter was 6% smaller than average. The Moon was only 404,163 km (251,135 mi) from the Earth's center. [1]
It was completely visible over eastern Asia, Australia, Pacific, Americas, western Europe, seen rising over northwestern Pacific Ocean and setting over the north Atlantic Ocean.
| Lunar eclipse series sets from 1969–1973 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascending node | Descending node | |||||||
| Saros | Date Viewing | Type Chart | Gamma | Saros | Date Viewing | Type Chart | Gamma | |
| 108 | 1969 Aug 27  | Penumbral | −1.54066 | 113 | 1970 Feb 21  | Partial | 0.96198 | |
| 118 | 1970 Aug 17  | Partial | −0.80534 | 123 | 1971 Feb 10  | Total | 0.27413 | |
| 128 | 1971 Aug 6  | Total | −0.07944 | 133 | 1972 Jan 30  | Total | −0.42729 | |
| 138 | 1972 Jul 26  | Partial | 0.71167 | 143 | 1973 Jan 18  | Penumbral | −1.08446 | |
| 148 | 1973 Jul 15  | Penumbral | 1.51782 | |||||
| Last set | 1969 Sep 25 | Last set | 1969 Apr 2 | |||||
| Next set | 1973 Jun 15 | Next set | 1973 Dec 10 | |||||
This is the third of five Metonic lunar eclipses.
The Metonic cycle repeats nearly exactly every 19 years and represents a Saros cycle plus one lunar year. Because it occurs on the same calendar date, the Earth's shadow will in nearly the same location relative to the background stars.
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saros | Date | Type | Saros | Date | Type | |
| 103 | 1951 Feb 21.88 | Penumbral | 108 | 1951 Aug 17.13 | Penumbral | |
 |  | |||||
| 113 | 1970 Feb 21.35 | Partial | 118 | 1970 Aug 17.14 | Partial | |
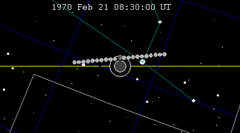 | 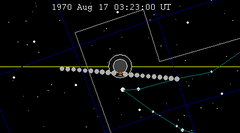 | |||||
| 123 | 1989 Feb 20.64 | Total | 128 | 1989 Aug 17.13 | Total | |
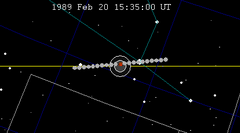 | 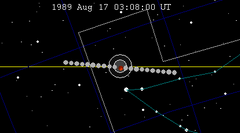 | |||||
| 133 | 2008 Feb 21.14 | Total | 138 | 2008 Aug 16.88 | Partial | |
 | 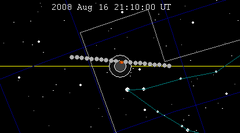 | |||||
| 143 | 2027 Feb 20.96 | Penumbral | 148 | 2027 Aug 17.30 | Penumbral | |
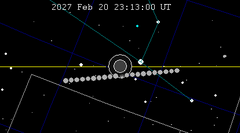 | 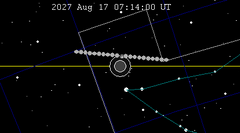 | |||||
A lunar eclipse will be preceded and followed by solar eclipses by 9 years and 5.5 days (a half saros). [2] This lunar eclipse is related to two total solar eclipses of Solar Saros 120.
| February 15, 1961 | February 26, 1979 |
|---|---|
 |  |

A total lunar eclipse took place on Friday 16 May 2003, the first of two total lunar eclipses in 2003, the other being on 9 November 2003. A shallow total eclipse saw the Moon in relative darkness for 52 minutes and 3.1 seconds. The Moon was 12.938% of its diameter into the Earth's umbral shadow, and should have been significantly darkened. The partial eclipse lasted for 3 hours, 15 minutes and 3.1 seconds in total. Occurring only 0.5 days after perigee, the Moon's apparent diameter was 6.2% larger than average. At greatest eclipse the Moon was only 357,693 km from the Earth, making it a Super Full Moon.

A total lunar eclipse took place on Sunday 9 November 2003, the second of two total lunar eclipses in 2003, the first being on 16 May 2003. It is the first total lunar eclipse of 21st century which happened on a micromoon day. The Moon barely edged into total eclipse for 21 minutes and 58 seconds. With the Moon just 1.78% of its diameter into the Earth's umbral shadow, the Moon may have been quite bright, but even so, this should have been worth seeing. The partial eclipse lasted for 3 hours, 31 minutes and 25 seconds. Occurring only 1.4 days before apogee, the Moon's apparent diameter was 6.4% smaller than average.

A total lunar eclipse took place on Tuesday 4 May 2004, the first of two total lunar eclipses in 2004, the second being on 28 October 2004.

A total lunar eclipse took place on Thursday 28 October 2004, the second of two total lunar eclipses in 2004, the first being on 4 May 2004. It was the first lunar eclipse to take place during a World Series game, which when seen from Busch Memorial Stadium in St, Louis, Missouri, provided a surreal sight on the night the Boston Red Sox won their first World Series in 86 years to end the Curse of the Bambino. Occurring 5.6 days before apogee, the Moon's apparent diameter was smaller. The moon was 10.1 days after perigee and 5.6 days before apogee.

A partial lunar eclipse took place on Monday 17 October 2005, the second of two lunar eclipses in 2005. A tiny bite out of the Moon may have been visible at maximum, though just 6.25% of the Moon was shadowed in a partial eclipse which lasted for nearly 56 minutes and was visible over east Asia, Australasia, and most of the North America. A shading across the Moon from the Earth's penumbral shadow should have been visible at maximum eclipse.

A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on 14 March 2006, the first of two lunar eclipses in 2006.

A partial lunar eclipse occurred on 26 June 2010, the first of two lunar eclipses in 2010. At maximum eclipse, 53.68% of the Moon was covered by the Earth's shadow.

A total lunar eclipse will take place between Monday and Tuesday, June 25-26, 2029. A central total eclipse lasting 1 hour and 41 minutes 53 seconds will plunge the full Moon into deep darkness, as it passes right through the centre of the Earth's umbral shadow. While the visual effect of a total eclipse is variable, the Moon may be stained a deep orange or red color at maximum eclipse. It will be able to be seen from most of the Americas, Western Europe and Africa. The partial eclipse will last for 3 hours and 39 minutes 32 seconds in total.

A total lunar eclipse occurred on Tuesday, 8 November 2022. The southern limb of the Moon passed through the center of the Earth's shadow. It surpassed the previous eclipse as the longest total lunar eclipse visible from nearly all of North America since 17 August 1989, and until 26 June 2029. Occurring only 5.8 days before apogee, the Moon's apparent diameter was smaller. The next total lunar eclipse will take place on 14 March 2025. A lunar occultation of Uranus happened during the eclipse. It was the first total lunar eclipse on Election Day in US history. This event was referred in media coverage as a "beaver blood moon".

A total lunar eclipse occurred on 15–16 May 2022, the first of two total lunar eclipses in 2022. The event occurred near lunar perigee; as a result, this event was referred to some in media coverage as a "super flower blood moon" and elsewhere as a "super blood moon", a supermoon that coincides with a total lunar eclipse. This was the longest total lunar eclipse visible from nearly all of North America since August 17, 1989 until the next eclipse on November 8.
A total lunar eclipse took place on Thursday, April 24, 1986, the first of two total lunar eclipses in 1986, the second being on October 17, 1986. The Moon was plunged into darkness for 1 hour, 3 minutes and 34.8 seconds, in a deep total eclipse which saw the Moon 20.217% of its diameter inside the Earth's umbral shadow. The visual effect of this depends on the state of the Earth's atmosphere, but the Moon may have been stained a deep red colour. The partial eclipse lasted for 3 hours, 18 minutes and 46.8 seconds in total. The Moon was just 1.2 days before perigee, making it 5.3% larger than average.
A total lunar eclipse took place on Friday, October 17, 1986, the second of two total lunar eclipses in 1986, the first being on April 24, 1986. The Moon was plunged into darkness for 1 hour, 13 minutes and 41 seconds, in a deep total eclipse which saw the Moon 24.545% of its diameter inside the Earth's umbral shadow. The visual effect of this depends on the state of the Earth's atmosphere, but the Moon may have been stained a deep red colour. The partial eclipse lasted for 3 hours, 36 minutes and 49.5 seconds in total. The Moon was 5.4 days before apogee, making it 3.3% smaller than average.
A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on Thursday, March 3, 1988, the first of two lunar eclipses in 1988, the second being on August 27, 1988. Earlier sources compute this as a 0.3% partial eclipse lasting under 14 minutes, and newest calculations list it as a penumbral eclipse that never enters the umbral shadow. In a rare total penumbral eclipse, the entire Moon was partially shaded by the Earth, and the shading across the Moon should have been quite visible at maximum eclipse. The penumbral phase lasted for 4 hours, 53 minutes and 50.6 seconds in all, though for most of it, the eclipse was extremely difficult or impossible to see. The Moon was 2.2 days after apogee, making it 6.1% smaller than average.
A penumbral lunar eclipse took place on Thursday, November 8, 1984, the last of three lunar eclipses in 1984. This subtle penumbral eclipse may have been visible to a skilled observer at maximum eclipse. 90% of the Moon's disc was partially shaded by the Earth, which caused a gentle shadow gradient across its disc at maximum; the eclipse as a whole lasted 4 hours and 28 minutes.
A total lunar eclipse will take place on Friday, March 14, 2025, the first of two total lunar eclipses in 2025. The Moon will take place near apogee during this eclipse, making it appear smaller than usual. The second eclipse will take place on 7-8 September 2025, happening near perigee. Occurring only 3.4 days before apogee, the Moon's apparent diameter will be 5.4% smaller than average.

A total lunar eclipse will take place on 7-8 September 2025. The Moon will barely miss the center of the Earth's shadow. It will be the second of two total lunar eclipses. Occurring roughly 3 days before perigee, the Moon will appear larger than usual.
A partial lunar eclipse took place on Monday, August 17, 1970, the second of two lunar eclipses in 1970, the first was on February 21 of that year. The Earth's shadow on the Moon was clearly visible in this eclipse, with 41% of the Moon in shadow; the partial eclipse lasted for 2 hours and 11 minutes. It was the second of two lunar eclipses in 1970.

A total lunar eclipse took place on Monday, April 24, 1967, the first of two total lunar eclipses in 1967, the second being on October 18, 1967.

A penumbral lunar eclipse took place at the Moon's ascending of the orbit on Sunday, June 5, 1955, with a penumbral eclipse magnitude of 0.62181 (62.181%). A penumbral lunar eclipse takes place when the Moon moves through the faint, outer part of Earth's shadow, the penumbra. This type of eclipse is not as dramatic as other types of lunar eclipses and is often mistaken for a regular Full Moon. The Moon shines because its surface reflects the Sun's rays. A lunar eclipse happens when the Earth comes between the Sun and the Moon and blocks some or all of the Sun's light from reaching the Moon. A penumbral lunar eclipse occurs when the Sun, Earth, and the Moon are imperfectly aligned. When this happens, the Earth blocks some of the Sun's light from directly reaching the Moon's surface and covers all or part of the Moon with the outer part of its shadow, also known as the penumbra. Since the penumbra is much fainter than the dark core of the Earth's shadow, the umbra, a penumbral eclipse of the Moon is often difficult to tell apart from a normal Full Moon. Occurring only 0.5 days after apogee, the moon's apparent diameter was 6.5% smaller than average.

A partial solar eclipse occurred on Thursday, October 23, 2014, with a magnitude of 0.81141. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A partial solar eclipse occurs in the polar regions of the Earth when the center of the Moon's shadow misses the Earth. Occurring only 5.7 days after apogee, the Moon's apparent diameter was smaller.